6
—Owner’s Manual
Touring the MT400
This section takes you on a tour of the MT400, identifying the various parts to familiarize you
with your new recorder.
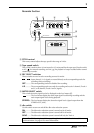
Input Channels
A
GAIN control
This rotary control adjusts the sensitivity of the MIC/LINE
INPUT jack
d
so that both microphone and line-level (such
as a synthesizer) signals can be handled with ease.
B
EQ control
These rotary controls are used to adjust a tonal quality of the
high, middle, and low frequency bands independently. They
boost (amplify) and cut (attenuate) the corresponding basic
frequency in the range of
±
12 dB. A flat setting (i.e., no boost
or cut) can be set quickly using the control’s center detentes.
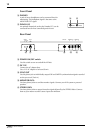
HIGH: Basic frequency 12 kHz (shelving type)
MID: Basic frequency 1 kHz (peaking type)
LOW: Basic frequency 80 Hz (shelving type)
C
AUX controls
These rotary controls are used to send the input channel (1–4) signal to the AUX SEND 1 and
2 outputs. They are commonly used to adjust the level of signal sent to external effects
processors.
D
CUE control
This control is used to adjust the level of Track (1–4) input signal and playback signal that will
be sent to the cue bus. The CUE bus signals are output from the PHONES jack or the
MONITOR OUT jack for monitoring.The CUE signal source depends on the [INPUT-FLIP]
switch
5
.
Note:
The AUX controls handle post-fader signals (signals that have passed through the
faders
7
). If the faders are lowered all the way, the AUX control settings will not be effective.
GAIN
HIGH
10
9
8
7
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
LINE MIC
–12 +12
MID
–12 +12
LOW
–12 +12
AUX
1
010
AUX
2
MIX CUE
010
010
PAN
INPUT-FLIP
TAPE
TAPE
MIC/
LINE
MIC/LINE
to L
LR
1
2
3
1
4
5
6
7
10k 20k1k10020
–15
–10
–5
0
5
10
15
Frequency (Hz)
50
5k2k500200
Response (dB)