18 Onyx 1220i
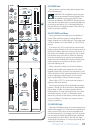
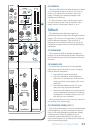
22. SEND FIREWIRE PRE/POST
Each channel of the mixer can send a FireWire output
to your computer or DAW. The FireWire output from
each channel can be tapped before (pre) or after (post)
the channel EQ. (The output is always pre-fader.)
If you want the mixer EQ to affect the FireWire
recording, then set this switch to post. This is useful
in recording channels in a studio (where the recording
includes the benefi cial effect of our Perkins EQ).
If you would rather record the straight signals from a
live performance, and EQ them later in your DAW, then
set this switch to pre. This is good for live work, where
you may have added EQ to adjust for the room, and yet
not want this added to your recording.
23. INPUT (LINE or FW 1-2)
Channel 11 and 12 can either be fed from the
1/4" line level inputs, or by two outputs from a computer
via FireWire. This switch lets you choose which to use.
Either way, the channels receive line-level analog audio
signals just prior to the gain control, so channel setup,
gain adjustment and EQ adjustment are the same for
line or FireWire. This is useful for virtual instruments
that want to be "just another channel" among hardware
instruments.
CHANNEL EQUALIZATION (EQ)
There are two different fl avors of EQ:
Mono Channels 1-4
3-band EQ with shelving high, shelving low, and
peaking mid EQ with adjustable mid frequency.
Stereo Channels 5-12
3-band EQ with shelving high, shelving low, and
peaking mid EQ.
Shelving means that the circuitry boosts or cuts all
frequencies past the specifi ed frequency. For example,
the low EQ boosts bass frequencies below 80 Hz and
continuing down to the lowest note you never heard.
Peaking means that certain frequencies form a “hill”
around the center frequency.
With too much EQ, you can really upset
things. We’ve designed a lot of boost and cut
into each equalizer circuit because we know
that everyone will occasionally need that. But if you max
the EQ on every channel, you’ll get mix mush. Equalize
subtly and use the left sides of the knobs (cut), as well
as the right (boost). If you fi nd yourself repeatedly using
a lot of boost or cut, consider altering the sound source,
such as placing a mic differently, trying a different kind
of mic, a different vocalist, changing the strings, or
gargling.
20. 48V PHANTOM POWER (Ch.1–4 only)
Most modern professional condenser mics require
48V phantom power, which lets the mixer send
low-current DC voltage to the mic’s electronics through
the same wires that carry audio. (Semi-pro condenser
mics often have batteries to accomplish the same
thing.) “Phantom” owes its name to an ability to be
“unseen” by dynamic mics (Shure SM57/SM58, for
instance), which don’t need external power and aren’t
affected by it anyway.
Press this switch in if your microphone requires
phantom power. (Always check the position of this
switch before connecting microphones.)
Never plug single-ended (unbalanced)
micro phones, or ribbon mics into the mic
input jacks if phantom power is on. Do not
plug instrument outputs into the mic XLR input jacks
with phantom power on, unless you know for certain it
is safe to do so. Be sure the main level [51] is turned
down when connecting microphones to the mic inputs
when phantom power is turned on, to prevent pops from
getting through to the speakers.
21. GAIN CONTROL
If you haven’t already, please read the level-setting
procedure on page 3.
The gain knobs adjust the input sensitivity of the mic
and line inputs. This allows signals from the outside
world to be adjusted to run through each channel at
optimal internal operating levels.
If the signal originates through the mic XLR jack,
there will be 0 dB of gain with the knob fully down,
ramping to 60 dB of gain fully up.
Through the 1⁄4" line input of channels 1-4, there is
20 dB of attenuation fully down and 40 dB of gain fully
up, with unity gain "U" at 11:00.
Through the 1⁄4" line input of channels 5-12, there is
20 dB of attenuation fully down and 20 dB of gain fully
up, with unity gain "U" at 11:00.
This 20 dB of attenuation can be very handy when
you are inserting a hot signal, when you want to add EQ
gain, or both. Without this “virtual pad,” there is more
chance of channel clipping.