4 RFID Introduction
RX2 User’s Guide E-EQ-RX2OGWW-B
RFID Introduction
Radio frequency identification, or RFID, is a generic term for technologies that use radio waves to
automatically identify individual items. The individual items identified/read by a RFID reader
contain a tag (also known as an electronic label or transponder). Unlike barcodes that must be read
by a beam passing over the barcode, RFID tags do not have to be in the line of sight of the reader
before the reader can collect the data from the tag but they do need to be within the established
reading range of the RFID-module.
See the “RX2 Reference Guide” for further information and configuration.
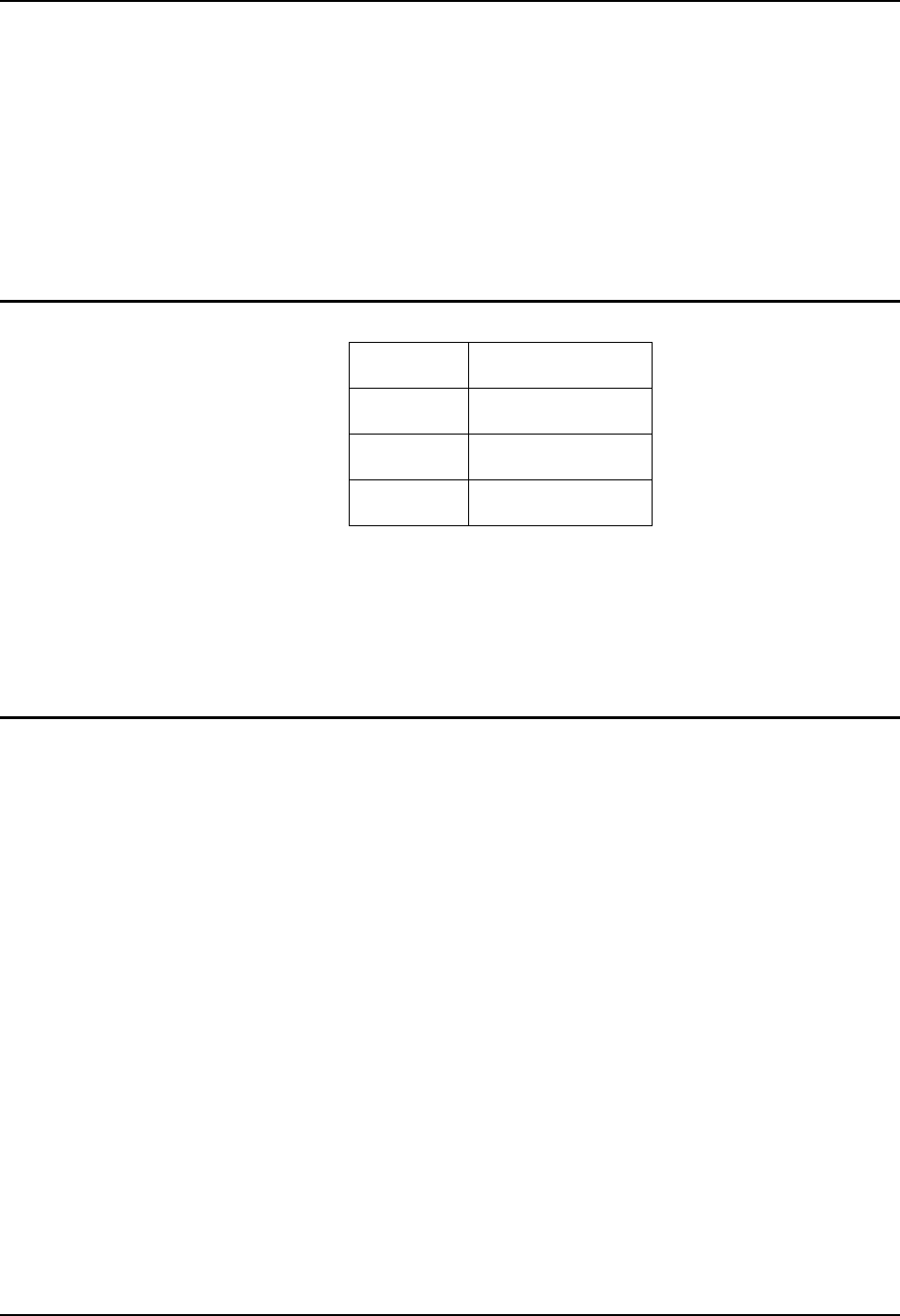
RFID Reader Scan Range
Type of Tag Scan Range
Class 0 Tag 9.8 feet / 3.0 meters
Class 1 Tag 9.8 feet / 3.0 meters
Gen2 Tag 9.8 feet / 3.0 meters
Figure 3 RFID Tag Reading Ranges
Unlike barcode scanners that require line-of-sight before successfully reading a barcode, the RFID
reader does not require line-of-sight when searching for and reading tags.
The range of the RFID reader is dependent on many outside influences including the tag
construction and orientation.
RFID Tag Data Collection
Generally, when the RX2 is on, the RFID reader is ready for use.
• While the RX2 is booting, the Power LED is lit solid. The RFID reader is not
available until the Power LED beings flashing and all drivers have finished loading.
• Please consult your system administrator for application details. Although the reader
is ready for use, the application may not yet have enabled the reader.
• If the battery charger is connected to the RX2, the RX2 remains Off, even if the
power switch is in the On position.
The reader supports Class 0 (read only) and Class 1 (read and write) tags as well as Class 1 Gen2
(read and write) tags.
The RFID information is relayed to the network via the 802.11 radio in the RX2. Data
transmission is application specific. Please refer to your system administrator for details.
