22
AUX
SENDS
STEREO AUX RETURNS
EFFECTS TO
MONITORS
TO AUX
SEND 2
TO AUX
SEND 1
1
2
PWR
PHAN
SOLO
SOLO
1
2
1
2
3
4
1
2
C
-
R / PHNS
ONLY
RETURNS
SOLO
MAIN MIX
TO SUBS
ASSIGN OPTIONS
1
–
2
3
–
4
U
OO
+20
U
OO
+20
U
OO
+15
U
OO
+15
U
OO
+20
U
OO
+20
U
OO
+10
U
OO
+10
LEFT RIGHT
PHONES
LAMP
12 V
0.5A
TAPE IN
SOLO
RUDE
SOLO
LIGHT
C
-
R / PHONES
SUBS 3
–
4
SUBS 1
–
2
MAIN MIX
SOURCE
TAPE
TAPE TO
MAIN MIX
MAIN
L
-
R MIX
RIGHT
1234
LEFT
RIGHT
LEFT
RIGHT
LEFT
RIGHT
LEFT
28
CLIP
10
7
4
2
2
0
4
7
10
20
30
ASSIGN TO MAIN MIX
LEVEL
SET
TM
MODE
(AFL)
LEVEL SET
NORMAL
(PFL)
CR1604
-
VLZ
16
-
CHANNEL MIC/LINE MIXER
U
OO
+20
OO
OO
MAX
0 dB=0 dBu
MAX
dB
30
20
10
OO
40
50
5
5
U
60
10
dB
30
20
10
OO
40
50
5
5
U
60
10
At Mackie, audio quality is much more im-
portant than the price of wall warts. All of our
mixers now employ VLZ and built-in power
supplies that deliver more than enough cur-
rent, resulting in sonic specifications that
rival consoles upwards of $50,000!
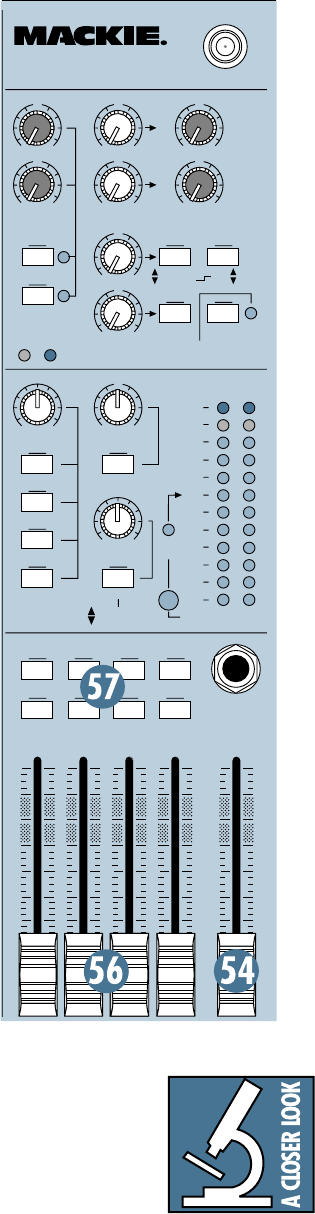
SUBGROUP FADERS
As you might expect, these faders control the
levels of signals sent to the
SUB OUTS
. All chan-
nels that are assigned to subgroups, not muted
and not turned fully down will appear at the
SUB OUTS
. Unlike the
MAIN OUT
, the sub-
group signals do not pass through an insert jack
on their way to the subgroup faders. That’s no
problem — should you want to send these sig-
nals through a serial effects processor, simply
patch from the
SUB OUTS
to the effect’s input,
and from the effect’s output to whatever the fi-
nal destination is, usually a multitrack recorder.
The subgroup signals is off when its fader is
fully down, the “
U
” marking is unity gain, and
fully up provides 10dB additional gain. Re-
member that if you’re treating two subgroups
as a stereo pair, subgroup
1
and
2
for example,
make sure that both subgroup faders “ride”
together, to maintain the left/right balance.
ASSIGN TO MAIN MIX
One popular use of the subgroups is to use
them as master faders for a group of channels
on their way to the
MAIN L-R MIX
. Let’s say
you’ve got a drum kit hogging up seven channels
and you’re going to want to fade them out at a
different rate than the other channels. You don’t
want to try that with seven hands or seven fin-
gers, so just un-assign these channels from
L–R
,
reassign them to subgroup
1–2
, engage the
AS-
SIGN TO MAIN MIX, LEFT
on subgroup
1
and
the
ASSIGN TO MAIN MIX, RIGHT
on subgroup
2
. Now you can ride the entire stereo drum mix
with two faders —
1
and
2
.
If you engage just one
ASSIGN TO MAIN
MIX
switch per subgroup
(
LEFT
or
RIGHT
),
the signal sent to the
MAIN L-R MIX
will be
the same level as the
SUB OUTS
. If you want
the subgroup to appear in the center of the
main mix, engage both the
ASSIGN TO MAIN
MIX, LEFT
and
ASSIGN TO MAIN MIX, RIGHT
switches. The signal will be sent to both sides,
and will be attenuated just enough to pre-
serve constant loudness , just like the
channel
PAN
knobs when set center.
OUTPUT SECTION DESCRIPTION
You’ve just learned about the
input channels and how the sig-
nals get in and out. The signals
come in via
MIC
and
LINE
input
jacks, are manipulated by the
channels, and then sent to the
output section. In the output
section, things get a bit more
complicated, so put on your
thinking caps.
MAIN L-R MIX FADER
As the name implies, this
fader controls the levels of
signals sent to the
MAIN OUT
1
/
4
" TRS jacks and
TAPE
OUTPUT
RCA jacks . All
channels and
AUX RETURN
s
that are assigned to the
MAIN
L-R MIX
, not muted and not
turned fully down will appear
at the
MAIN OUT
. Before the
main mix gets to this fader, the
signals pass through the
MAIN
INSERT
.
The
MAIN L-R MIX
signals
are off with the fader fully
down, the “
U
” marking is unity
gain, and fully up provides
10dB additional gain. This ad-
ditional gain will typically
never be needed, but once
again, it’s nice to know it’s
there. The fader itself is a ste-
reo version of the channel and
subgroup faders — same su-
persmooth custom taper, same
dead silence when turned fully
down. This is the fader to pull
down at the end of the song
when you want “The Great Fade-Out.”
VLZ MIX
ARCHITECTURE
When designing a mixing
circuit, the lowest noise and
best crosstalk specs are
achieved by using Very Low Impedance (VLZ).
To implement VLZ in a mixer, the power supply
must be able to deliver plenty of current to the
circuitry. That’s why those “wall wart” mixers are
often noisy — they can’t power a VLZ circuit.


















