Chapter 7: Technology Background
221
.
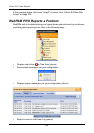
Ranges of Disk Array Expansion
There are limitations to how large you can expand a disk array, depending on the
size of your current disk array.
The current SCSI and Fibre Channel HBA cards and PC Operating Systems
support a 10-byte LBA format. This means that a disk array can have up to 4
billion address blocks or sectors.
Multiply the number of blocks by the sector size to find the capacity of a disk
array:
4,000,000,000 blocks x 512 bytes per sector = 2,048,000,000,000 bytes
of data for a 2TB drive.
Note that you cannot change the size of the sectors nor can you increase the
number of address blocks above 4 billiion.
As a result, there are range limits imposed upon disk array expansion as shown
in the table above. For example:
• You can expand a 2.5 TB disk array up to 4 TB
• You can only expand a 1.9 TB disk array up to 2 TB
See the chart on the next page.
Important
• The Target disk array may require more disk drives than the
Source disk array
• If the Target disk array requires an EVEN number of disk
drives but the Source disk array has an ODD number, ADD a
disk drive as part of the migration process
• You cannot reduce the number of disk drives in your disk
array, even if the Target disk array requires fewer disk drives
than the Source disk array
• RAID 1 (mirroring) works with two drives only. Only a single-
drive RAID 0 disk array or a single-drive JBOD can migrate to
RAID 1. Other RAID Levels use too many drives to migrate
• You cannot migrate a disk array when it is Critical or
performing activities such as Synchronizing, Rebuilding and
PDM