Chapter 5: Oscillators and Filters
ANDROMEDA A6 REFERENCE MANUAL 117
HOW FILTERS ARE DESIGNED
As important as the amount of audio frequencies that pass through the filter is the
type of filtering that is employed. The basic filtering process depends, therefore, on
the mode of the filter – whether it’s low pass, high pass, band pass or notch filtering.
Let’s take a moment to describe these modes.
Filter Modes
A filter determines what harmonics pass through it by its mode. The four filter
modes of the
FILTER 1 describe how harmonics pass (the keyword here is pass)
through the filter:
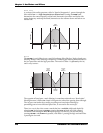
Low Pass
As its name implies, low frequency harmonics (including the fundamental wave) are
passed through the filter. This means that high frequencies are filtered out.
FILTER 1
provides low-pass filtering in addition to high-pass, band-pass and notch filtering.
FILTER 2 is low-pass only.
1 kHz 2 kHz 5 kHz 10 kHz 20 kHz
FREQUENCY
AMPLITUDE
HARMONIC
SPECTRUM
CUTOFF
FREQUENCY
High Pass
High pass filtering is the opposite of low pass: high frequency harmonics are passed
through the filter. This means that low frequencies, including the fundamental
wave, are filtered out (if the frequency of the filter is above the fundamental). In
essence, a high pass filter just passes some of the harmonics.
1 kHz 2 kHz 5 kHz 10 kHz 20 kHz
FREQUENCY
AMPLITUDE
HARMONIC
SPECTRUM
CUTOFF
FREQUENCY