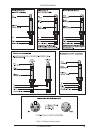
18
EURORACK MX2004A
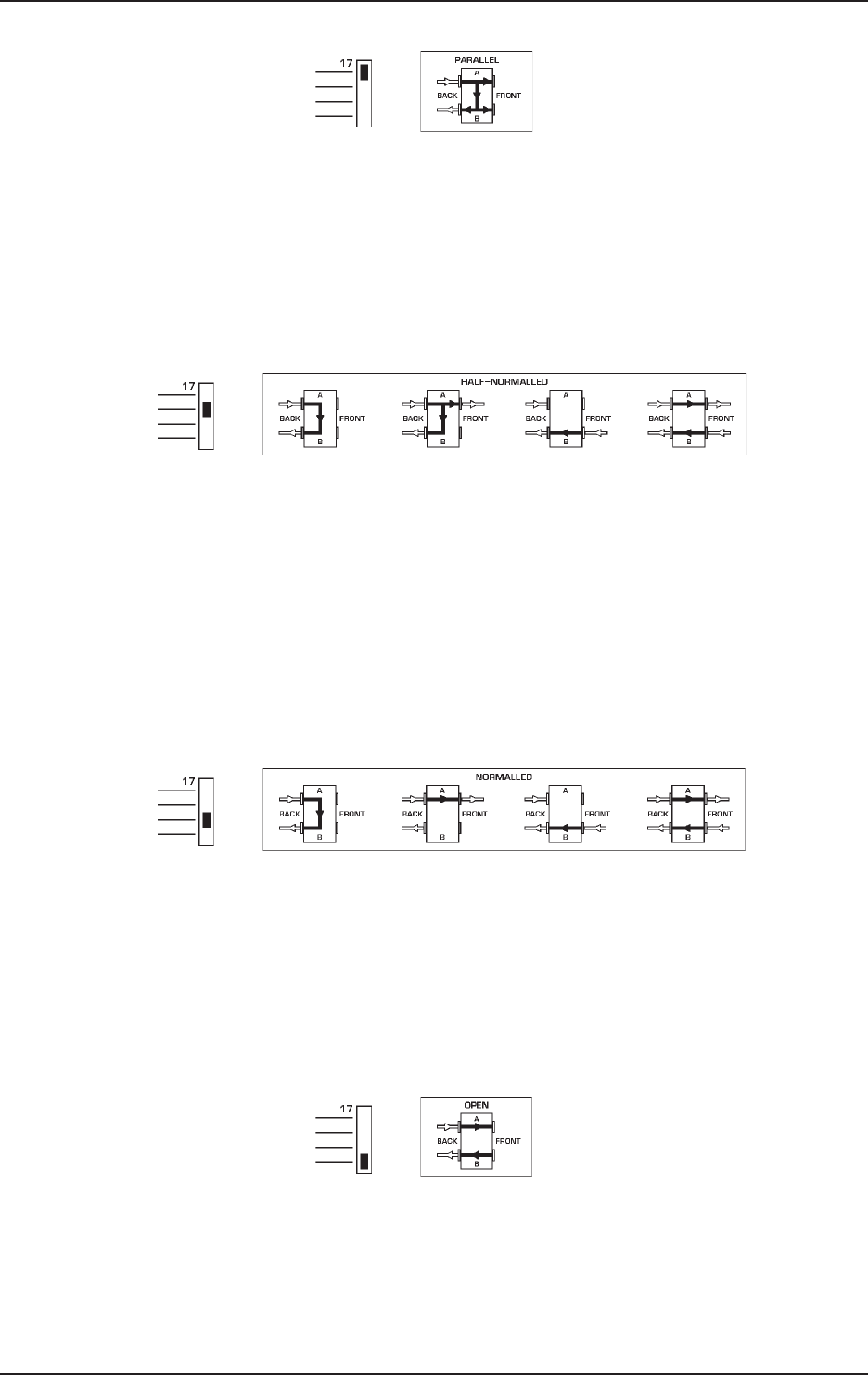
6.4.2 Parallel
Fig. 6.2: Patchbay mode “parallel”
In this mode, all terminals of one module are interconnected. This configuration doesn’t make sense at first glance
but is used to split up and send one audio signal (e.g. aux send) to several destinations (e.g. effects devices).
6.4.3 Half-normalled
Fig. 6.3: Patchbay mode “half-normalled”
In this configuration, the contacts of the two jacks on the rear are interconnected. When you insert a plug into the
upper front jack, the signal routed through the rear path is not interrupted. Only when the lower front jack is used
will the rear panel route be split up, so that the two upper and the two lower phone jacks are connected to one
another. This configuration is called “input break” and is used mainly for insert paths. So you can easily patch the
signal from a mixing console channel at the Patchbay without interrupting the signal flow in the channel.
6.4.4 Normalled
Fig. 6.4: Patchbay mode “normalled”
Here, and in contrast to the “half-normalled” setup, the signal route of the rear phone jacks is interrupted when
you insert a plug both into the upper and lower front jacks.
6.4.5 Open
Fig. 6.5: Patchbay mode “open”
This mode is used to connect devices such as sound modules or CD players having no inputs of their own. This
saves space, as you can route the left and right outputs to one module (left - top; right - bottom) or patch two
devices to one module (top and bottom). Effects devices and 2-tracks can be configured this way, so the inputs
6. APPLICATIONS