Chapter 9. SIP Traffic
Method
Enter the name of the SIP method. This should be the name used in RFC 3261.
Traffic to
Here, you select the direction of the traffic. Local domains means that traffic to Local SIP Domains of this
Telecommuting Module is affected by this row. Other domains means that traffic to all domains which are not
Local SIP Domains of this Telecommuting Module is affected by this row. Both means that this row affects all
traffic for the method, regardless of where the traffic is bound.
Allow
Select if the method in this direction should be allowed or not. For methods that are not allowed, the
Telecommuting Module sends a 403 (Forbidden) response.
Auth
In the base Telecommuting Module, authentication will not be performed, and this setting will have no effect.
Delete Row
If you select this box, the row is deleted when you click on Add new rows or Save.
Create
Enter the number of new rows you want to add to the table, and then click on Create.
Save
Saves the SIP Methods configuration to the preliminary configuration.
Cancel
Clears and resets all fields in new rows and reset changes in old rows.
Routing
Here, you configure routing of the SIP signaling received by the Telecommuting Module The options are: to
forward all SIP requests to a server, regardless of what they concern (Outbound Proxy), and to forward all requests
addressed to a specific SIP domain to a SIP server (DNS Override For SIP Requests).
You can also select to process class 3xx messages in the Telecommuting Module or pass them on to the client.
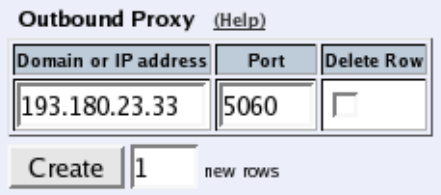
Outbound Proxy
Here, you can enter an external SIP proxy to which all SIP requests should be sent. This could be useful e.g. if the
Telecommuting Module separates two local departments of a company, and all SIP requests should be processed by
the main firewall connected to the Internet.
83


















