Voice over Wireless LAN Solution Guide v1.0 December 2005
______________________________________________________________________________________________________
Page 58
3.2.2 WLAN Handset 2210/11/12
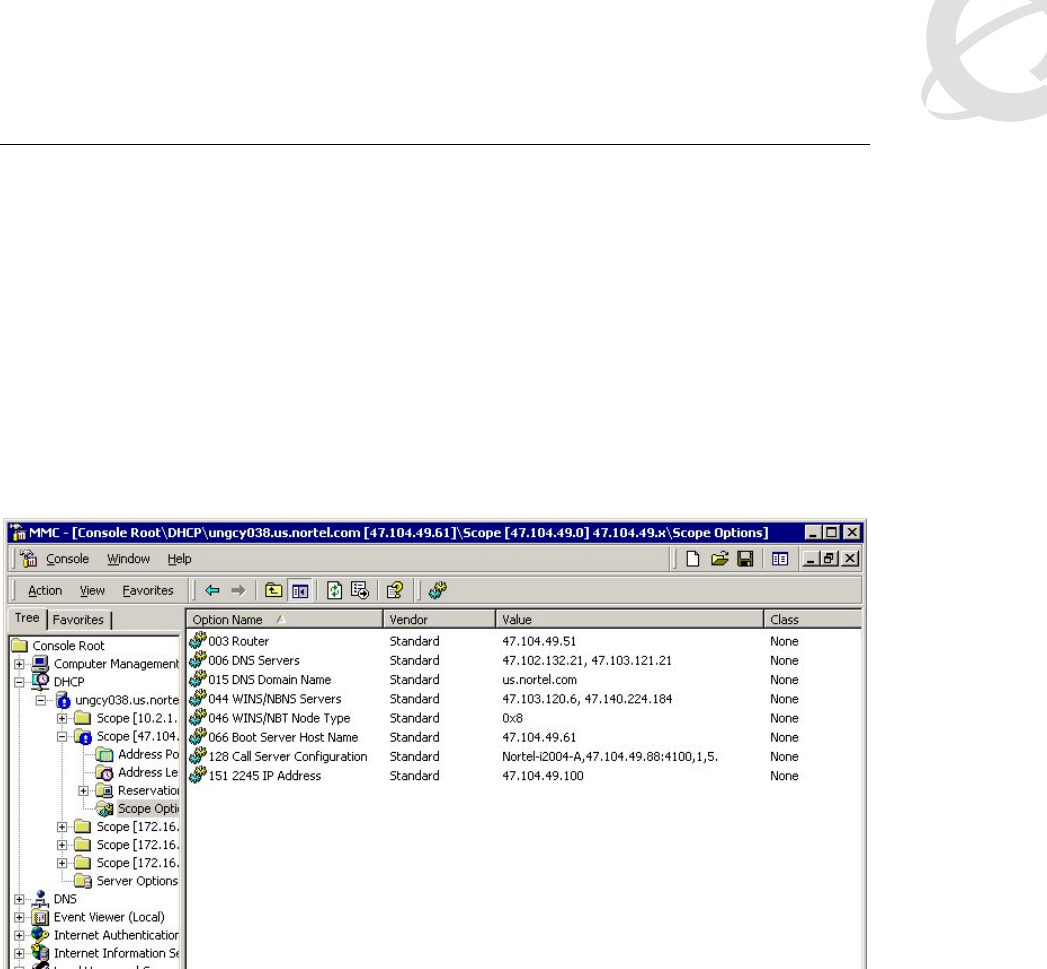
The WLAN Handset 2210/11/12 also supports numerous DHCP extensions for assigning various
configuration options. Like the AP 2330, the WLAN Handset 2210/11/12 supplies a vendor class
string, which in this case is Nortel-221x-A. Unlike the AP 2330, the WLAN Handset 2210/11/12
does not accept these options from the DHCP server encapsulated in a 43 Vendor Type option
(which is the normal way vendor classes work). Consequently, you do not define these options as
part of a vendor class on the DHCP server. Instead you define them as simply new options that
are assigned using the native code numbers that you give them. The WLAN Handset 2210/11 will
also specifically request a list of options in the DISCOVER message. The list of options (aside
from the IP address, subnet mask, and so on) needed by a WLAN Handset 2210/11 are as
follows: (66) TFTP Server, (128) Signaling Server Address and other parameters, (151) WTM
2245 Address, (152) WAG 2246 Address. Refer to Figure 24 for an example DHCP reservation
for a particular handset.
Figure 24: Assigning parameters to a WLAN Handset 2210/11/12
Another use for a DHCP server is to make code upgrades to the handset easier. If the handset
has an address for a Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP) server configured or assigned by
DHCP, it will not finish booting if the TFTP server is not present. So after the initial code upgrade,
the solution will be more robust if the handset does not look for a TFTP server upon boot up. You
accomplish this by assigning the special value of 255.255.255.255 for the TFTP server address.
This address causes the handset to no longer check for code upgrades. At a later time, when
new code is available, you can set up the TFTP server, and the DHCP server can assign the
proper TFTP server address to handsets, which will then download the code. After the upgrade is
complete, you can set the DHCP server to assign 255.255.255.255 once again as the TFTP
server address.
One last problem deserves mention. Suppose, for example, the company employing this handset
solution is a retailer with many stores. Also suppose that each store has a local call server for the
local employees who use various VoIP devices, so all the attributes are defined at the scope
level. What happens if a supervisor who travels from store to store wants to use their WLAN
Handset 2210/11/12 at each one? The supervisor would get assigned, potentially, to a signaling
server that does not recognize their phone. The best way to support this user is to create a
unique reservation in each remote scope for that user’s WLAN Handset 2210/11/12 and specify


















