2
Bosch Security Systems | 04-2003 | 3922 988 43318 en
Digital Congress Network | Installation and Operating Manual | Chapter 10 - Installation Techniques
en | 10-6
Calculating the PCF of a System with respect to cable length
10.4 Calculating the PCF of a System with respect to cable
length
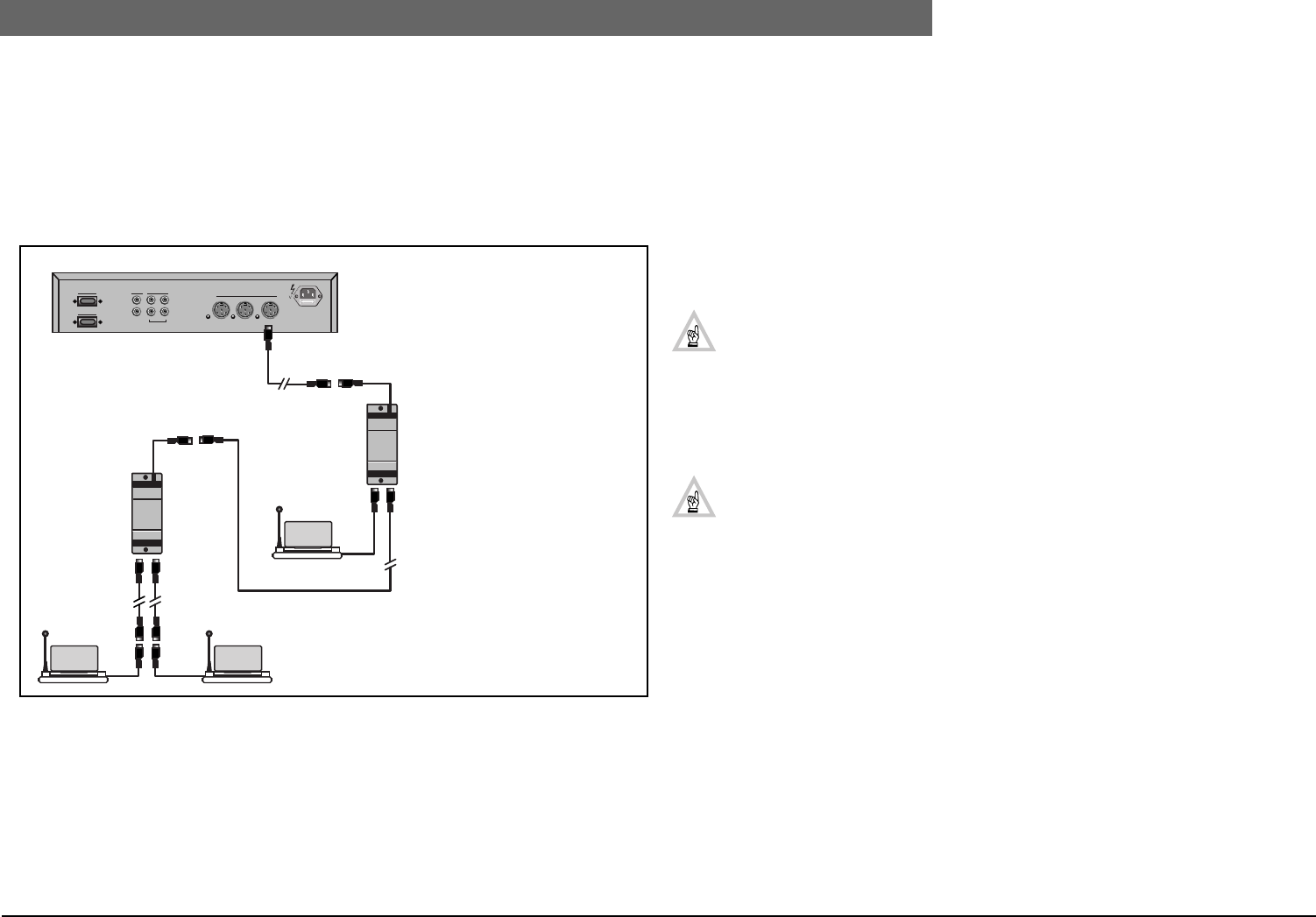
As stated, the length of cable used in a system has a direct influence on the PCF of a system. In the
example shown in FIG 10-7, the second in-line trunk-splitter has two extension cables connected to
it, with lengths of 20 m (65.6 ft.) and 50 m (164 ft.) When determining the cable length of a trunk-
outlet or tap-off connector, the longest extesion cable only is taken in to account - in this example,
the 50 m (164 ft.) cable. Therefore, in this example the total extension cable length from a single
trunk-outlet of the CCU is calculated as 20 (65.6)+10 (32) +50 (164)= 80 m (262 ft.).
