87
Creating/
selecting a song
Assign audio inputs
to the mixer
Basic
operation
RecordingPlayback
Changing the
time location
Using the
mixer
Using
effects
MixdownTrack
editing
Song
editing
Rhythm/tempo
settings
DataDriveUSBUpdating
the system
MIDI
What is MIDI?
MIDI stands for Musical Instrument Digital Interface,
and is a world-wide standard that allows a variety of
musical information to be exchanged between electronic
musical instruments and computers.
1. MIDI connections
Special MIDI cables are used to transmit and receive
MIDI messages. Connect these cables between the MIDI
connectors of the D1600mkII and the MIDI connectors of
the external device with which you wish to exchange
data.
MIDI IN connector: MIDI messages from another MIDI
device are received here. Connect this to the MIDI OUT
connector of the external device.
MIDI OUT connector: The D1600mkII transmits MIDI
messages from this connector. Connect this to the MIDI
IN connector of the external device.
MIDI channel settings
MIDI allows information for multiple MIDI devices to be
conveyed over a single MIDI cable by using sixteen
MIDI channels, 1–16. If MIDI messages are being
transmitted on MIDI channel “1”, the messages will not
be received unless the receiving device is also set to MIDI
channel “1.”
2. MIDI messages used by the
D1600mkII
Note, aftertouch, velocity, pitch bend: This data is used
by the D1600mkII to control effects.
Program change: This data is used by the D1600mkII to
select scenes.
Control change: This data is used by the D1600mkII to
control mixer parameters.
MMC (MIDI Machine Control): MMC messages can be
transmitted to control an external sequencer or recorder.
MMC messages can also be received to control the
D1600mkII from an external sequencer or recorder.
MTC (MIDI Time Code): MTC messages can be
transmitted to make an external sequencer or recorder
operate in synchronization with the D1600mkII. MTC
messages can also be received to synchronize the
D1600mkII with another device.
About the MIDI implementation chart
The owner’s manual of each MIDI device contains a
MIDI implementation chart. This chart makes it easy for
you to verify the MIDI messages that the device can
transmit and receive. When using two MIDI devices
together, compare their MIDI implementation charts to
verify the types of MIDI message that they are able to
exchange.
• For more details on the MIDI specifications, refer to the
separate MIDI implementation. To obtain the MIDI
implementation, please contact your Korg distributor.
3. Using MIDI
Controlling the D1600mkII from a MIDI sequencer
Here’s how the MMC messages transmitted from a MIDI
sequencer can be used to stop/play/fast-forward/
rewind/record/locate the D1600mkII.
You must use a MIDI sequencer that supports MMC.
These following operations are not possible with a
sequencer that does not support MMC.
1. Make MIDI connections.
Use a MIDI cable to connect the MIDI OUT connector
of your MIDI sequencer to the [MIDI IN] connector of
the D1600mkII.
2. Make settings on your MIDI sequencer so that it
will output MMC messages to control external
devices.
For details refer to the owner’s manual for your MIDI
sequencer.
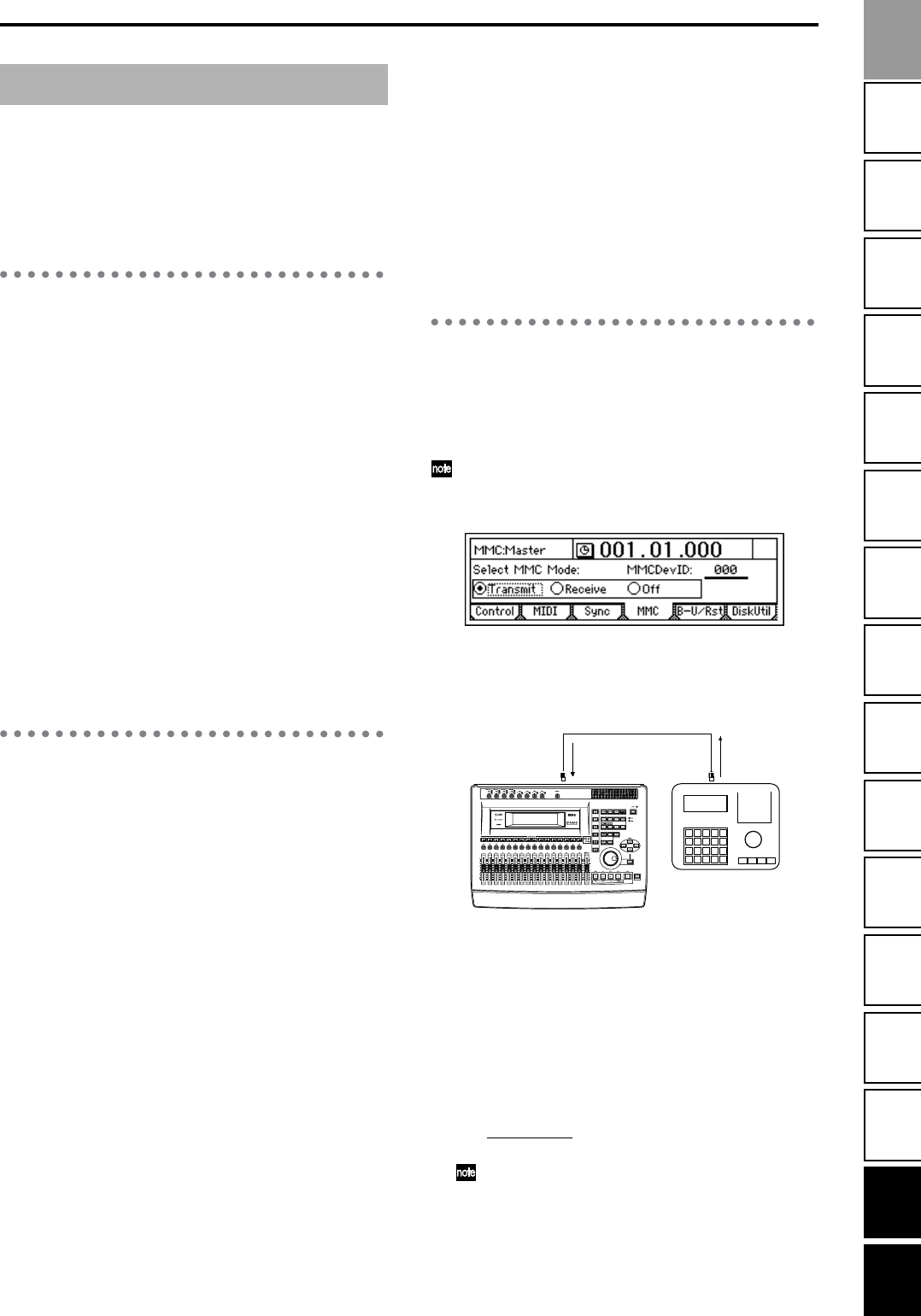
3. Turn on MMC reception.
In the [SYSTEM/USB] “MMC” tab page, set “Select-
MMCMode” to “Receive.”
4. Set the device ID settings to match.
Set “MMCDevID
” to the same setting as the MMC
device ID of your MIDI sequencer.
Since the device ID specifications may differ
depending on the type of your MIDI sequencer, it
may not be necessary for the number to be the
same.
MIDI
MIDI
IN
MIDI
OUT
D1600mkII
MIDI Sequencer
Updating
the system
MIDI


















