R
e
f
e
r
e
n
c
e
DGX-505/305 Owner’s Manual 79
Connecting To a Computer
Nearly all of the electronic musical instruments made today – particularly synthesizers,
sequencers and computer music related devices – use MIDI. MIDI is a worldwide standard that
allows these devices to send and receive performance and setting data. Naturally, this instru-
ment lets you save or send your keyboard performance as MIDI data, as well as that of the
songs, styles and panel settings.
The potential MIDI holds for your live performance and music creation/production is enormous
– simply by connecting this instrument to a computer and transmitting MIDI data. In this sec-
tion, you'll learn the basics of MIDI and the particular MIDI functions of this instrument.
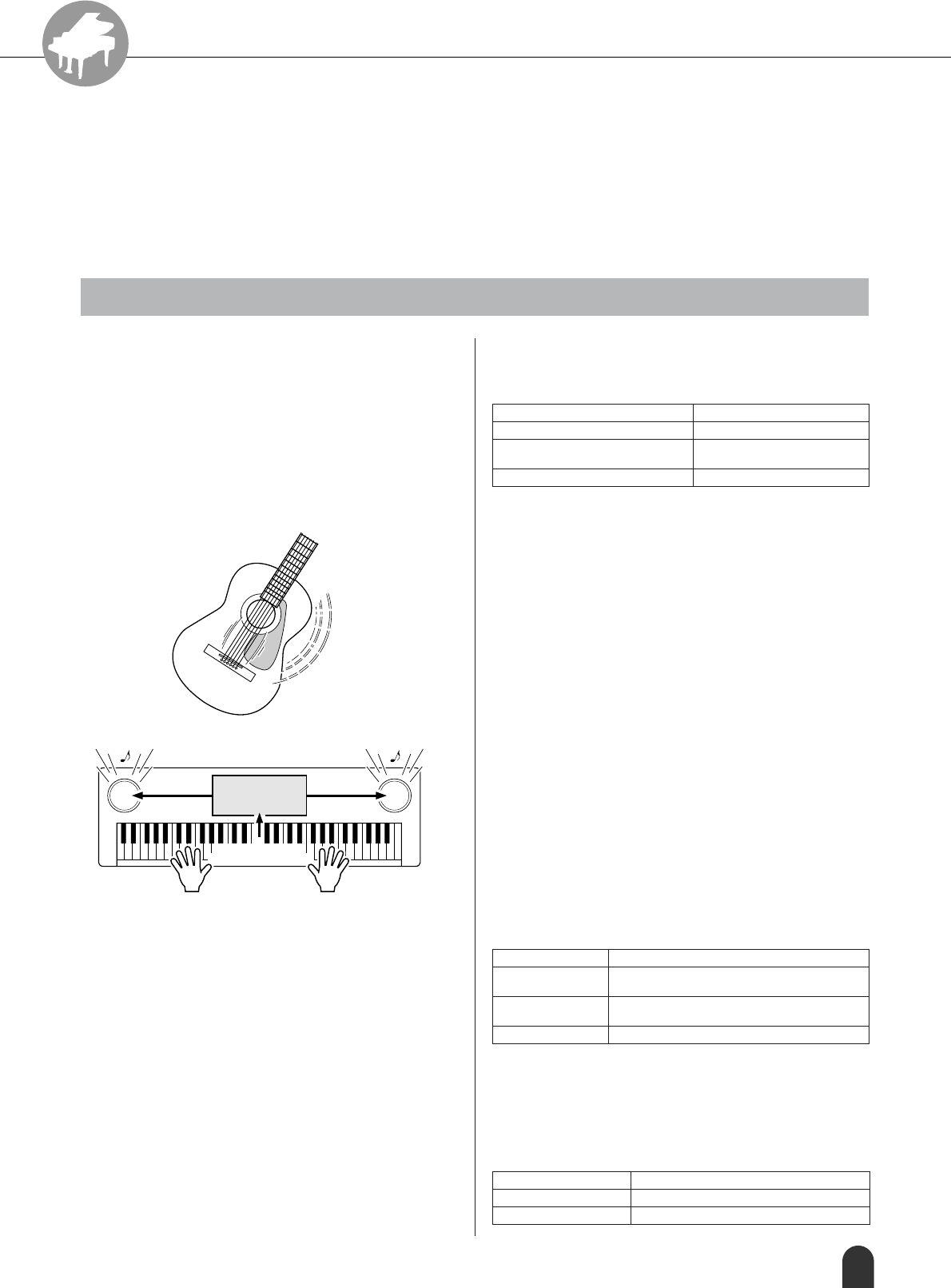
No doubt you have heard the terms “acoustic instru-
ment” and “digital instrument.” In the world today,
these are the two main categories of instruments. Let's
consider a grand piano and a classical guitar as repre-
sentative acoustic instruments. They are easy to under-
stand. With the piano, you strike a key, and a hammer
inside hits some strings and plays a note. With the gui-
tar, you directly pluck a string and the note sounds. But
how does a digital instrument go about playing a note?
