© Copyright 2013 TRENDnet. All Rights Reserved.
TRENDnet User’s Guide
TEW-811DRU
21
HT Physical Mode
This section outlines available management options under the HT Physical Mode section
for both 2.4GHz and 5GHz wireless sections.
• Channel Bandwidth: Select the appropriate channel width for your wireless
network. This setting only applies to 802.11n and 802.11ac. For greater 802.11n
performance in 2.4GHz, select 40MHz (Options: 20MHz or 40MHz). For greater
802.11ac performance in 5GHz, select 80MHz (Options: 20MHz, 40MHz, or 80MHz)
It is recommended to use the default channel bandwidth settings.
Note: Please note that this setting may provide more stability than the higher
channel bandwidth settings such as 40 MHz or 80MHz for connectivity in busy
wireless environments where there are several wireless networks in the area.
o 20 MHz – This mode operates using a single 20MHz channel for
wireless devices connecting at 802.11n on both 2.4GHz and 5GHz. This
setting may provide more stability than 40MHz or 80MHz for
connectivity in busy wireless environments where there are several
neighboring wireless networks in the area.
o 40 MHz or 80MHz –When 40MHz or 80MHz is active, this mode is
capable of providing higher performance only if the wireless devices
support the channel bandwidth settings. Enabling 40MHz or 80MHz
typically results in substantial performance increases when connecting
an 802.11n or 802.11ac client. Note: Please note that 80MHz channel
bandwidth is only available for 802.11ac 5GHz.
• MCS: Select the speed you would like your wireless network to operate.
Note: It is recommended to keep the default setting – Auto.
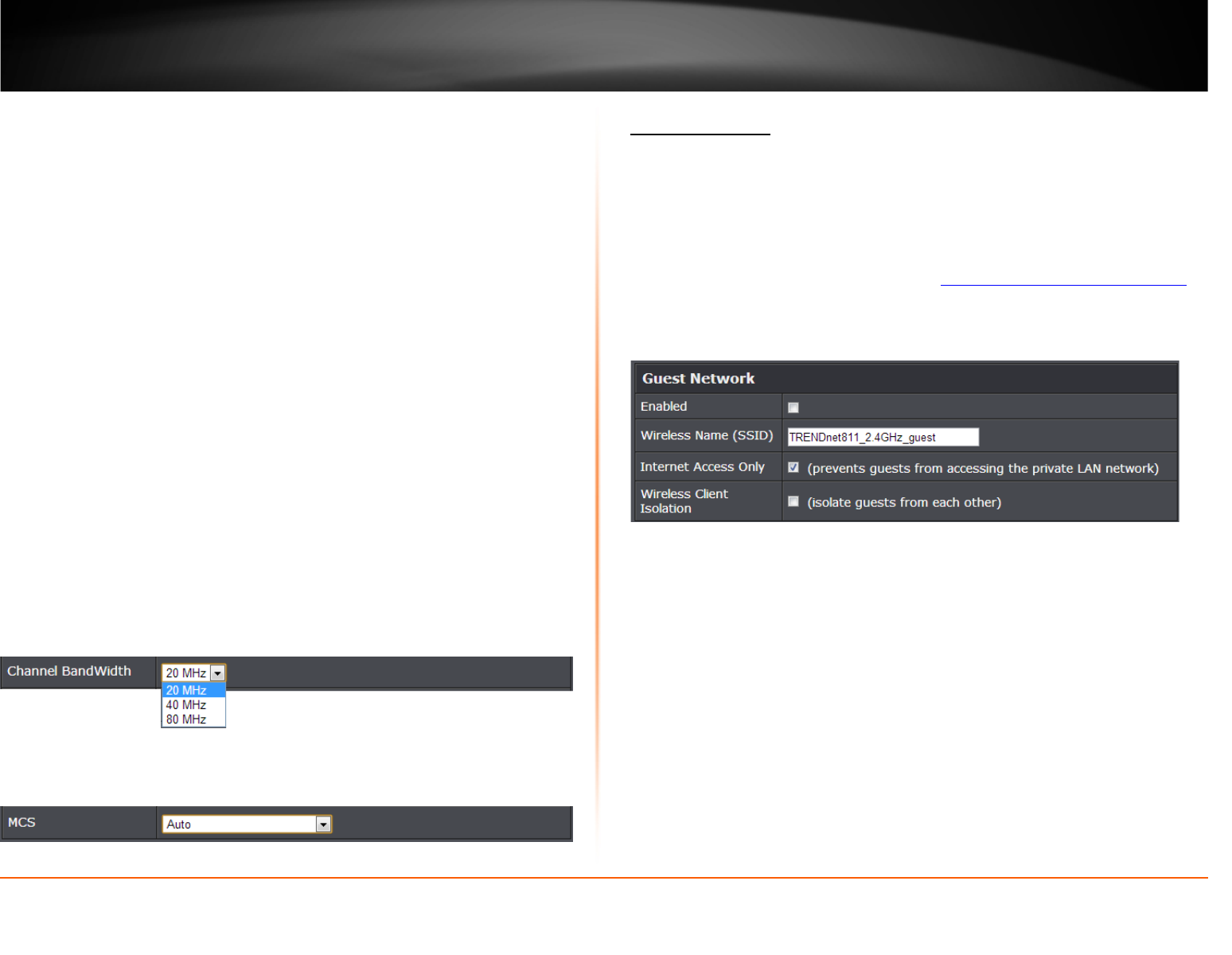
Guest Network
Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) > Guest Network
Creating an isolated and separate wireless guest network (2.4GHz or 5GHz) allows
wireless clients to connect to your network for Internet access only and keep your local
LAN network safe by restricting guest access to your LAN network resources such as
shared documents and media files on your computers, network storage, and printers.
1. Log into your router management page (see “Access your router management page
”
on page 31).
2. Click on Wireless (2.4GHz or 5GHz) and click on Guest Network.
3. Review the Guest Network settings, click Apply when finished.
• Enabled: Check the option to enable the Guest Network.
• Wireless Name (SSID): This acronym stands for Service Set Identifier and is the
name of your wireless network. It differentiates your wireless network from others
around you. It is recommended to use a different name from your primary wireless
network to a name that you can easily identify and differentiate from the primary.
You can reference your guests to access this network instead of the primary.
• Internet Access Only: By default, the option is checked to allow guests to only
access the Internet and restrict access to your local LAN network. Please note that
unchecking this option will open access to local LAN network to guests.
• Wireless Client Isolation: Checking this option will restrict guests from
communicating with each other over the guest network such as share files.
4. Under Security Policy, you can apply a different wireless security type and key to the
guest network. Please refer to page 15 to find out about different security types and
page 16 for wireless security configuration.
