MIDI functions
V-Accordion
r
79
Your FR-7/FR-5 also transmits and receives MIDI data. In this chapter we’ll look at what MIDI is and does and which MIDI
functions are available on the FR-7/FR-5.
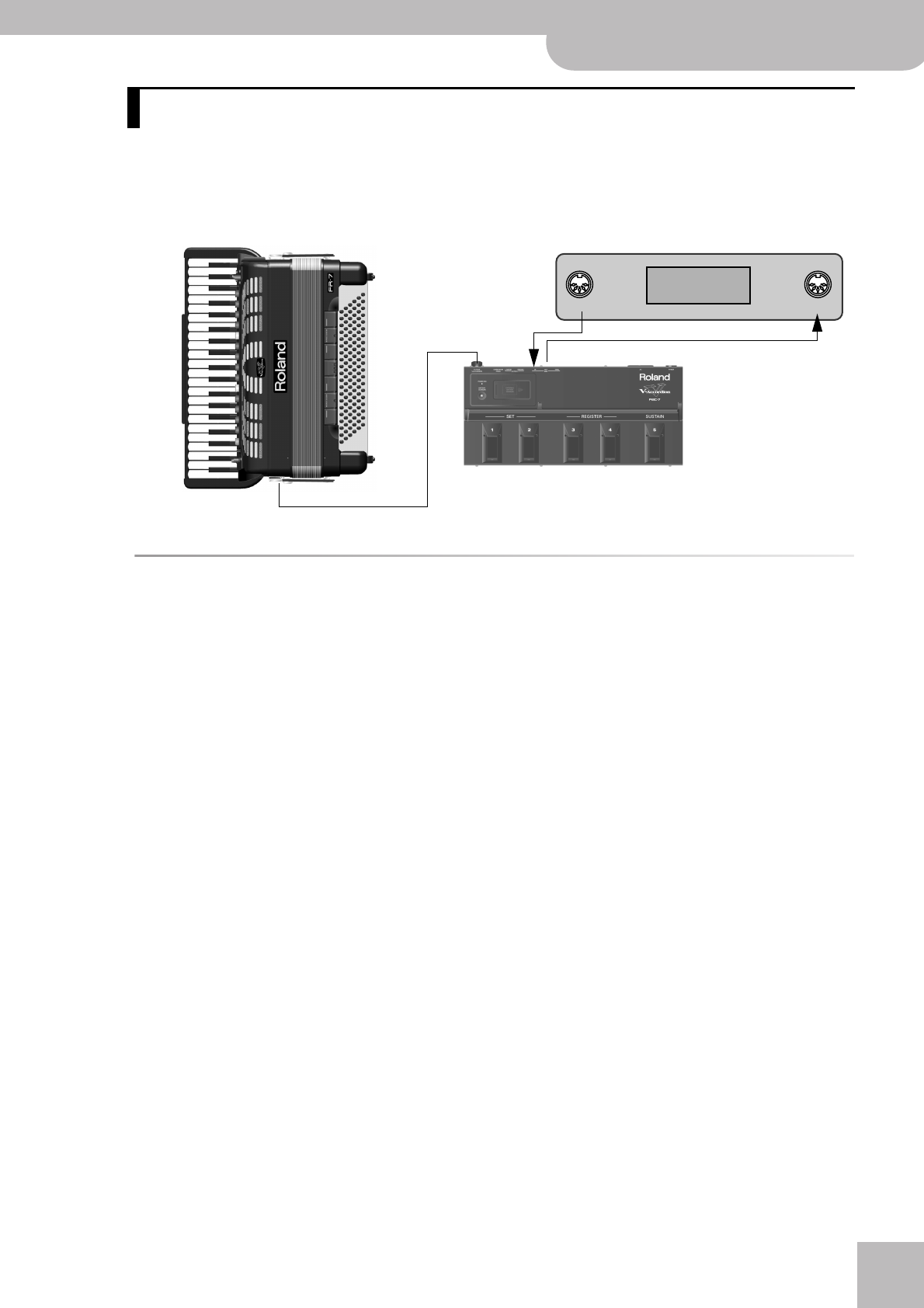
IMPORTANT REMARK: To take advantage of the FR-7/FR-5’s MIDI functions, you must connect it to the supplied FBC-7,
because the FR-7/FR-5 itself has no MIDI sockets.
About MIDI
Even though your FR-7/FR-5 is already a remarkably
flexible instrument (quite unlike any other accordion
available today), you may also want to use it with other
MIDI-compatible instruments, sequencers and comput-
ers to record your performances in the same way as
keyboard players, drummers, guitarists, etc., have been
doing for a while.
Another important application for the FR-7/FR-5’s MIDI
functions is controlling an arranger module that sup-
plies the accompaniment. “Arranger modules” use short
accompaniment patterns that can be selected in real-
time and whose key depends on the note information
they receive. You can select those patterns by assigning
the corresponding MIDI messages to the FBC-7’s foot-
switches (see p. 68), so that you do not have to stand or
sit next to your arranger module.
Both module types (and all MIDI-compatible sound
sources) also allow you to use the FR-7/FR-5’s Treble
and Bass keyboards for playing sounds the FR-7/FR-5
does not provide.
This is possible thanks to a common language for musi-
cal applications, which is called “Musical Instrument
Digital Interface” or “MIDI” for short. MIDI has a lot in
common with the internet: you can link one or several
instruments to one another via a cable (but you don’t
need a telephone line).
You can also use the FR-7/FR-5 as “master keyboard”,
i.e. an instrument that transmits MIDI messages to a
device (or software program) that can record MIDI mes-
sages. Such a device or program is called a “sequencer”.
To take advantage of the FR-7/FR-5’s MIDI functions,
you must connect the FBC-7 as follows:
MIDI OUT: This socket transmits messages describ-
ing actions (such as playing on a keyboard) to the
MIDI IN jack on the external device. The receiving
MIDI device executes the incoming MIDI messages
and plays notes, selects other sounds, etc.
MIDI IN: This socket receives the MIDI messages
transmitted by an external MIDI device.
MIDI THRU: This socket retransmits the MIDI mes-
sages received via the FBC-7’s MIDI IN port. You can
connect it to the MIDI IN port of an another MIDI
device.
Note: The MIDI THRU port does not transmit the MIDI mes-
sages generated by the FR-7/FR-5. Those messages are only
sent to the FBC-7’s MIDI OUT port.
MIDI can simultaneously transmit and receive messages
on 16 channels, so that up to 16 instruments (or parts
of a module or synthesizer) can be controlled. Nowa-
days, most instruments –like your FR-7/FR-5– are mul-
titimbral, which means that they can play several musi-
cal parts with different sounds. This requires the use of
several MIDI channels. The FR-7/FR-5, for instance, has
several accordion and orchestral sections that can be
played simultaneously. They can transmit and receive
on different channels.
7. MIDI functions
MIDI OUT MIDI IN
External MIDI device


















