SECTION 4
26
REVERB
Reverb can be thought of as a great number of distinct echos, called
reflections, that occur so fast that our ear hears them blurred together as
one. In nature, different size spaces give distinctly different sounding
reverbs, depending upon the size and shape of the space (called Reverb
Density), and the texture of the surfaces that the reflections bounce off of
(called Reverb Diffusion). The various parameters of the MIDIVERB III
make it possible to simulate nearly any natural reverberant space that
can be imagined, and a few artificial ones as well.
The programmable parameters are:
REVERB ALGORITHM
There are 20 different Reverb Algorithms, or Reverb versions, in the
MIDIVERB III. Each algorithm has a different sound and simulates a
different acoustic environment. See Figure 5.
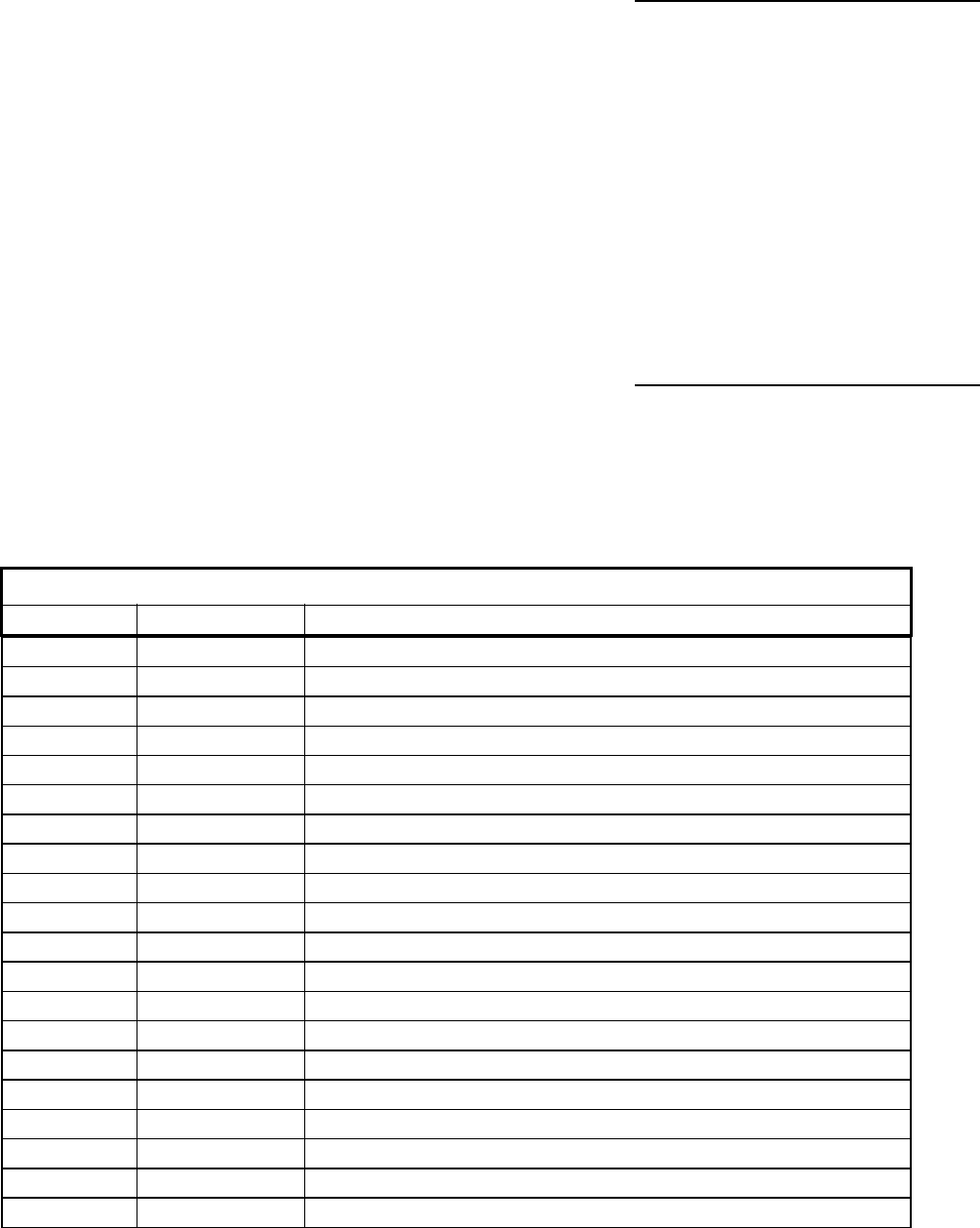
FIGURE 5
REVERB ALGORITHMS
DISPLAY ALGORITHM CHARACTERISTICS
ro1 Room 1 SMALL ROOM High density; low diffusion
ro2 Room 2 SMALL ROOM High density; high diffusion
ro3 Room 3 MEDIUM ROOM Medium density; medium diffusion
ro4 Room 4 LARGE ROOM Low density; high diffusion
HL1 Hall 1 SMALL HALL Medium density; high diffusion
HL2 Hall 2 SMALL HALL High density; low diffusion
HL3 Hall 3 MEDIUM HALL Medium density; medium diffusion
HL4 Hall 4 LARGE HALL Low density; low diffusion
CH1 Chamber 1 MEDIUM CHAMBER Medium density; medium diffusion
CH2 Chamber 2 MEDIUM CHAMBER Medium density; high diffusion
CH3 Chamber 3 LARGE CHAMBER High density; low diffusion
CH4 Chamber 4 PERCUSSION CHAMBER Medium density; high diffusion
PL1 Plate 1 PERCUSSION PLATE High density; low diffusion
PL2 Plate 2 TIGHT PLATE High density; medium diffusion
PL3 Plate 3 SOFT PLATE Medium density; medium diffusion
PL4 Plate 4 VOCAL PLATE Low density; high diffusion
gt1 Gate 1 BRIGHT GATE High density; low diffusion
gt2 Gate 2 POWER GATE Medium density; medium diffusion
rE1 Reverse 1 MEDIUM REVERSE High density; low diffusion
rE2 Reverse 2 SLOW REVERSE Low density; low diffusion


















