AUDIO OPERATIONS 4-15
REMOTE
SITE
STUDIO
M
ain
P
rogram
O
utput
+
+
T
elephone
M
ix-Minus
R
emote
M
ix-Minus
Studio Console
Other
Sources
for
music,
etc.
Phone
Hybrid
+
Local send
plus
ISDN receive
Zephyr or
ZephyrExpress
Remote anncr
to studio
Music +
phone to
remote
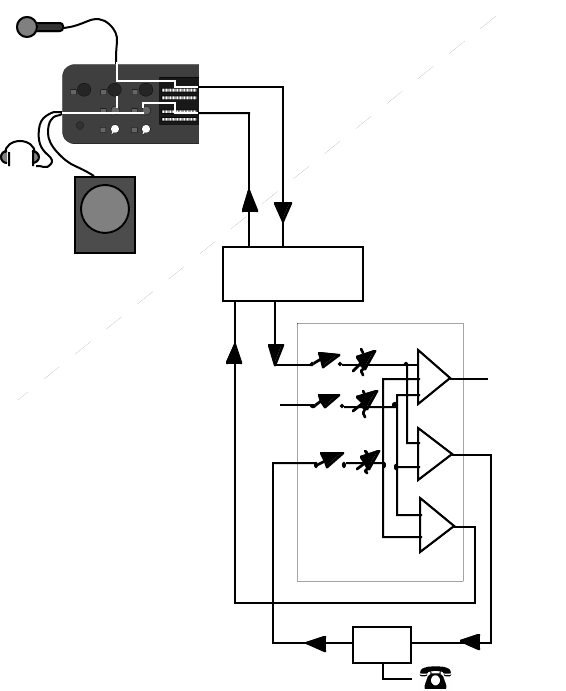
Diagram showing system set-up for remotes with delay in the transmission path and phones
taken at the studio. Note that this is the same as required for satellite links.
Another issue worth considering is the round trip delay. The apparent on-air response
time of the talent to callers’ comments will be the sum of {studio-to-remote delay +
remote-to-studio delay + talent’s thinking time}. For this reason the studio-to-remote
path will generally use the G.722 mode, sacrificing high-fidelity for speed: after all, who
needs a high-fidelity line to relay a phone call? If G.722 proves too ragged to use for
music or commercials being sent from the studio to a remote site’s public address
system, use a Layer 3mono mode for high-quality audio but send the telephone caller’s
audio on ZephyrExpress’ second line as a POTS signal.
Other intermediate tradeoffs are possible and will be dependent on your format. You
may also be able to significantly speed up the talent’s thinking time by judicious
applications of black coffee.
For information on the tradeoff between audio quality and delay, refer to the next
section.