Parameter Guide
37
Tri
This is a triangle, which has weaker overtones and a stron-
ger fundamental than a sawtooth wave or square wave. It
is suitable for mellow bass sounds.
• Control1
You can modify the waveform by adjusting this value.
A setting of 0 will produce a triangle wave, and a setting
of 127 will produce a waveform with a pitch that is one
octave and a fifth higher.
• Control2
LFO1 is used to apply WFM (wave form modulation) to
the waveform specified by “Control1.” The “Control2”
setting specifies the depth of the modulation produced
by LFO1.
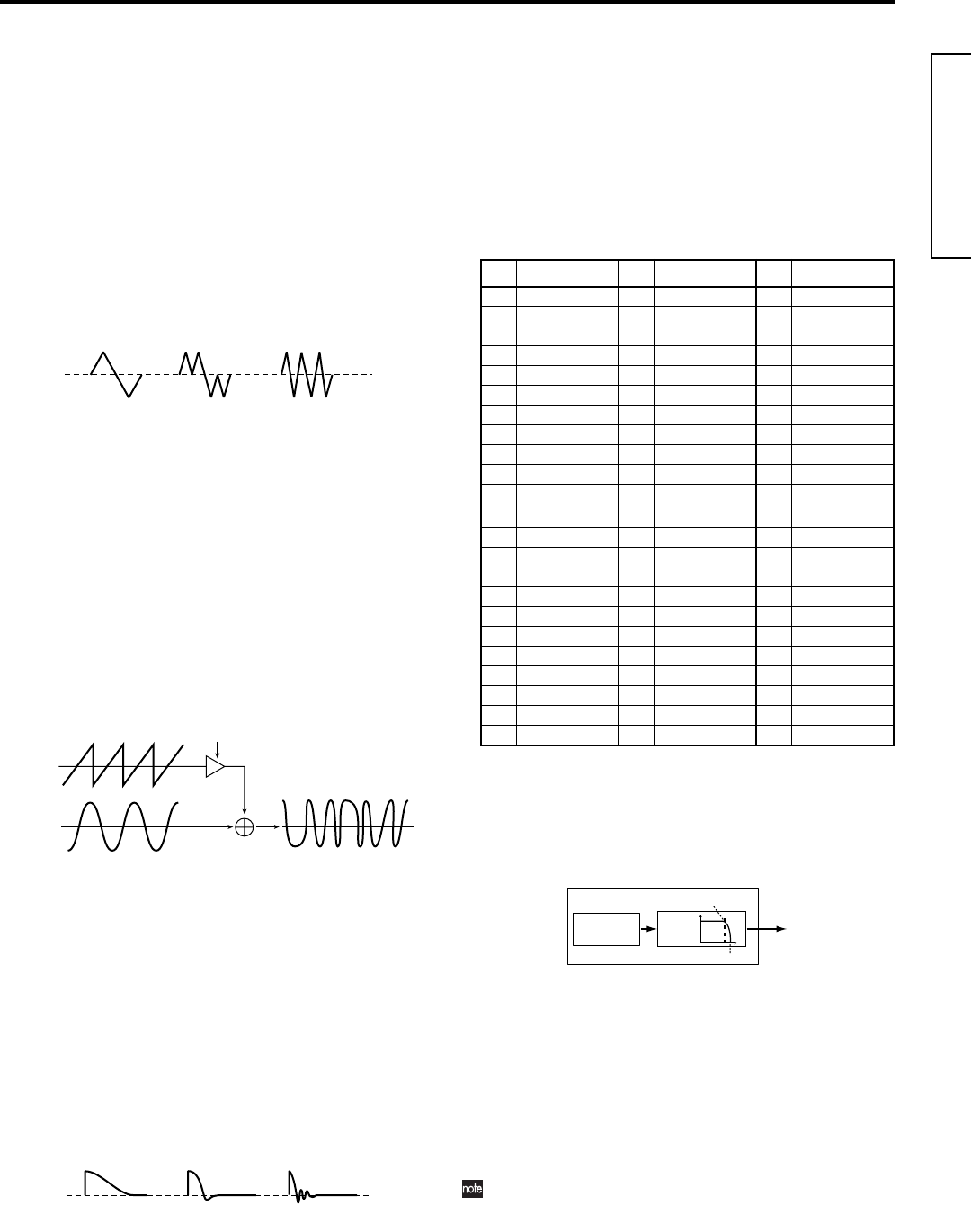
Sin (Cross)
This is basically a sine wave, but oscillator 2 is used to
apply cross modulation.