As shown in the illustration above, in an electronic
instrument the sampling note (previously recorded note)
stored in the tone generator section (electronic circuit)
is played based on information received from the key-
board. So then what is the information from the key-
board that becomes the basis for note production?
For example, let’s say you play a “C” quarter note using
the grand piano sound on the instrument. Unlike an
acoustic instrument that puts out a resonated note, the
electronic instrument puts out information from the key-
board such as “with what voice,” “with which key,”
“about how strong,” “when was it pressed,” and “when
was it released.” Then each piece of information is
changed into a number value and sent to the tone gener-
ator. Using these numbers as a basis, the tone generator
plays the stored sampling note.
Example of Keyboard Information
Your keyboard performance and all panel operations of
this instrument are processed as MIDI data. The songs,
auto accompaniment (styles), and User songs are also
made up of MIDI data.
MIDI is an acronym that stands for Musical Instrument
Digital Interface and it allows different musical instru-
ments and devices to instantly communicate with each
other, via digital data. The MIDI standard is used all
over the world and was designed to transmit perfor-
mance data between electronic musical instruments (or
computers). Thanks to MIDI, you can control one
instrument from another and transmit performance data
between the devices-taking your creative and perfor-
mance potential to even higher levels.
MIDI messages can be divided into two groups: Chan-
nel messages and System messages.
● Channel Messages
This instrument is capable of handling 16 MIDI chan-
nels simultaneously – meaning it can play up to sixteen
different instruments at the same time. Channel mes-
sages transmit information such as Note ON/OFF, Pro-
gram Change, for each of the 16 channels.
● System Messages
This is data that is used in common by the entire MIDI
system. System messages include messages like Exclu-
sive Messages that transmit data unique to each instru-
ment manufacturer and Realtime Messages that control
the MIDI device.
What Is MIDI?
● Acoustic guitar note production
Pluck a string and the body
resonates the sound.
● Digital instrument note production
Based on playing information from the keyboard, a sampling note
stored in the tone generator is played through the speakers.
Playing the keyboard
Tone Generator
(Electronic circuit)
LR
Sampling
Note
Sampling
Note
Voice number (with what voice) 1 (grand piano)
Note number (with which key) 60 (C3)
Note on (when was it pressed) and
note off (when was it released)
Timing expressed numerically
(quarter note)
Velocity (about how strong) 120 (strong)
Message Name Instrument Operation/Panel Setting
Note ON/OFF Performance data of the keyboard (contains
note number and velocity data)
Program Change Instrument selection (including bank select
MSB/LSB, if necessary)
Control Change Instrument settings (volume, pan, etc.)
Message Name Instrument Operation/Panel Setting
Exclusive Message Reverb/chorus settings, etc.
Realtime Messages Start/stop operation


