FIG 10-7 Calculating the length of extension cables
10.4.1 Calculating Step-by-Step
Before calculating the PCF of a system, consider the following:
• How many units will be connected, and what is their total PCF value?
• What is the total length of cables used per CCU trunk-outlet, and what is the total length of
extension cable used on this trunk-outlet?
Calculation Method
• Using the PCF table (Table 10.1) and the graph (FIG 10-10) calculate the PCF value required for
the system. If the PCF value exceeds 60, then more than one of the CCU’s Trunk outlets must
be used.
• Calculate the length of the cable for each Trunk outlet. “Maximum cable lengths using Trunk
outlets and Tap-offs” when attaining the length of an extension cable.
• A unit with a regenerative tap-off should be placed every 100 m (328 ft.). This length includes
the 2 m (6.5 ft.) cable length of each attached unit.
1. Using the graph, check for each CCU outlet that the cross-over point according to the extension
cable length and the PCF value is within the approved system limits. The approved system limits
are defined by the grey shaded area of the graph.
NOTES:
1. If only one CCU Trunk outlet is needed, step 2 is not applicable.
2. An Microsoft Excel based DCN calculation tool for use on a PC is available on request.
2. Using the data obtained in step 1, (i.e. the PCF value and the length of extension cable) use the
cable correction graph to calculate the PCF value for the relevant Trunk outlets. The PCF values
with cable correction are shown within small white squares. Once done add the PCF value for
each trunk-line. This summed total gives the system PCF value.
NOTE:
This method of calculation is used for all units with Trunk outlets and Tap-offs
The maximum PCF capacities are:
• 60 PCF for each of the Trunk outlets and Tap-offs
• 90 PCF in total for the LBB 3500/05 Central Control unit
• 180 PCF in total for the LBB 3500/15 and LBB 3500/35 Central Control unit
• 90 PCF in total for the LBB 3508/00 Audio Media Interface unit
• 180 PCF in total for the LBB 4106/00 Extension Power Supply unit
When using Trunk-splitters or Tap-off units, their PCF must also be taken into account
(see PCF Table 1).
EXAMPLE:
These examples are based on the system configurations shown in FIG 10-8 and FIG 10-9. These
configurations show two systems using all three trunk-line connectors.
1. Using the graph shown (FIG 10-10) check that each trunk-line in use is within the approved sys-
tem limits (i.e. within the grey shaded area).
2. Using the PCF extension cable correction graph, locate the PCF value on the
‘Y’ axis, that are be
connected to the trunk-line. On the
‘X’ axis, locate the length of extension cable needed. Using
standard graph reading procedures join the two together to obtain the PCF value including exten-
sion cable length correction. The actual PCF value is shown within small shaded squares.
Table No.10.2 gives the PCF value for the example shown in FIG 10-8
Table No.10.3 gives the PCF value for the example shown in FIG 10-9
Port 1
Rec.
Line
In
Out
In
Out
Trunk
115V-T4A 230V -T2A
Port 2
LBB 3500/xx Central Control Unit
20 m (65.6 ft.)
10 m (32.8 ft.)
50 m (164 ft.)20 m (65.6 ft.)
