Chapter 2 Quick Start 17
Introductory Example
information that it needs to perform RC4 encryption. In Step 4, we can enter the data
to encrypt with the
B_EncryptUpdate function. Chapter 4 of the Reference Manual
provides the following description and prototype:
The first argument is our algorithm object,
rc4Encrypter
.
The other arguments call for the plaintext input and encrypted output. Because the
output depends on the input, we start with the fifth and sixth arguments, which
describe the input.
We name our input
dataToEncrypt
and declare it as follows:
Crypto-C needs to know how many bytes our input is, so we use
strlen:
If your data is not a string — that is, if it does not end with a
NULL-terminating
character — do not use
strlen to determine its length.
The output is described by the second, third, and fourth arguments.
The second argument is described in the prototype as
unsigned char *partOut. This
does not mean you simply declare a variable to be
unsigned char * and pass it as the
argument. The output argument that you pass is a pointer to a buffer of allocated
memory. This is an important point; see “Algorithm Choosers” on page 116 for a
detailed discussion of this topic.
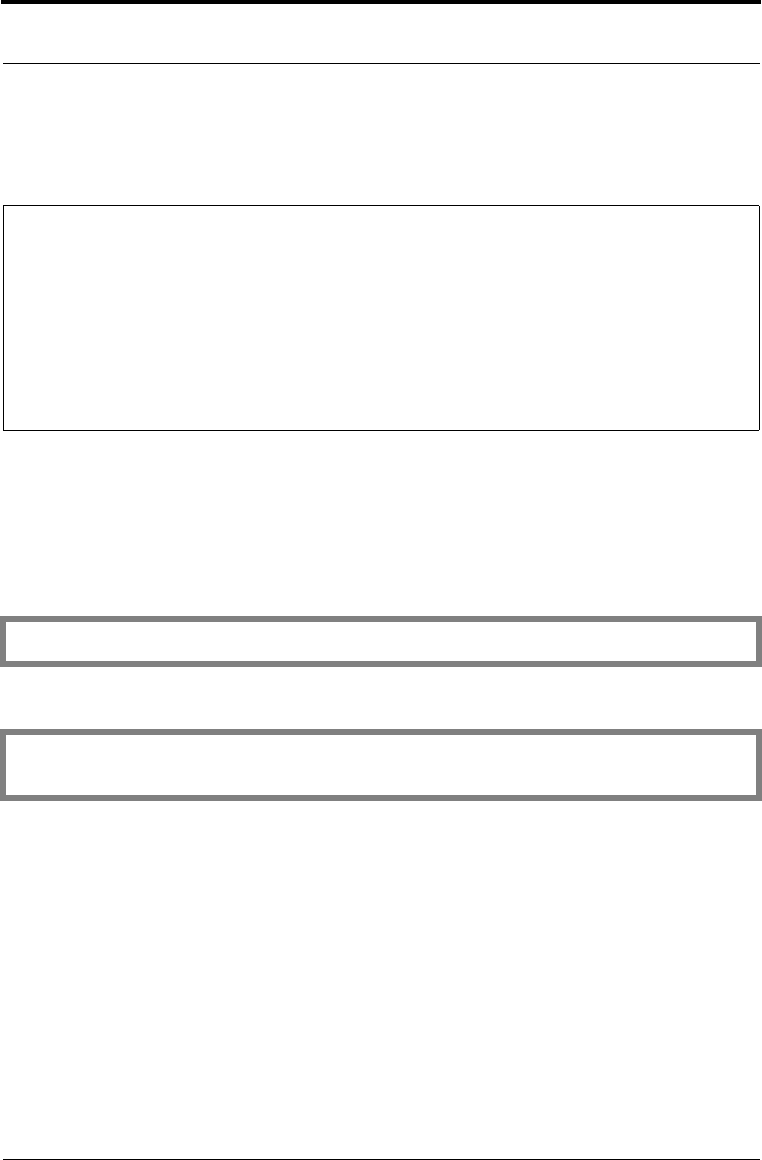
int B_EncryptUpdate (
B_ALGORITHM_OBJ algorithmObject, /* algorithm object */
unsigned char *partOut, /* output data buffer */
unsigned int *partOutLen, /* length of output data */
unsigned int maxPartOutLen, /* size of output data buffer */
unsigned char *partIn, /* input data */
unsigned int partInLen, /* length of input data */
B_ALGORITHM_OBJ randomAlgorithm, /* random byte source */
A_SURRENDER_CTX *surrenderContext /* surrender context */
);
static char dataToEncrypt[] = “Encrypt this sentence.”;
unsigned int dataToEncryptLen;
dataToEncryptLen = (unsigned int)strlen (dataToEncrypt) + 1;
