17
New effects algorithms
Dither Off, 24–8bit
By adding a minute level of noise (dither), this smoothes the
transition between playback audio and silence.
Level -80–+6dB
This adjusts the overall volume level of the sound that has
passed through the limiter (Lmt).
Modeling various speakers
(Speaker Modeling)
You can model the acoustical characteristics of a
variety of speakers, ranging from high-level
professional monitor speakers used in studios
worldwide, to the speakers of small televisions or
portable radios.
NOTE
Speaker modeling has been calibrated so that
the optimal effect
will be obtained when Roland DS-90 powered monitors
are connected digitally
. If you are using other speakers, you
may not be able to obtain the desired effect.
fig.3-08
SpMod (speaker modeling)
Model
THRU, Super FLAT, Powered GenBlk, Powered
E-Bas, Powered Mack, Small Cube, White
Cone, White C +tissue, Small Radio, Small TV,
Boom Box, BoomBox LoBoost
Select the speaker whose characteristics will be simulated
(modeled).
THRU: Modeling will not be applied, and the sound
will be output without change. Use this as a
comparison with the speaker-modeled sounds.
Super FLAT: Modeling is used to compensate the DS-90, to
produce an even flatter sound with a wider
range.
Powered GenBlk: A widely used model of powered
monitors (two-way type, with a woofer
diameter of 170 mm (6-1/2 inches)).
Powered E-Bas: Powered monitors characterized by a
bright tone.
Powered Mack: Powered monitors characterized by an
extended low-frequency response.
Small Cube: Small full-range speakers widely used
in recording studios.
White Cone: Sealed enclosure two-way speakers
known for their white woofers and
widely used in recording studios.
White C + tissue: A more mild sound, with tissue paper
affixed over the tweeters of the above
“White Cone” speakers.
Small Radio: Small pocket-type radio.
Small TV: Speakers built into a 14 inch size
television.
Boom Box: Radio cassette recorder.
BoomBox LoBoost:Radio cassette recorder with the Low
Boost switched on.
Phase NRM, INV
Specifies the phase of the speakers.
NRM: Same phase as the input.
INV: Opposite phase of the input.
BCut (Bass-cut filter)
This removes unwanted low-frequency components, such as
pop noise.
Sw (Switch) Off, On
Switches the bass-cut filter on/off.
Freq (Frequency) Thru, 20–2,000Hz
Adjusts the cutoff frequency of the bass-cut filter.
LFT/HFT (Frequency trimmer)
Sw (Switch) Off, On
Turns the frequency trimmer on/off.
Gain -12–+12dB
For each trimmer, adjusts the gain (amount of boost/cut).
Freq (Frequency) 20–2,000Hz
Freq (Frequency) 1.0–20.0kHz
Set the center frequency of each trimmer.
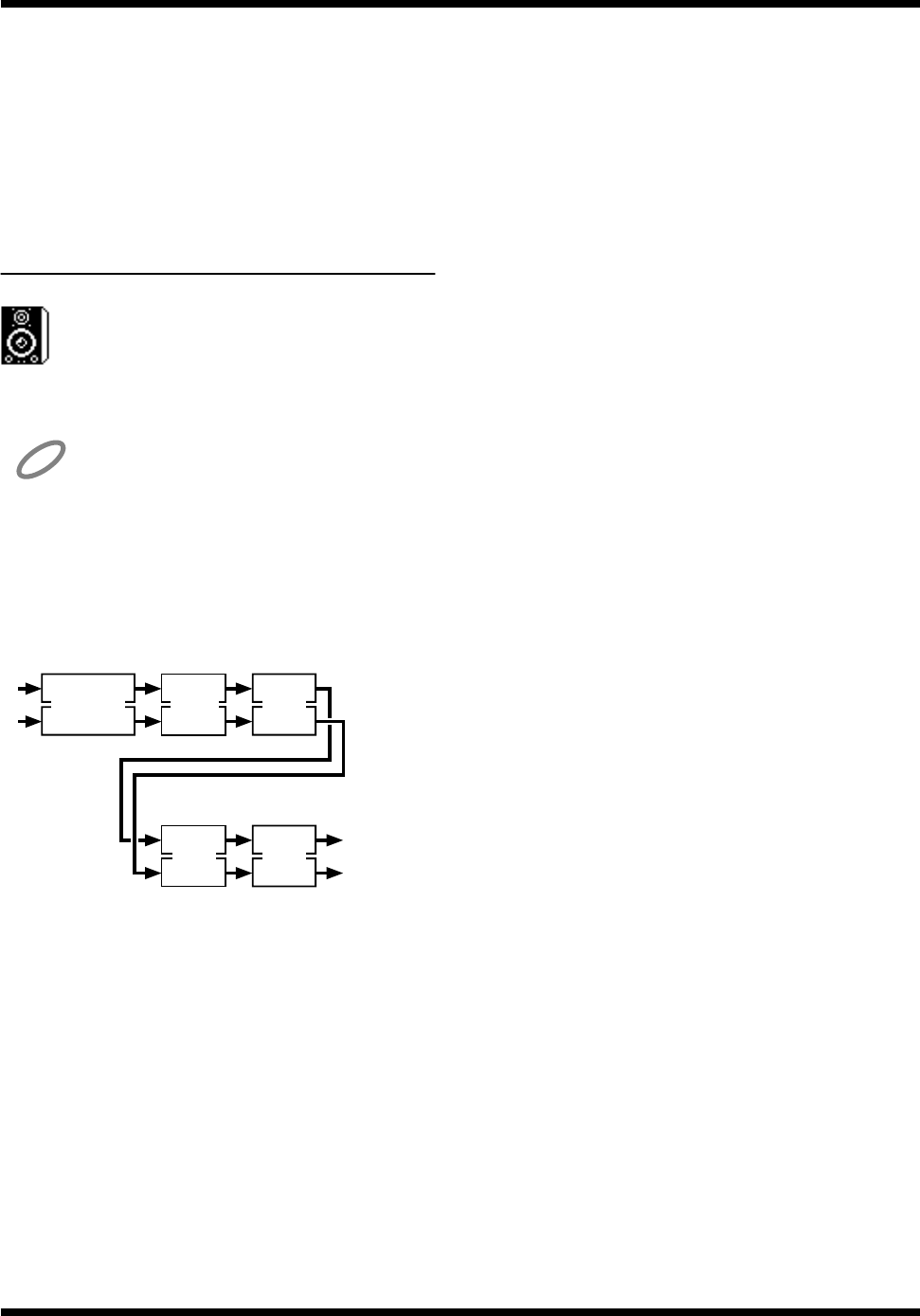
Bass Cut
L
R
SpMod
BCut
Speaker
Modeling
HI Trim
Limiter
HFT Lmt
Low Trim
LFT