2-11
Site Survey Guide for Deploying Cisco 7920 IP Phones
OL-6315-01
Chapter 2 Survey Tools
Survey Tools for Packet Jitter
Survey Tools for Packet Jitter
Typically, voice packets are sent every 20 ms. Voice calls are usually bursty, consisting of a group of
tightly packed packets in a transmit direction followed by a tightly packed group in a receive direction.
The users of WIPT are typically mobile users who have active calls while moving between WLAN
coverage cells and hence roaming between coverage cells. AirMagnet Surveyor provides a tool for this
type of possible packet jitter and the trace decode tool provides interpacket timings. Over-the-air packet
jitter tools measure the WLAN packets. A WIPT call will also at some point be on a wired segment or
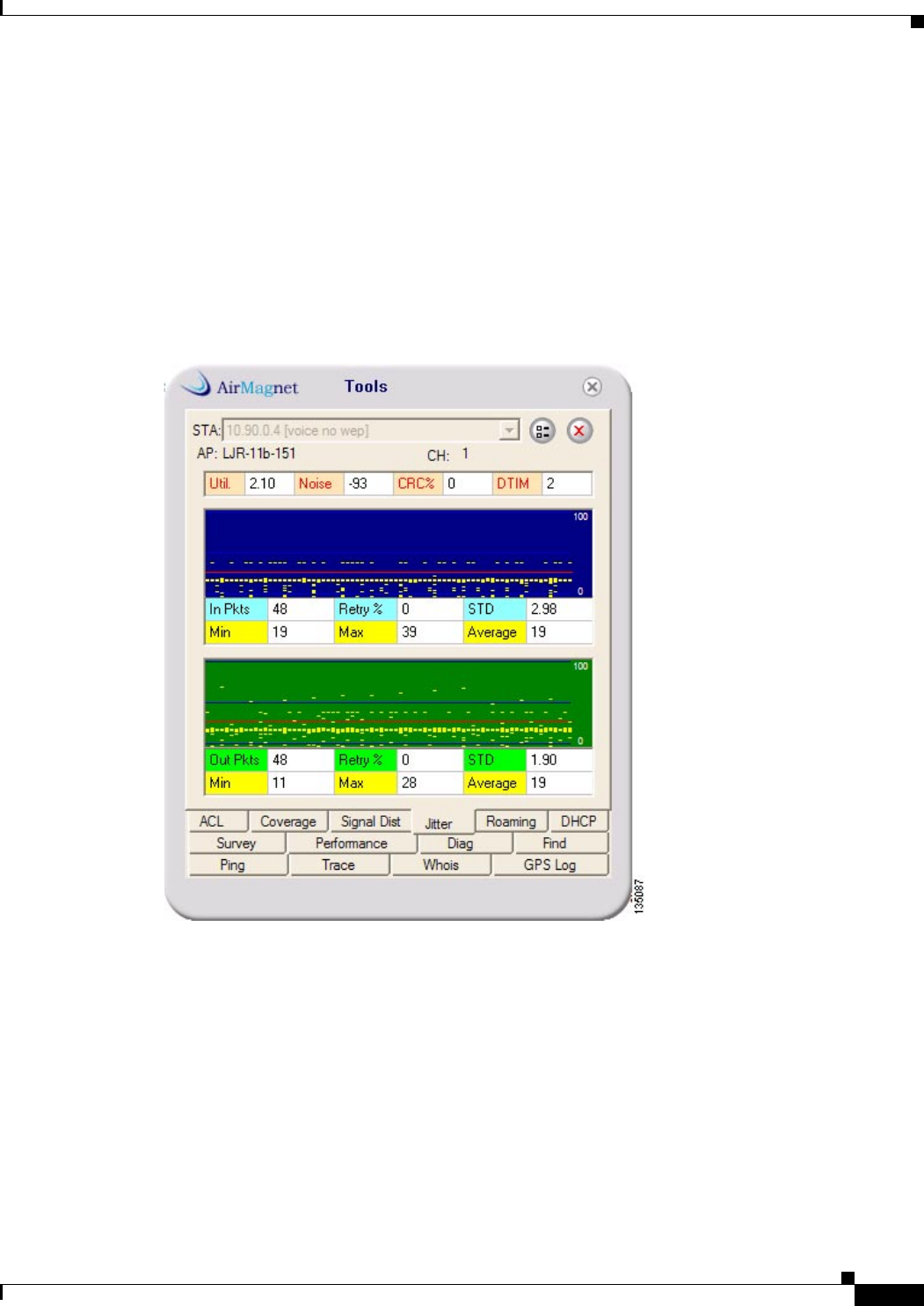
segments, which could also be a source of jitter. Figure 2-13 shows the AirMagnet jitter tool.
Figure 2-13 AirMagnet Jitter Tool
The AirMagnet jitter tool allows for the monitoring of a WIPT client during an active call. The tool
reports the standard deviation (STD) of the transmit side and the receive side of the client packets. It
reports the average interpacket delay plus the minimum and maximum delays. The jitter measurement
of this tool is just from access point to WIPT client and WIPT client to the access point. This is not an
end-to-end measurement of jitter or latency for a VoIP call.
Figure 2-14 shows there is significant data and noise on all channels. The effect of the data and noise on
the quality of voice is shown with STD values of 4.87 and 6.02. The channel utilization is 30.65. The
Cisco AVVID design guide states for quality VoIP calls the Delay Variation (Jitter) should not exceed
30 ms. In an office with heavy use of 802.11, the average in-packet delay might vary from 19ms to a high
of 32ms, and the average out-packet delay might vary from 18 ms to a high of 41 ms. Those delay
averages would produce intermittent but noticeable jitter during active calls and a noticeable delay
during roams.
