Parameter guide
30
PROG P2: OSC/Pitch
These pages control the first and most basic elements of
RADIAS program’s sounds: the waveform that the
oscillators play, the pitch, and output level at which it plays
them. For instance, you can:
• Select the oscillator 1 waveform and modulation type,
and specify waveform parameters according to the
modulation type.
• Select the oscillator 2 waveform and modulation type,
and specify the pitch.
• Specify the output level of each oscillator, including the
noise generator.
• Specify the oscillator pitch.
• Specify the vibrato effect applied by the +Y axis of the
joystick.
• Specify the pitch bend range.
• Specify the portamento.
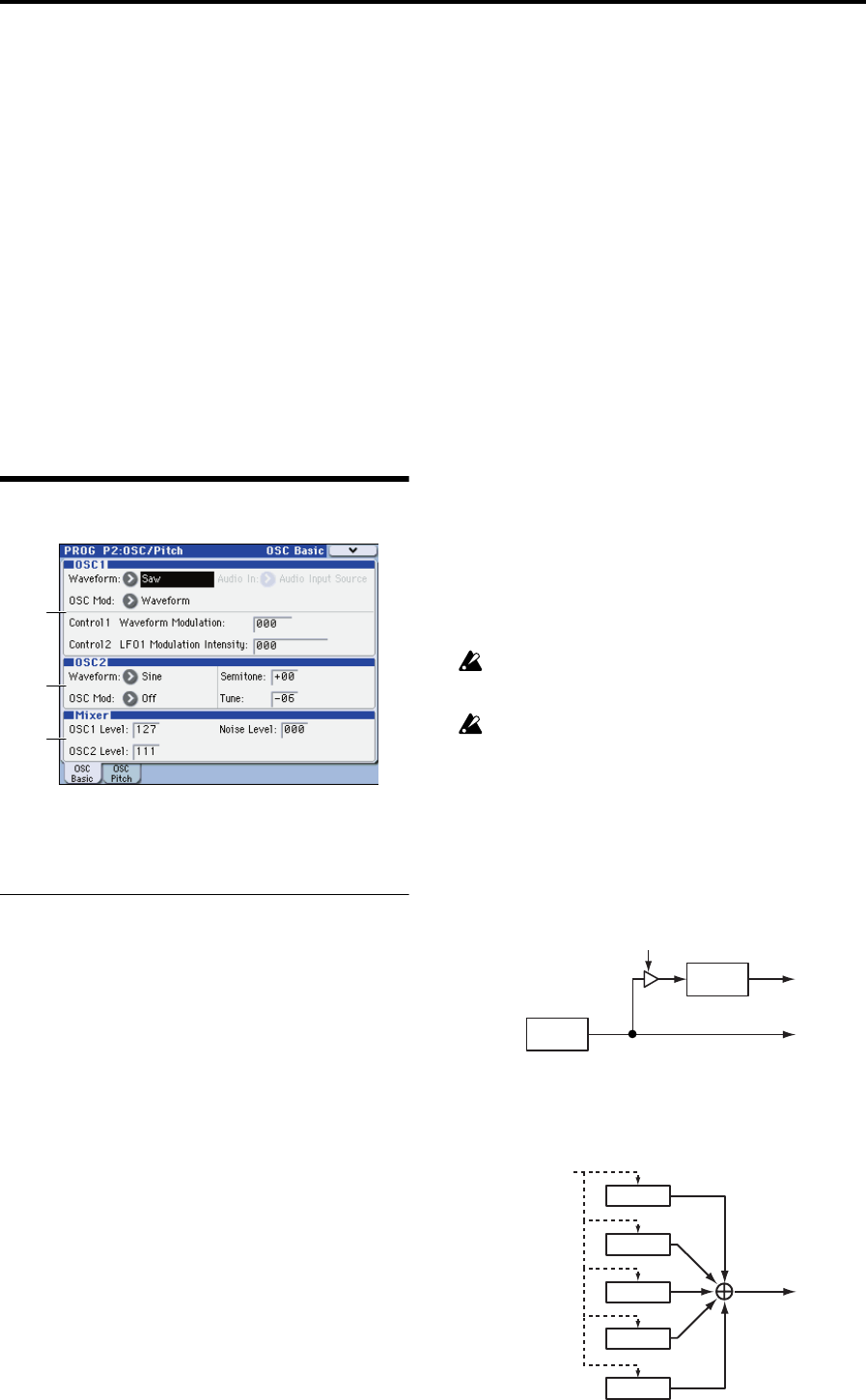
2–1: OSC Basic
These parameters affect the waveform and output of each
oscillator. You can create complex waveforms by using the
two oscillators 1 and 2.
