116
Chapter 6. Creating a Rhythm Set
Modifying the Brightness of a
Sound with a Filter (TVF)
The settings for the TVF (Time Variant Filter) allow you to
change a Rhythm Tone’s timbral content by altering its
brightness or thickness.
TVF FILTER
Type (TVF filter type)
This selects a filter type. A filter typically reduces, or
attenuates, a specific frequency range within a Tone in order
to accentuate its other frequencies.
OFF: No filter is used.
LPF: A Low Pass Filter reduces the volume of frequencies
above the cutoff frequency in order to round off, or un-
brighten, the sound. This is the most common filter used in
synthesizers.
BPF: A Band Pass Filter reduces the volume of frequencies
below and above the cutoff frequency range. This is most
effective when creating sounds with strong characteristics
since it can accentuate a desired range of frequencies
anywhere in the sound.
HPF: A High Pass Filter reduces the volume of the
frequencies below the cutoff frequency. This is suitable for
creating percussive sounds by rolling of their lower
frequencies, thus emphasizing their higher ones.
PKG: A Peaking Filter emphasizes frequencies around the
cutoff frequency by raising their level. You can use this to
create wah-wah effects by employing an LFO to change the
cutoff frequency cyclically.
LPF2: Low Pass Filter 2. This reduces the volume of all
frequencies above the cutoff frequency. This differs from LPF
in that you can control the amount of the reduction using the
TVF ENVELOPE settings while still maintaining a fixed
cutoff frequency.
This can be very effective with acoustic-instrument-based
Tones, since nothing is done to weaken the power and
energy of the sound.
* This disables the Resonance setting.
LPF3: Low Pass Filter 3 reduces the volume of frequencies
above the cutoff frequency. While similar to LPF2, it filter
reduces the frequencies more gently than LPF2.
This can be very effective with acoustic-instrument-based
Tones, since nothing is done to weaken the power and
energy of the sound.
* This disables the Resonance setting.
Cutoff (TVF cutoff frequency) 0–127
This selects the frequency at which the filter begins to have
an effect on the waveform’s frequency components.
With LPF/LPF2/LPF3 selected for the Filter Type parameter,
lower cutoff frequency settings reduce a Rhythm Tone’s
upper harmonics for a more rounded, warmer sound. Higher
settings make it sound brighter.
When Filter Type is BPF, the cutoff frequency setting
determines the range of frequencies within the Rhythm Tone
that will be heard. This can be useful when creating
distinctive sounds.
When Filter Type is HPF, higher settings of the cutoff
frequency decrease the level of the Rhythm Tone’s low
frequencies, preserving its brighter qualities.
When Filter Type is PKG, the cutoff frequency setting
determines the range of frequencies to be emphasized.
Resonance (TVF resonance) 0–127
This increases the level of the cutoff frequency to add a
popular classic synth character to the sound. Excessively
high settings can produce oscillation, causing the sound to
distort.
fig.6-09.e
TVF VELOCITY
This sets the amount of change to the original cutoff
frequency in response to differences in velocity, as well as the
velocity response curve and velocity’s effect on Resonance.
V-Cutoff (TVF cutoff velocity sensitivity) -63–
+63
This sets the amount of change to the Cutoff setting to be
applied as a result of changes in playing velocity. With
higher settings, there is a greater amount of change between
softly and strongly played notes. Negative (-) settings reverse
the direction of change.
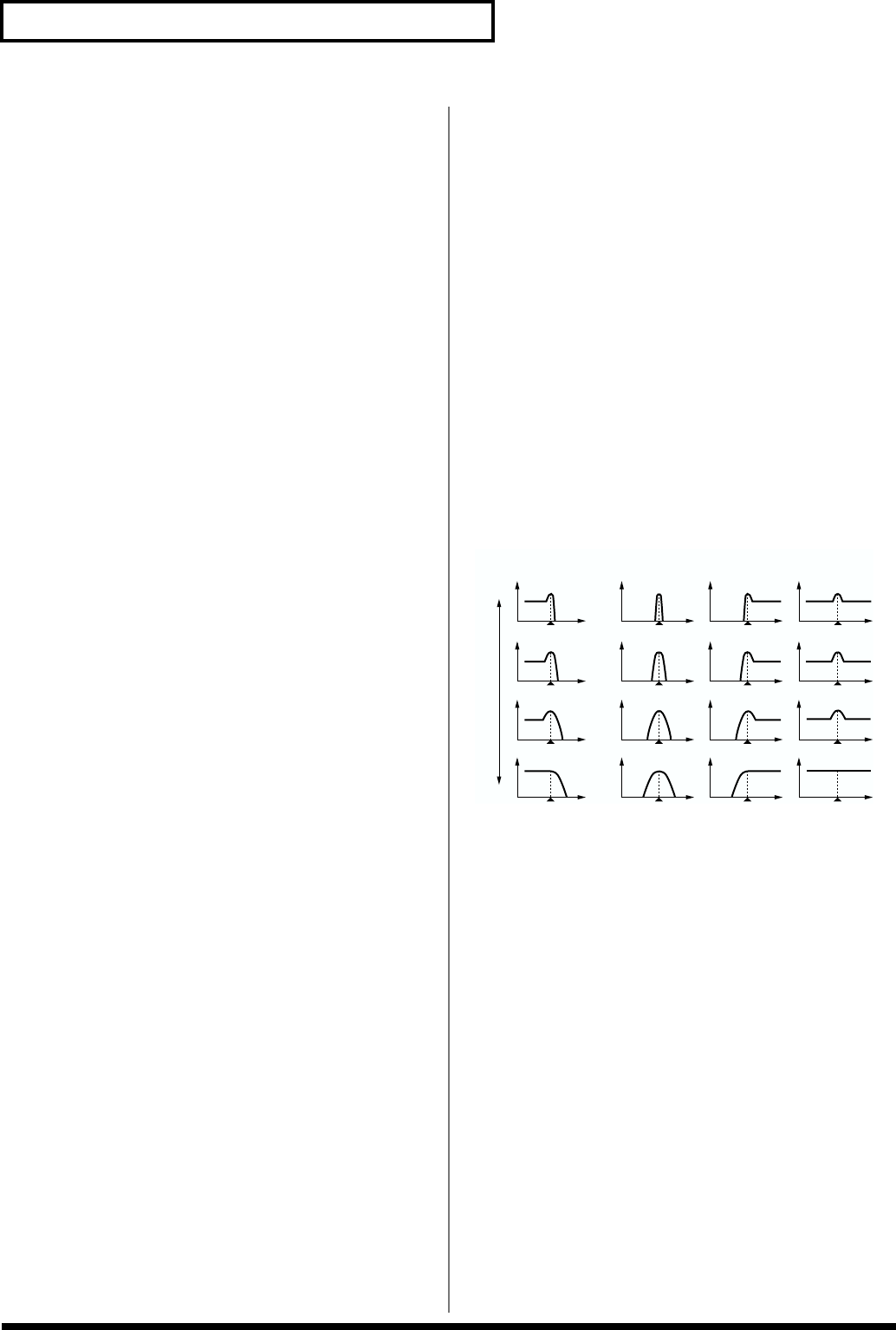
V-Curve (TVF cutoff velocity curve) FIXED/1–7
This selects one of seven curves that determine how
keyboard playing dynamics (velocity) influence the Rhythm
Tone’s cutoff frequency. The selected curve is displayed
graphically to the right of its value.
When V-Curve is set to “FIXED,” the cutoff frequency
remains unchanged regardless of how hard or soft the keys
are played.
LPF BPF HPF PKG
parameter value
Level
Cutoff frequency
Frequency
High
Low


















