1 - 9
MELSEC-Q
1 PRODUCT OUTLINE
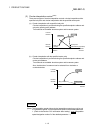
(b) 2-axis linear interpolation control
(Note)
This controls interpolation along a linear locus from the start point address
(current stop position) defined by two axes.
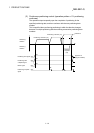
[Control using the absolute system]
1) This performs linear interpolation using two axes from the start point
address to the endpoint address.
2) The start point address and the specified address determine the
direction of travel.
[Example]
The operation when the start point address is 800 for axis 1 and 2000
for axis 2 and the positioning address specified to 2000 for axis 1 and
8000 for axis 2, is shown below.
2000
800
8000
2000
0
Axis 1
Axis 2
Specified address
(8000, 2000)
Positioning operation
Start point address
(2000, 800)
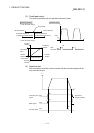
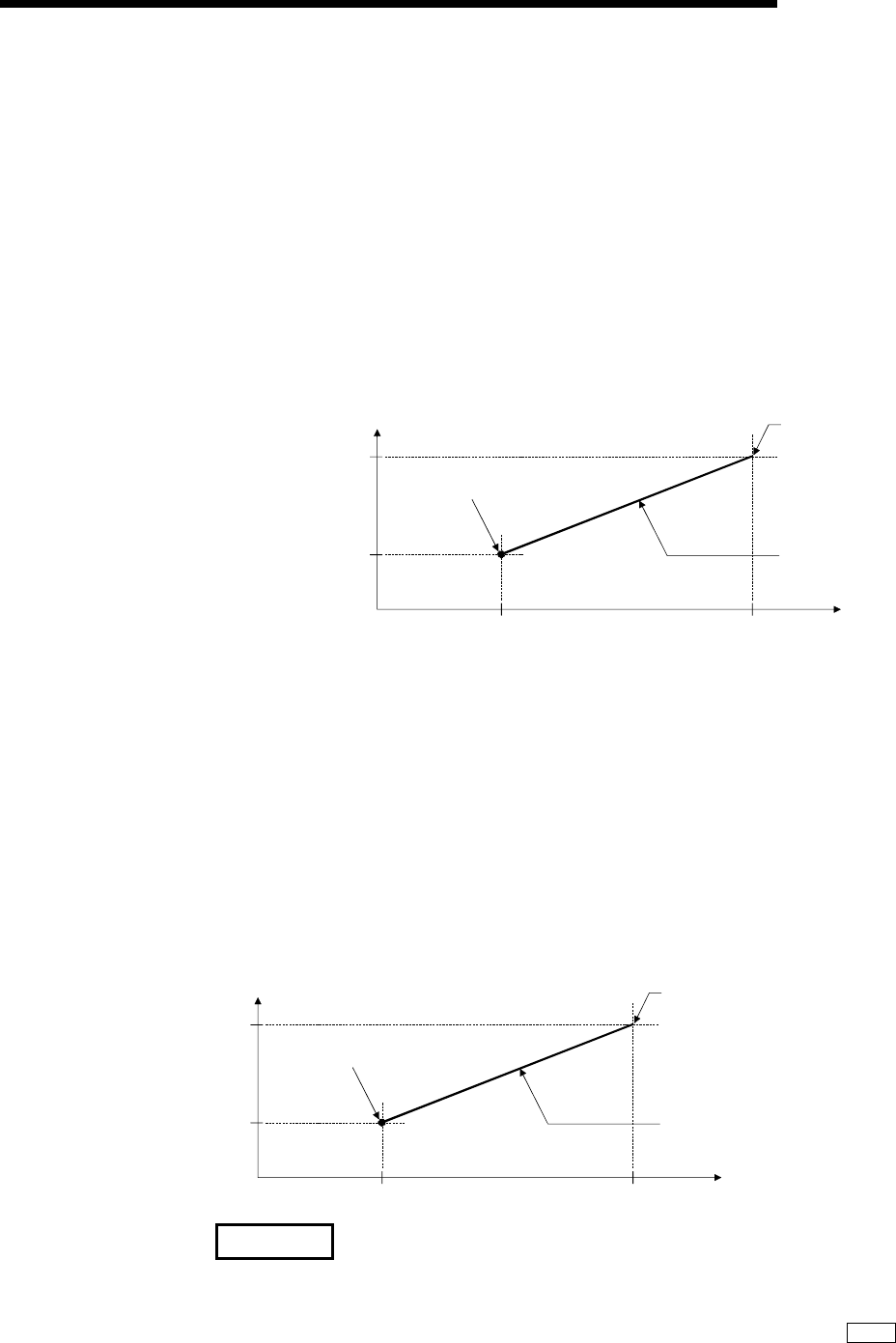
[Control using the increment system]
1) This performs positioning from the specified increment of travel from the
start point address.
2) The sign of the travel increment determines the direction of travel.
• For positive travel increment…….Positioning in the positive direction
(direction of address increase)
• For negative travel increment…….Positioning in the negative direction
(direction of address decrease)
[Example]
The operation when the start point address is 800 for axis 1 and 2000
for axis 2 and the positioning address specified to 1200 for axis 1 and
6000 for axis 2, is shown below.
2000
800
8000
2000
0
Axis 1
Axis 2
End position when the travel incremen
t
is 1200 for axis 1 and 6000 for axis 2.
Positioning operation
Start point address
(2000, 800)
REMARK
(Note): The interpolation speed during linear interpolation control can be selected
from "synthesized axis" and "reference-axis speed" using the detailed
parameter 1. (Refer to the Section 5.2.3 information about setting "
Pr.20
Interpolation speed designation method" of the detailed parameter 1.)