User Precautions
Speaker Protection
All loudspeakers have electrical, thermal, and physical limits which must be observed to prevent damage or
failure. Cone or compression drivers can be damaged (sometimes to the point of failure) from excessive
power, low frequencies applied to high frequency drivers, severely clipped waveforms, and DC voltage. All
CA Series amplifiers automatically protect speakers from DC voltages and subsonic signals. For more
information, see the TourClass Protection section.
Mid- and high-frequency transducers–compression driver in particular–are highly susceptible to damage
from overpowering, clipped waveforms, or frequencies below their rated passband. When using an electron-
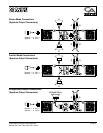
ic crossover, make absolutely certain that the low and mid bands are connected to the correct amplifiers and
drivers—and not accidentally connected to those for a higher or lower frequency band.
The amplifier’s clipping point is its maximum peak output power. At maximum peak output power, Crest
Audio CA Series amplifiers will deliver more power than many speakers can safely handle. Be sure the
peak power capability of the amplifier is not excessive for your speaker system. To ensure that the speakers
never receive excessive power, and to prevent amplifier clipping, use a properly adjusted external limiter (or
a compressor with a ratio of 10:1 or higher) to control power output. Use one compressor/limiter for each
frequency band in systems with active electronic crossovers.
The ACL clip limiting circuit will automatically limit the duration of squared-off, continuous waveforms
applied to the speakers. The amplifier will, however, allow normal musical transient bursts to pass. Of
course, when the amplifier does clip, it is operating at its maximum output power. Note that some speaker
systems are packaged with proprietary “processors” that have power limiting circuits and therefore should
not require additional limiting.
Do not drive any low-frequency speaker enclosure with frequencies lower than its own tuned frequency; the
reduced acoustical damping could cause a ported speaker to “bottom out” even at moderate power. Consult
the speaker system specifications to determine its frequency limits, and employ a roll-off filter if necessary.
Recommended Speaker Cabling
The wire gauge charts will assist you in determining the optimum copper wire gauge for your speaker
cables. Remember that the speaker cable resistance robs amplifier power in two ways: through power lost
directly to resistance (often referred to as I
2
R loss), and through increased total load resistance, which
decreases the amount of power available from the amplifier. The charts (Appendix C) give cable length fig-
ures in feet/AWG wire gauges and in metric values.
Crest Audio CA Series Power Amplifiers Page 15
Models CA2, CA4, CA6, CA9, CA12, CA18