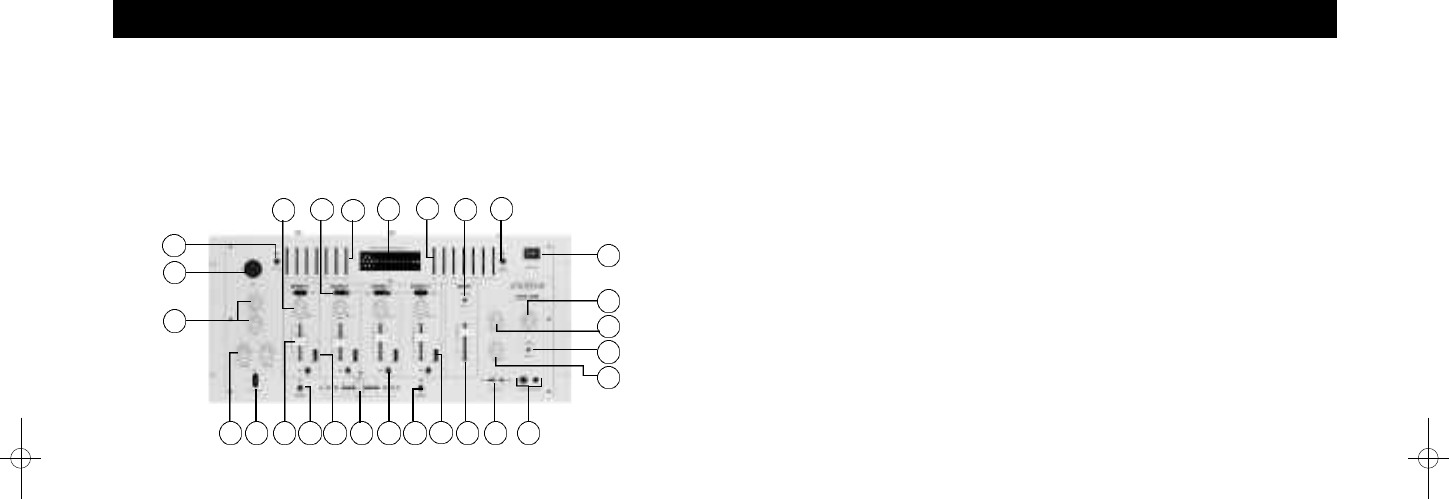
Description of Function
At this point, you’re pretty much ready to start mixing. So if you’re a
know-it-all, or you’re just one of those people who like to learn by
trial-and-error, you are free to throw down. But if you wanna go for
the gold and get your pilot’s license, take a moment and learn what
each of the RM-22’s front-panel controls are about.
15
13
8 9
7 6
14
16
11
1
4
5
3a
108
12
1. Power switch: Turns the power “On” or “Off”.
2. Zone Meter switch: Press this when you want the Output Level
meter (23) to display the Zone output instead of the Master output.
3a. Zone Level knob: Adjusts the level being sent to the Zone
outputs (i.e. monitors).
3b. Booth Level knob: Adjusts the level being sent to the Booth
outputs (i.e. monitors).
4. Cue Level knob: Adjusts the cue level being sent to the
Headphone outputs. Keep this at a reasonable level to avoid
hearing loss.
5. Cue Stereo/ Split toggle switch: Select whether you prefer to
hear the Cue mix and Master output in stereo, or split with the
Cue mix on one side and the Master on the other.
17
18
19
20
21
22 23
22
2
3b
Description of Function
6. Headphone outputs: Connect up to two pairs of stereo
headphones using 1/4-inch and 1/8-inch jacks.
7. Cue Pan slider: This adjusts the relative headphone balance
between the Cue mix (PFL) and Master output (PGM).
8. Fader Start switch: Lets you automatically start a CD player from
the cue point by moving the crossfader (requires a compatible CD
player like the Stanton S-Series).
9. Crossfader: Creates a gradual fade between two channels, as
determined by the Crossfader Source selectors (14). Essential for
scratching and smooth house mixing.
10. Master fader: Adjusts the overall level of the Master output
signal.
11. Master Stereo/Mono toggle switch: Selects whether the Master
output will be stereo or summed to mono.
12. PFL switch: Push this to assign the channel to the Cue mix in
headphones. (Pop quiz: Do you know what “PFL” stands for?
Answer: “Pre-Fader Level.” In other words, the Channel fader
does not affect the level you hear in the headphone cue mix.)
13. Channel fader: Controls the input channel level.
14. Crossfader Source selectors: These select whether the input
channel is assigned to the left side (A) or right side (B) of the
crossfader. Select “BYPASS” if you don’t want the channel
assigned to the crossfader at all.
15. Input Gain knobs: Use these to adjust the level of inputs. For
optimum signal-to-noise, raise the knob until the “max” LED
lights occasionally. (usually around the 2 o’clock position)
14








