RLC
2003 Avaya Inc. All Rights Reserved.
Page 2 of 12
Local Survivable Processor S8300.doc
1. Introduction
Communication is the life-blood of any company, and ensuring that
communications will be available at any time is critical. This is increasingly difficult to
provide in today’s changing environment from pure voice networks to converged data
and voice networks. Avaya offers a strong line of products to assist in creating the most
robust network possible. This portfolio of solutions includes the Avaya S8700 Media
Server and the Avaya S8300 Media Server. The S8700 Media Server runs in duplex
mode with a standby server ready to take control with no loss of communication should a
cataclysmic event occur to the primary server. The duplicated S8700 Media Server
protects the network against a server failure, but increasing distances between
headquarters and remote branch offices increases the chance of a network facilities
outage causing loss of communications. Avaya offers the Local Survivable Processor
(LSP) to continue to provide service in the case of broken connectivity between remote
sites and main locations. In addition, Avaya empowers the administrator with the ability
to define how the system behaves in the case of lost network connectivity. The priority
can be placed on maintaining a solid network or on a speedy switch to the LSP and short
downtime.
This document is intended to describe how the LSP provides the added layer of
survivability, how to administer the behavioral priorities, and how to design a network to
take full advantage of the LSP’s capabilities.
2. Overview
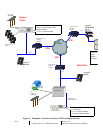
The Avaya Local Survivable Processor (LSP) solution utilizes the Avaya S8300
Media Server hardware and software components and requires an Avaya MultiVantage™
Software license to activate the LSP feature. This software license allows the S8300
Media Server to be a survivable call-processing server for remote/branch customer
locations, as well as a redundant call controller for a standalone S8300 Media Server.
In the event that the communication link is broken between the remote Avaya
G700 Media Gateway and the primary call controller (either an Avaya S8300 Server or
an Avaya S8700 Server), the LSP will provide service for the Avaya IP Telephones and
G700 Media Gateways that were controlled by the primary call controller. A large
enterprise customer may have a main media server controlling multiple remote G700
Media Gateways configured with LSPs.
The strategy by which Avaya G700 Gateways and IP endpoints change control
from the primary gatekeeper to the LSP is driven by the endpoints themselves, which use
a list of gatekeepers. During initialization, each IP endpoint and G700 Gateway receives
a list of gatekeepers. The IP endpoints ask each gatekeeper in the list for service until one
responds with a positive reply. If the link to that gatekeeper fails at some later time, the
endpoint will try to receive service from the other gatekeepers in the list, including the
LSP. The LSP will provide service to all G700s and IP endpoints that register with it.
When the primary gatekeeper is prepared to provide service, the LSP needs to be
manually reset. This will inform the IP endpoints to try their gatekeeper list again, and
return to the primary gatekeeper for service.