2–1a: OSC1
Waveform (Oscillator1 Waveform)
[Saw, Square, Tri, Sine, Formant, Noise, DWGS,
AudioIn]
Selects the waveform of oscillator 1. The parameters
controlled by the Control1 knob and Control2 knob will be
different based on the waveform you select here and on the
OSC Mod setting.
Saw: This sawtooth wave is appropriate for creating a wide
range of sounds typical of analog synthesizers, including
basses and pads.
Square: This is a pulse wave suitable for electronic sounds
and wind instruments. By adjusting the pulse width you can
produce sounds reminiscent of clavi or sax.
Tri: Triangle wave has fewer overtones than sawtooth wave
or square wave, and is suitable for mild tone such as bass or
pads.
Sine: Sine wave is a mild tone that contains only the
fundamental frequency with no overtones.
Formant: The formant waveform has a tonal character
reminiscent of a human voice.
Noise: Generates noise. Control1 boosts the pitched
component within the noise, and Control2 adjusts the
brightness.
DWGS: This provides various DWGS waveforms taken
from acoustic instruments and digital synthesizers. You can
choose one of 64 different DWGS waveforms.
AudioIn: This lets you use the input source specified by
Audio In as the oscillator output.
Audio In [Audio Input Source, AUX Bus Source]
Selects the audio input source. This is valid only if
Waveform is set to AudioIn. Use Control1 Gain to adjust
the input volume, and Control2 Balance to adjust the
balance.
Audio Input Source: The audio input source will be the
signal from the input jack selected by Audio Inputs (Send
to RADIAS) (Program 1-1c). If the P1: Program Basic page
Unison parameter is Off, the signal will be mixed to mono.
AUX Bus Source: The audio input source will be the signal
from the AUX bus selected by AUX Bus (Send to RADIAS).
Note: In order to use the AUX buses, you must first assign
audio signals to the AUX buses using the audio in post-IFX
AUX setting (Program 8-2) or the drum track AUX setting
(Program 1-4c ☞ “AUX Bus (Send to RADIAS)” on page 26).
If the P1: Program Basic page Unison setting is Off, the
signal will be mixed to mono.
OSC Mod (Oscillator Modulation Type)
[Waveform, Cross, Unison, VPM]
Selects the modulation type for oscillator 1.
The maximum number of voices will change
depending on the combination of Waveform and OSC
Mod settings.
You can’t apply modulation if Waveform is set to
Formant, Noise, DWGS, or AudioIn. This field will be
shown as Waveform.
Waveform (Waveform Modulation): Use Control1 to
modify the waveform.
Cross (Cross Modulation): Cross Modulation uses the
output waveform of oscillator 2 (the modulator) to
modulate the frequency of oscillator 1 (the carrier) at high
speed to produce a modulated sound. The waveform
selected by Waveform will be the carrier.
Unison: Unison skews the pitch of five oscillators within a
single oscillator and outputs them together to create a richer
sound.
2–1a
2–1b
2–1c
OSC2
OSC1
Cross Modulation Depth
OSC2
Output
OSC1
Output
OSC1
Freq Mod
OSC1–1
OSC1–2
OSC1–3
OSC1 Output
Unison Detune
OSC1–4
OSC1–5


















