8 18-CD22D1-8
Installer’s Guide
The furnace must also be elevated a minimum of 6
inches to allow clearance for the condensate drain to
exit the cabinet in the horizontal position.
The horizontal furnace may also be suspended from the
joists using 3/8" all-thread rods with pieces of angle iron
underneath the furnace to form a hanging rack at both
ends and the midpoint. The rods need to be of sufficient
length to allow for proper clearances from combustible
materials. The angle iron needs to be at least 32" in
length to allow for access to service panels.
AIR FOR COMBUSTION AND VENTILATION
If these furnaces are installed in a nondirect vent capac-
ity then the adequate flow of combustion and ventilat-
ing air must not be obstructed from reaching the fur-
nace. Air openings provided for combustion air must be
kept free of obstructions which restrict the flow of air.
Airflow restrictions affect the efficiency and safe opera-
tion of the furnace. Keep this in mind should you
choose to remodel or change the area which contains
your furnace. Furnaces must have a free flow of air for
proper performance.
The furnace may be placed horizontally in a crawl space
on a pad or other noncombustible material which will
raise the unit for sufficient protection from moisture.
The furnace must be supported at both ends and the
middle when installed horizontally.
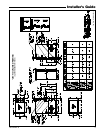
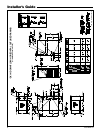
4
UPFLOW/
HORIZONTAL
SHOWN
50 CU. FT. OR MORE
PER 1000 BTU/HR. INPUT
ALL EQUIP. INSTALLED
UNCONFINED
5
Provisions for combustion and ventilation air shall be
made in accordance with latest edition of Section 5.3,
Air for Combustion and Ventilation, of the National
Fuel Gas Code, ANSI Z223.1 — CAN/CGA B149.1 or ap-
plicable provisions of the local building codes. Special
conditions created by mechanical exhausting of air and
fireplaces must be considered to avoid unsatisfactory
furnace operation.
OUTSIDE AIR IS RECOMMENDED
The use of indoor air for most applications is acceptable,
unless there is the presence of corrosive chemicals
or contamination. Certain types of installation will
require the use of outside air for combustion.
The following types of installations will require use of
OUTDOOR AIR for combustion, due to chemical expo-
sures:
* Commercial buildings
* Buildings with indoor pools
* Furnaces installed in “confined” laundry rooms
* Furnaces installed in “confined” hobby or craft rooms
* Furnaces installed near chemical storage areas.
Exposure to the following substances in the combustion
air supply will also require OUTDOOR AIR for combus-
tion:
* Permanent wave solutions
* Chlorinated waxes and cleaners
* Chlorine based swimming pool chemicals
* Water softening chemicals
* Deicing salts or chemicals
* Carbon Tetrachloride
* Halogen type refrigerants
* Cleaning solvents (such as perchloroethylene)
* Printing inks, paint removers, varnish, etc.
* Hydrochloric acid
* Cements and glues
* Antistatic fabric softeners for clothes dryers
* Masonry acid washing materials
Furnace locations may be in a “confined space” or an
“unconfined space”.
Unconfined space
is defined in Figure 5. These spaces
may have adequate air by infiltration to provide air for
combustion and ventilation. Buildings with tight
construction (for example, weather stripping, heavily
insulated, caulked, vapor barrier, etc.), may need addi-
tional air to be provided as described for confined space.
Confined spaces
are installations with less than 50 cu.
ft. of space per 1000 BTU/ hr input from all equipment
installed. Air for combustion and ventilation require-
ments can be supplied from inside the building as in
Figure 8 or from the outdoors, as in Figure 9.