VOICE MODE
116
● ACCESSING FILTER PARAMETERS
To access the Filter parameters function, from within Voice
Edit Mode, press [F4] ( Filt ) or TRACK [12].
TONE - To specify the filter Tone parameters for each
element, from within the Filter parameters function,
press [F7] ( Tone ).
CUTOFF (-127 ~ +127) - Position the cursor over
the Cutoff offset field and use the JOG, INC/DEC
or the KEYPAD to set the cutoff frequency, or the
frequency at which the filter begins to affect the
sound, for the selected element. Lower cutoff values
produce a lower cutoff frequency and higher values
produce a higher cutoff frequency. With an LPF
response, a lower cutoff frequency reduces the range
of high frequencies passed, thus making the sound
darker, or rounder. With an HPF response, a higher
cutoff frequency reduces the range of low frequen-
cies passed, thus making the sound thinner, or
sharper.
VELOCITY BAND SENSITIVITY (-63 ~ +63) -
Position the cursor over the V.Band offset field
(displayed when the filter type is a BPF or BEF) and
use the JOG, INC/DEC or the KEYPAD to determine
how the filter cutoff frequency changes in response
to velocity changes (keyboard dynamics) as you
play. Positive settings produce higher cutoff frequen-
cies in response to higher velocity values, i.e., the
harder a key is played, the higher the cutoff fre-
quency will be. The maximum setting of +63
produces the maximum level variation in response
to velocity changes. Negative settings produce the
opposite effect lower cutoff in response to higher
velocity. A setting of +0 results in no cutoff
variation.
TEMPLATE TYPE (00 ~ 59) - Position the cursor
over the Type number field and use the JOG, INC/
DEC or the KEYPAD to select the type of filter
envelope generator (FEG)
template
, which gives you
instant access to the basic EG shapes of many types
of sounds. There are a wide variety of EG types to
choose from, including those from all major acoustic
and many electronic instruments. A setting of 00 is
the default EG for the preset voice. The Thru
setting turns the filter off. The type of EG shape
selected will determine the levels of each EG
segment (Attack, Decay 1, Decay 2, Release). (To see
a list of the various template types, refer to the
W5/
W7 Technical Information
booklet, provided sepa-
rately.)
NOTE: The template type determines the maximum and
minimum range. Therefore, an offset which exceeds the
range of the template type will have no effect.
FILTER ENVELOPE GENERATOR - To specify the
Filter Envelope Generator (FEG) parameters, from
within the Filter parameters function, press [F8] ( EG ).
ATTACK (-63 ~ +63) - Position the cursor over the
Attack offset field and use the JOG, INC/DEC or
the KEYPAD to determine the attack rate of the FEG.
The attack rate determines how the filter envelope
begins. A value of 0 represents normal level.
Negative values cause the attack to begin below
normal level. Positive values cause the attack to
begin above normal level.
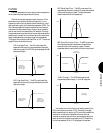
RESONANCE/BAND (-99 ~ +99) - Position the
cursor over the Reso./Band offset field and use the
JOG, INC/DEC or the KEYPAD to determine filter
resonance or bandwidth settings (depending on the
current filter type). Resonance determines the degree
of filter resonance when the LPF filter is activated.
This parameter has a similar effect to the resonance
settings on traditional analog synthesizer filters, i.e.,
it determines the height of a peak in the filter
response at the cutoff frequency. Higher resonance
values produce a higher resonant peak and reduce
the overall bandwidth of the filter, passing a narrow
band of frequencies at the filter s cutoff. Band
determines the width of the frequency pass for the
BPF (Band Pass Filter) or elimination band for the
BEF (Band Elimination Filter). The minimum setting
of -99 produces an extremely narrow pass or
elimination band, while the maximum setting of +99
produces a wide pass or elimination band.
VELOCITY SENSITIVITY (-127 ~ +127) -
Position the cursor over the Vel. offset field and
use the JOG, INC/DEC or the KEYPAD to determine
the amount of tonal change produced by the FEG.
Positive settings permit strongly played notes to
cause a greater change in tone. Negative settings
permit lightly played notes to cause a greater change
in tone.