By using oscillator 2 to modulate the frequency of oscilla-
tor 1, cross modulation produces a complex overtone
structure.
• Control1
Specify the depth of cross modulation.
At a setting of 0 a sine wave will be produced.
• Control2
LFO1 is used to apply further modulation to the depth
of cross modulation that was specified by “Control1.”
“Control2” specifies the depth of modulation produced
by LFO1.
Vox Wave
This simulates a waveform similar to human vocal cords.
Even if the oscillator pitch is changed, the frequency spec-
trum will be maintained, which makes this effective when
used for vocal-type sounds or as a vocoder oscillator.
Select HPF or BPF as the filter, and adjust “Cutoff” to cre-
ate a vocal-type sound.
• Control1
Adjusting this value will modify the waveform.
• Control2
LFO1 is used to apply modulation to the waveform
specified by “Control1.” Control2 sets the depth of the
modulation applied by LFO1.
DWGS
This is waveform data created by harmonic additive syn-
thesis. 64 types of waveform are provided.
• Control1
This has no effect.
• Control2
This selects the waveform.
You can select one of the following waveforms.
DWGS List
Noise
This generates white noise. Within the oscillator, a LPF
(Low Pass Filter) is provided to process the noise.
• Control1
This sets the cutoff frequency of the LPF.
Adjusting this will affect the noise waveform.
• Control2
This controls the resonance of the LPF.
If you raise this enough to produce an identifiable pitch,
the cutoff frequency will move according to the key-
board location you play, and the change will be heard as
a pitch.
If you want the oscillation produced by resonance to
match the reference pitch, set “Control1” to 24.
0 63 127
OSC2
OSC1
X-mod Depth + X-mod Depth Mod
OSC1 Output
0 63 127
No Name No Name No Name
1 SynSine1 24 5thWave1 47 Clav1
2 SynSine2 25 5thWave2 48 Clav2
3 SynSine3 26 5thWave3 49 Guitar1
4 SynSine4 27 Digi1 50 Guitar2
5 SynSine5 28 Digi2 51 Guitar3
6 SynSine6 29 Digi3 52 Bass1
7 SynSine7 30 Digi4 53 Bass2
8 SynBass1 31 Digi5 54 Bass3
9 SynBass2 32 Digi6 55 Bass4
10 SynBass3 33 Digi7 56 Bass5
11 SynBass4 34 Digi8 57 Bell1
12 SynBass5 35
Endless
*
*: The 35 Endless waveform simulates an endless scale, in which notes one octave
apart have the identical pitch. You can play an ascending or descending scale as far
as you wish, producing the sensation that a scale of the same pitch is continuing
infinitely.
58 Bell2
13 SynBass6 36 E.Piano1 59 Bell3
14 SynBass7 37 E.Piano2 60 Bell4
15 SynWave1 38 E.Piano3 61 Voice1
16 SynWave2 39 E.Piano4 62 Voice2
17 SynWave3 40 Organ1 63 Voice3
18 SynWave4 41 Organ2 64 Voice4
19 SynWave5 42 Organ3
20 SynWave6 43 Organ4
21 SynWave7 44 Organ5
22 SynWave8 45 Organ6
23 SynWave9 46 Organ7
LPF
Cutoff
Resonance
Noise
Genarator
Program parameters


















