Real–Number Functions 4–9
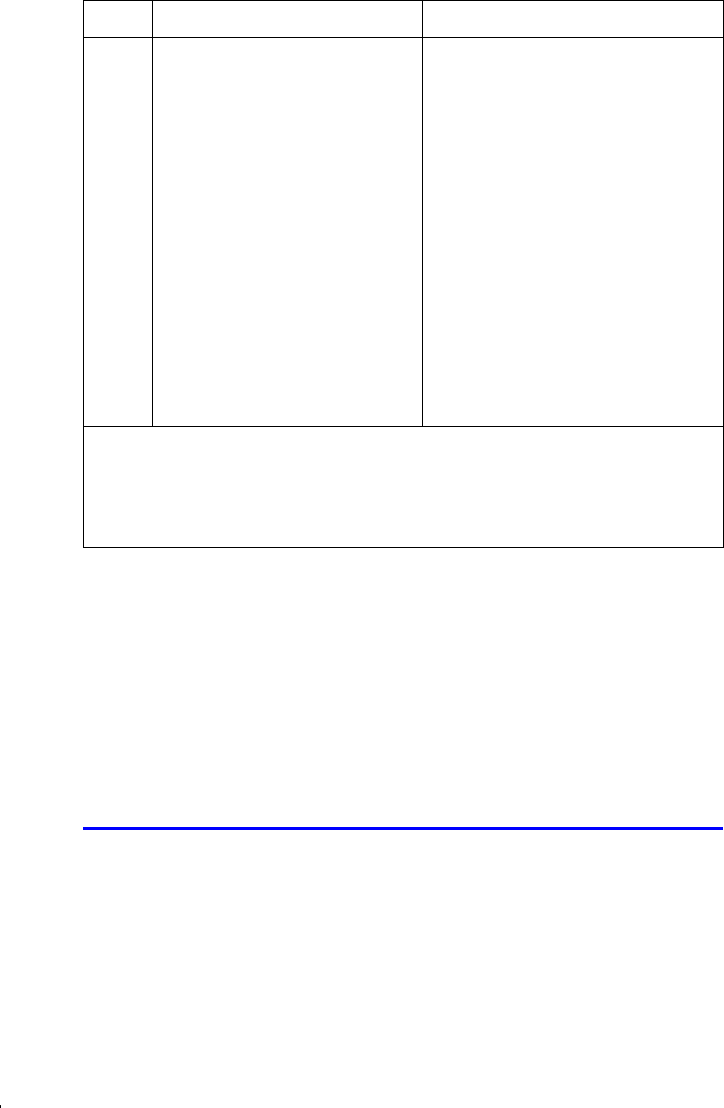
Items Description Value
{
TH
} Classical electron radius 2.817940285
×
10
–15
m
{
'
µ
} Characteristic impendence of
vacuum
376.730313461
Ω
{
λ
F
} Compton wavelength 2.426310215
×
10
–12
m
{
λ
FQ
} Neutron Compton wavelength 1.319590898
×
10
–15
m
{
λ
FR
} Proton Compton wavelength 1.321409847
×
10
–15
m
{
α
} Fine structure constant 7.297352533
×
10
–3
{
σ
} Stefan–Boltzmann constant 5.6704
×
10
–8
W m
–2
K
–4
{
V
} Celsius temperature 273.15
{a
VP
} Standard atmosphere 101325 Pa
{
͋
R
} Proton gyromagnetic ratio 267522212 s
–1
T
–1
{
} First radiation constant 374177107
×
10
–16
W m
2
{
} Second radiation constant 0.014387752 m K
{
µ
} Conductance quantum 7.748091696
×
10
–5
S
Reference: Peter J.Mohr and Barry N.Taylor, CODATA Recommended Values of
the Fundamental Physical Constants: 1998, Journal of Physical and Chemical
Reference Data,Vol.28, No.6,1999 and Reviews of Modern Physics,Vol.72,
No.2, 2000.
To insert a constant:
1.
Position your cursor where you want the constant inserted.
2. Press
|
to display the physics constants menu.
3. Press
(or, you can press
|
to access
the next page, one page at a time) to scroll through the menu until the constant
you want is underlined, then press
to insert the constant.
Conversion Functions
There are four types of conversions: coordinate (polar/rectangular), angular
(degrees/radians), time (decimal/minutes–seconds), and unit (cm/in, °C/°F, l/gal,
kg/lb).
