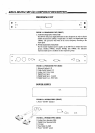
kHz
The letters used to represent Kilo Hertz, a measure of frequency referenced in
thousands per second. (ex. lldtz = 1000 times/sec.)
~z Light Emitting Diodes.
The letters used to represent Mega Hertz, a measure of frequency referenced
in millions per second. (ex. 1MHz = 1,000,000 times/sec.)
MULTIPLEX
In digital audio processors, multiplexing divides source signals between mul-
tiple processing circuits (i.e. DACs, Processors...). It allows processing at higher
speed than the individual circuits can do alone. The trade off to multiplexing in the
analog domain is the requirement to reconstruct the complete signal through
summing.
OP-AMP
Integrated circuits used as OPerational AMPlifiers. Despite their significant
sonic colorations, OP-AMPs are often used in audio components due to their
cost effectiveness.
OPTO-COUPLING
Optically transferring information from one circuit to another in CD’s, DAT’s,
and Digital to Analog processors. Opto-coupling does add colorations to music, but
it is much less expensive than designing more advanced, quiet circuits. Opto-coupling
is often used to isolate digital noise from analog circuits.
OVERSAMPLING
A method by which additional samples are plotted in between the original
recorded samples in order to increase the time domain resolution of the playback
waveform.
POLYNOMIAL
Polynomials, simply stated, are long, high order equations which can be used
to specify exacting oversampled points which accurately follow the natural profile of
a musical waveform.
QUANTIZATION
The process by which analog music is converted into digital data.
SAMPLES
A digital sample is a quantized coordinate representing a specific amplitude at
a specific time. Thousands of samples per second are quantized during recording to
digitally represent the original music.
SAMPLING RATE
The frequency at which analog data is sampled in the recording process (ex.
Sampling Rate of 44. lkHz which is used in recording CD’s represents 44,100 quan-
tized samples per second).
SCALING
In this application scaling is a term referring to the rounding off of computed
numbers due to the overfiowing of a processor’s accumulator. This results in a loss
of accuracy in oversampled data points.
SUMMING
Summing, in the analog domain, is a process by which sections of information
are reconstructed (summed) after multiplexing and processing.
TIME DOMAIN
In this application, another way of stating the Digital Domain.
TRANSIENT
A signal which travels from a low amplitude to high amplitude in an extremely
short time.
WORD
Used in the digital context, a word is a group of bits and or bytes which combine
to determine the size of a data path.