10 Agilent E1538A Enhanced Frequency/Totalize/PWM SCP
is to maintain a constant-level digital output while the input varies from
millivolts to several tens of volts.
For simple sensing of switches and open collector logic devices, a channel’s
pull-up resistor can be connected by closing its PU switch.
VRS Mode
Input Operation (SCP
channels 0 & 1 only)
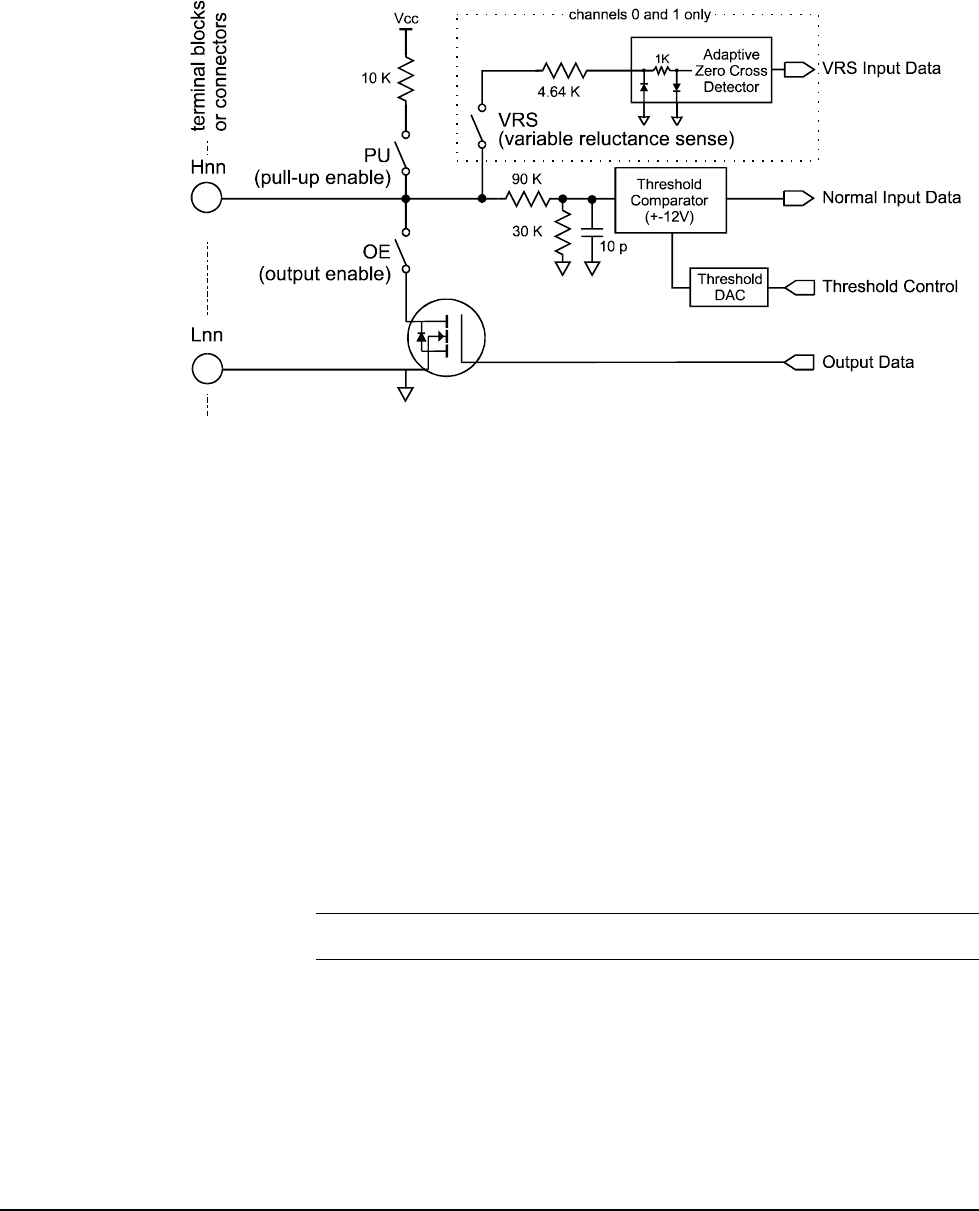
When the VRS configuration switch is set to on, the input signal conditioning
for that channel is changed to make it compatible with a typical variable
reluctance sensor. The variable reluctance sensor is commonly used to detect
rotational shaft position and/or velocity. Because the voltage output of a VRS
is proportional to the rate of change of a magnetic field, different rotational
velocities generate different signal amplitudes. The VRS-configured channel
detects the negative going zero-crossing point of the signal. To minimize the
effects of input noise, the zero-crossing detector can only be triggered if the
positive-going portion of the signal exceeded an "arming" threshold. The
arming circuit is reset when zero-crossing detector is triggered so it can’t
re-trigger until after the signal exceeds the arming threshold again. The
arming threshold tracks the positive peak input level and is 80% of this peak
value. By sensing the "zero-crossing" point of the input signal, the VRS mode
isolates signal amplitude changes from affecting signal timing.
Note VRS enable ON is not allowed if PU enable is ON.
At high rotational speeds, variable reluctance sensors can generate voltage
levels over 100VAC. The VRS inputs must be protected against signal levels
over 17.5 Volts. If your VRS will generate voltages over 17.5, you must
provide a resistor in series with the VRS input. The user-supplied resistor,
together with the VRS input’s 5.38K input impedance form a voltage divider
that attenuates the input signal at the channel’s Hi input terminal. Use the
Figure 6. The E1538A Input/Output Characteristics