Connections: Chapter 3
CHAPTER 3
CONNECTIONS
BASIC MIDI HOOKUP
MIDI is an internationally-accepted protocol that allows musical-related data to be
conveyed from one device to another. See the MIDI Supplement in Appendix B if you
are not familiar with how MIDI works.
The QS has three MIDI connectors which provide the following functions:
• MIDI IN This port is for receiving MIDI information (notes, program
changes, etc.) from a source such as another QS or MIDI
keyboard, controller, or computer.
• MIDI OUT This port is for transmitting MIDI information to another MIDI
keyboard, sound module, or computer.
• MIDI THRU This port is for passing on (echoing) MIDI information received
by the MIDI IN port. In simple MIDI setups, the THRU port is
used to connect additional devices that will all be “listening” to
the same source.
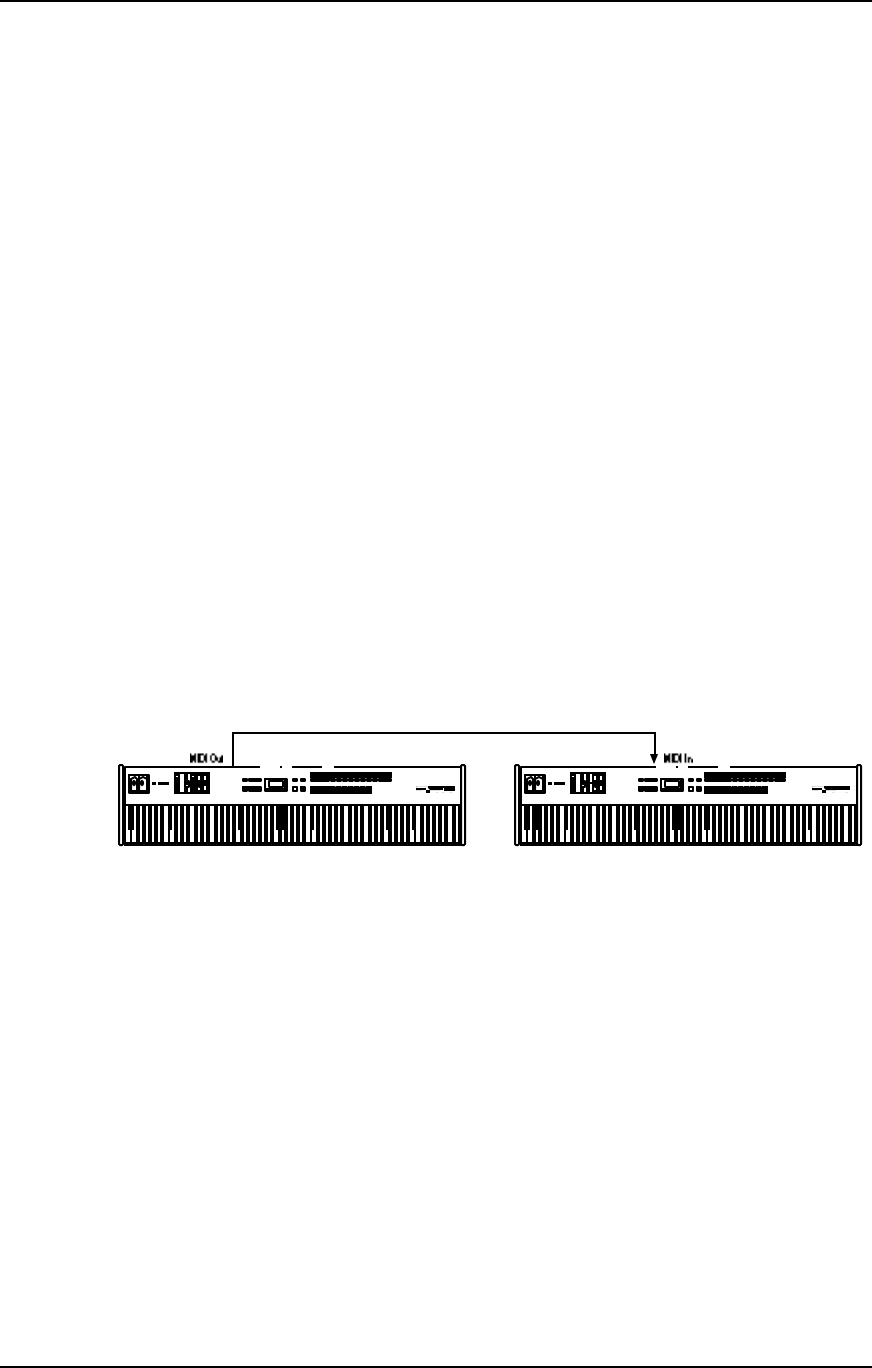
To play the QS from a MIDI control device (keyboard, drum pad, guitar or bass
controller, sequencer, etc.), connect the control device’s MIDI OUT to the QS’s [MIDI
IN]. The illustration below depicts a master QS connected to a slave QS. When both
are set to a common MIDI channel, you can hear both when playing the master QS’s
keyboard.
The QS’s [MIDI OUT] connector sends MIDI data from the QS’s keyboard to other
MIDI devices, but can also send System Exclusive data (see the MIDI supplement) to
a storage device for later recall.
If you are using the QS in the middle of the MIDI chain (example: as the second unit
of a three device chain), connect the QS’ [MIDI THRU] to the third device’s MIDI IN
connector in order to route the first device’s MIDI out information to the third device.
QS7/QS8 Reference Manual 21


















