56
Chapter 2. Creating Your Own Sounds
Oscillator Sync synchronizes the wave output from OSC 1 to the
wave output by OSC 2. When set to the OSC 2 pitch as shown in the
figure, Oscillator Sync forces the OSC 1 to return to the start of the
OSC 2 wave’s cycle, producing a complex waveform.
(image figure)
fig.02-12.e
The Oscillator Sync effect is only applied to OSC 1; the OSC 2
tone is not changed. If the Oscillator Sync effect is not
sufficiently evident, raise [BALANCE] (toward the OSC 1 end).
Moving [BALANCE] allows you to alter the ratio of the OSC 1
sound, to which Oscillator Sync is applied, and the normal OSC
2 sound.
• On the SH-32, the Oscillator Sync function cannot be used
together with the sound generator section’s filter functions.
If you want to add a simple filter effect to a patch that uses
Oscillator Sync, use INS-FX as the filter type (p. 64).
• Patches using Oscillator Sync are sounded only in mono.
Furthermore, in Performance mode, they can be used only in
Part 1. When used with Part 2 or 3, the Oscillator Sync function
switches off automatically.
• When using Oscillator Sync, you cannot select a variation for the
OSC 1 waveform. When you press [WAVE] to select the
waveform group, an exclusive variation especially for synching
is selected automatically.
• The Suboscillator function (p. 54), PWM function (p. 55) and
Unison function (p. 62) cannot be used at the same time that a
Patch using Oscillator Sync is active.
• In some cases, a reoccurring, cyclic noise may be audible in the
low-frequency range in Patches using Oscillator Sync. This is a
characteristic of the SH-32’s synching operations, and does not
indicate any malfunction.
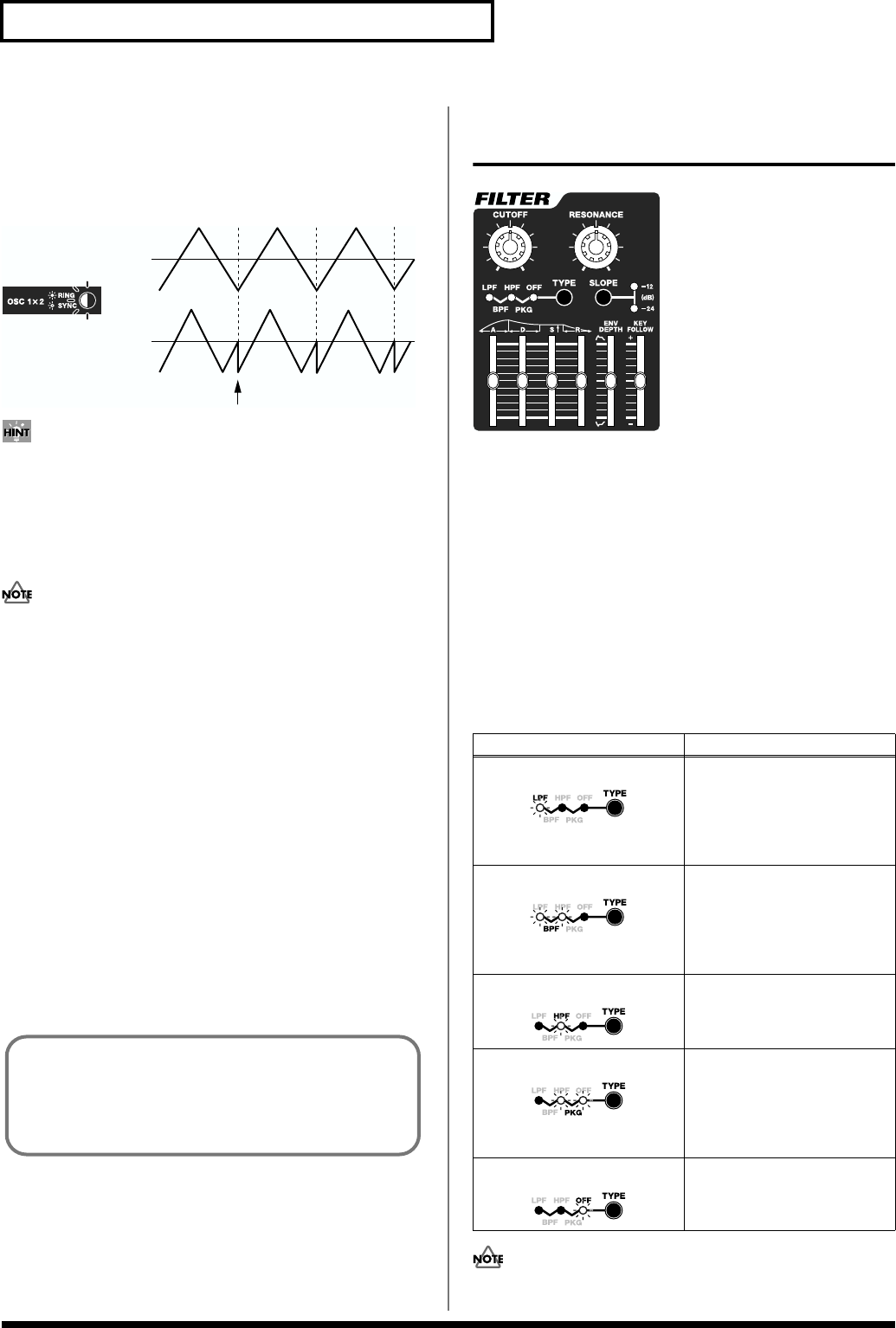
Changing the Characteristics of
Sounds (FILTER)
fig.02-13
This creates sounds filled with numerous harmonics of different
frequencies, but by using filters to pass only certain frequency bands
while blocking other frequencies, you can also change the
characteristics of the sound. By adjusting the filters in the FILTER
section, you can change the output waveforms in a variety of ways,
thus changing the sound.
Internal Filter Types and Functions
(TYPE, SLOPE)
[TYPE]
Selects the type of filter.
When the Oscillator Sync function (p. 55) is in use, this is
automatically set to “OFF” (filter cannot be used).
OSC 2
OSC 1
Return to beginning of period
Changing Tones with Oscillator Sync
Turning [OSC 1X2 SYNC] on and then adjusting [PITCH
COARSE] and [PITCH FINE] changes the sound to produce a
variety of different tones.
Filter Type Description
LPF (Low Pass Filter) This filter passes low-frequency
harmonics under the cutoff fre-
quency. This is the filter that is
most generally used, and it is ef-
fective for making sounds softer
and mellower.
BPF (Band Pass Filter) This filter passes harmonics with
frequencies near the cutoff fre-
quency. This emphasizes the
midrange. This works well for
creating sounds with Particular
sound qualities.
HPF (High Pass Filter) This filter passes high-frequency
harmonics above the cutoff fre-
quency. It is effective for creating
a brighter, sharper sound.
PKG (Peaking Filter) This filter boosts harmonics with
frequencies near the cutoff fre-
quency. You can use this to create
wah effects by employing an LFO
to change the cutoff frequency
cyclically.
OFF No filter is used.