71
Basic functions
Saving dataLoading dataProgram
settings
Combination
settings
Producing
songs
Sampling
settings
Creating a
CD
SMF
playback
System
settings
Drum kit
settings
Arpeggiator
settings
Effects
settings
Other
functions
“Intensity (AMS Intensity)” specifies the depth of vibrato
that will be applied by the LFO when an AMS (Alternate
Modulation Source) is used. For example if “AMS (LFO1
AMS)” is set to After Touch and you set an appropriate
value for “Intensity (AMS Intensity),” vibrato will be
applied when you apply pressure to the keyboard or
when MIDI aftertouch messages are received.
Pitch EG page
Here you can adjust the settings for the pitch EG.
When you wish to create sound effects etc., set the pitch
EG to make major changes in pitch over time.
To realistically simulate the slight change in pitch that
occurs when a string is plucked or at the attack of a brass
or vocal sound, you can use the EG to create a subtle
change in pitch at the attack (☞PG p.12).
EG and LFO
By using an EG (envelope generator) to apply time-vary-
ing change or by using an LFO (Low Frequency Oscilla-
tor) to apply cyclic change to pitch, filter, or amp, you can
create changes in the pitch, tone, or volume.
EG (Envelope Generator)
TRITON STUDIO provides a Pitch EG, Filter EG, and
Amplifier EG, which produce time-varying changes in
pitch, tone, and volume respectively.
LFO (Low Frequency Oscillator)
For each oscillator, TRITON STUDIO provides two LFO’s
that can be used to apply cyclical change in pitch, tone,
and volume.
Examples of this are vibrato (cyclical change in pitch),
wah (cyclical change in tone), and tremolo or auto-pan
(cyclical change in volume).
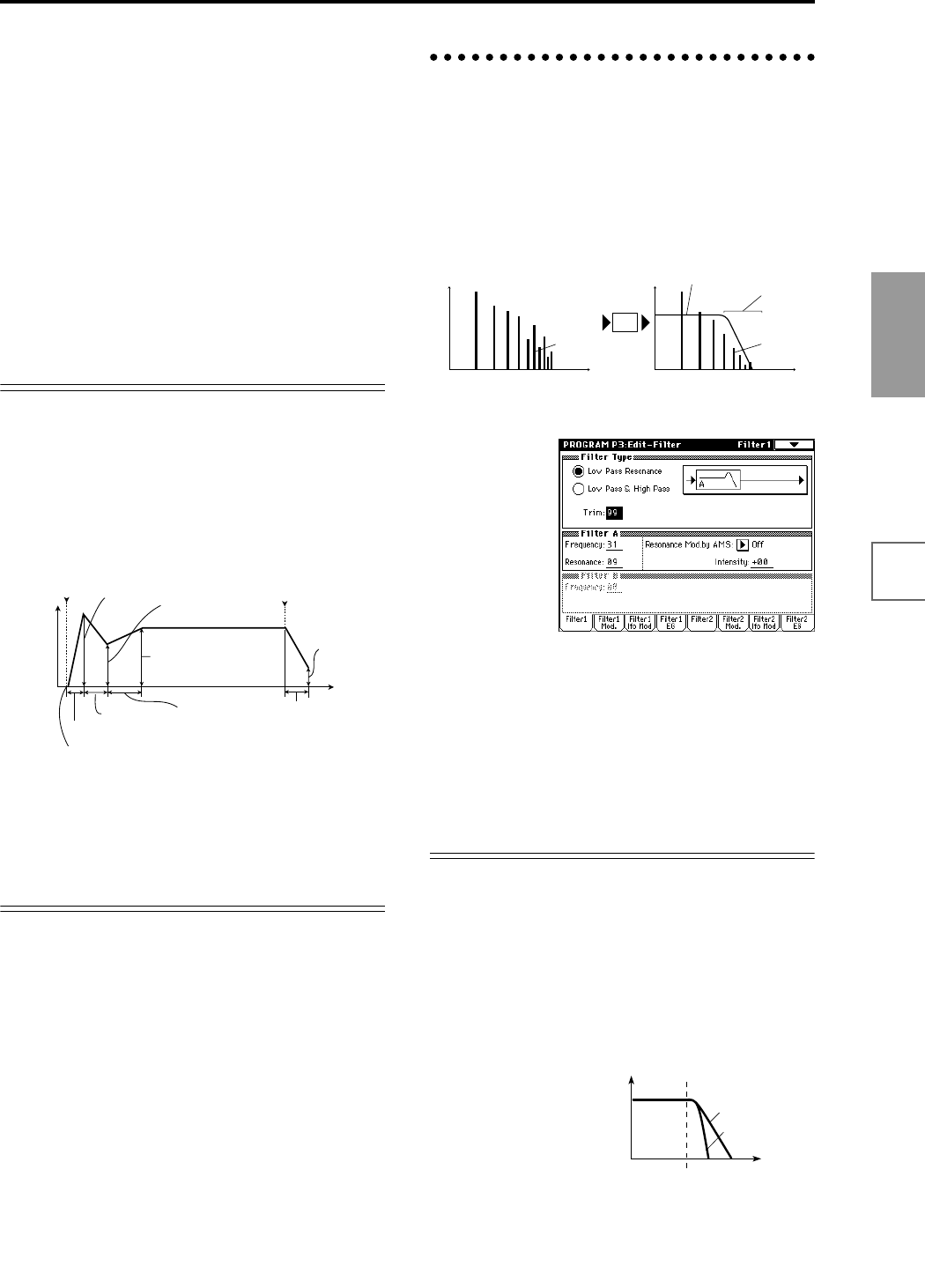
Filter settings P3: Edit-Filter
The filter allows you to diminish or emphasize specified
frequency areas of the multisample selected for the oscil-
lator.
The tone of the sound will depend significantly on the
filter settings.
TRITON STUDIO provides Filter 1 for OSC1 and Filter 2
for OSC2. For each of these filters, you can select from two
types (Low Pass Resonance or Low Pass & High Pass).
Filter 2 can be used if “Oscillator Mode” is set to Double.
Filter1 page
Filter Type, Filter A, Filter B
Selects the type of filter, and specify the “Frequency” (cut-
off frequency) and “Resonance” (resonance level).
• Low Pass Resonance (24 dB/oct low pass filter with
resonance): Make settings for filter A.
• Low Pass & High Pass (12 dB/oct low pass filter and
12 dB/oct high pass filter in series connection): Make
low pass filter settings in filter A, and high pass filter
settings in filter B.
Low pass filter
This is the most common type of filter, which allows the
low frequency range to pass and cuts the high frequency
range. When the overtones of the high range are cut, a
bright sound will become darker (more mellow).
24 dB/oct and 12 dB/oct refer to the steepness of the cut.
24 dB/oct means that the gain will decrease 24 dB in one
octave (i.e., as the frequency doubles). A 12 dB/oct filter
would decrease the gain 12 dB in one octave. The 24 dB/
oct filter produces a steeper cut.
Level
Time
Attack Time
Decay Time
Slope Time
Release Time
Attack Level
Start Level
Sustain Level
Break Level
note-on note-off
Release Level
Level
Frequency (pitch)
Overtones included
in the original multisample
Level
Frequency (pitch)
Filter characteristics
Overtones after
passing through
the filter
This area of
overtones will
be diminished
Filter
Frequency
Level
Low Pass
12dB/oct
24dB/oct


















