14-4
Sampling and Live Mode
Sampling Analog Signals
Another consideration in selecting sample rate is the K2661’s transposition range during sample
playback. The K2661 transposes samples by changing the sample playback rate; the higher the
playback rate, the higher the pitch of the sample. The K2661 can achieve a maximum sample
playback rate of 96 KHz. Normally, a sample made at 48 KHz can be transposed up a maximum
of one octave, since the playback rate doubles for every octave of upward transposition. If you
set the SmpSkp (sample skipping) parameter (on the KEYMAP page in the Program Editor) to
Auto or On, you can transpose up two octaves at 48 KHz. A sample made at 29.4 KHz can be
transposed up approximately 21 semitones (an octave and a sixth)—or 42 semitones with
SmpSkp set to Auto or On. There is no limit on downward transposition, regardless of the
sample rate.
Each portion of a sample (each individual sample element made by the K2661 during the
sampling process) takes up two bytes of sample memory. A one-second stereo sample at 48 KHz
consists of 96,000 individual samples (48,000 x 2), taking up 192,000 bytes (about 188K) of
sample memory. The same sample taken at 32 KHz takes up about 125K. A one-second mono
sample taken at 32 KHz takes up about 63K.
If you plan to do a lot of sampling, you may be able to add more sample memory to your K2661
(if it’s not already maxed out at 128 MB). SIMMs (Single In-line Memory Modules) are available
at your dealer, or at most computer stores or mail-order houses. Be sure to read Choosing and
Installing SIMMs for K2661 Sample Memory in the K2661 Musician’s Reference before you go SIMM
shopping, though.
At a sampling rate of 44.1 KHz, each megabyte of sample RAM that you add increases your
sample time by about 11.5 seconds (5.5 seconds for stereo samples). At 48KHz, each megabyte
gives you about 10 seconds of mono sampling, and about 5 seconds of stereo sampling.
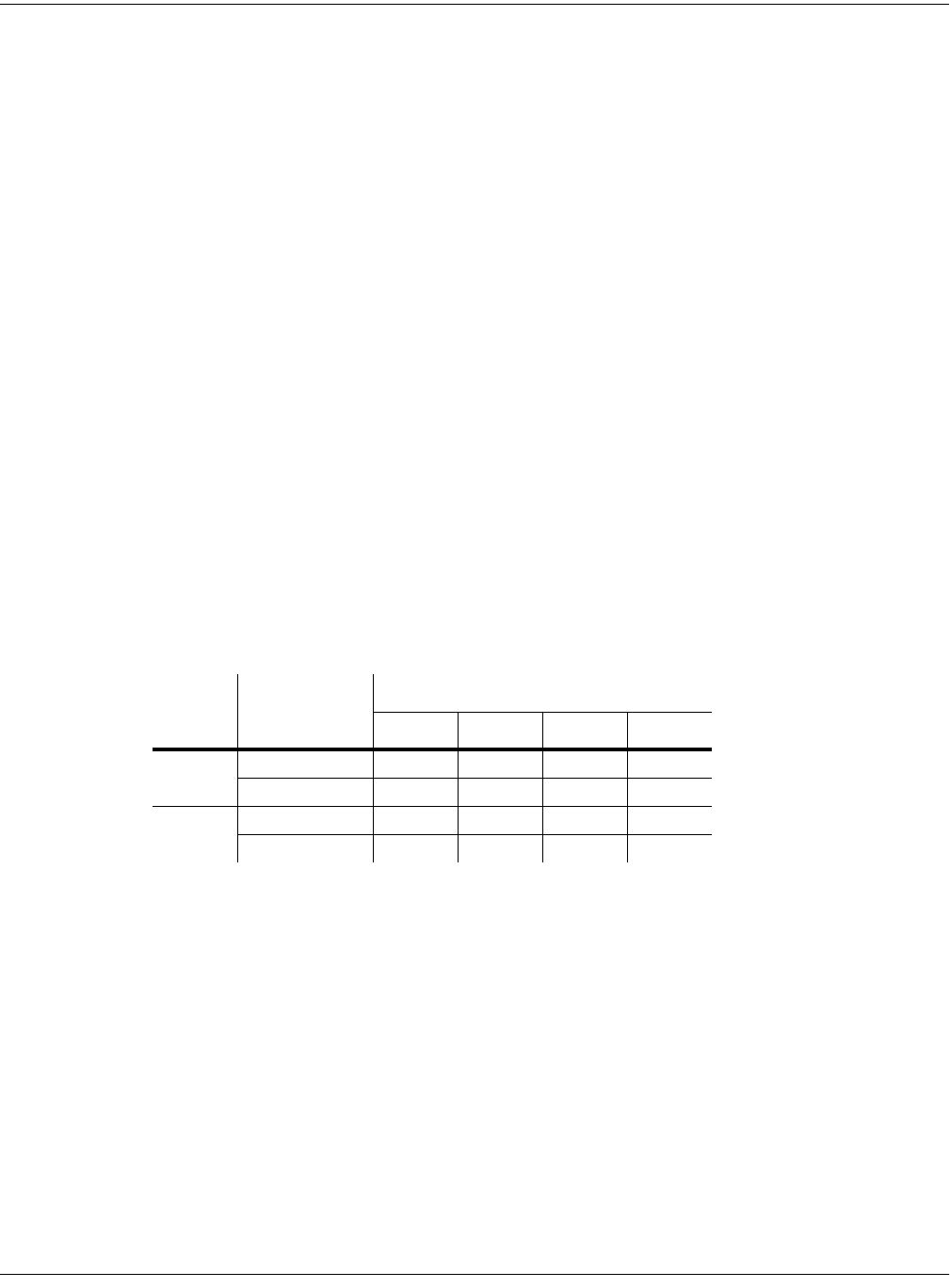
Table 14-1 lists the most common sample RAM configurations and their total sample time
capacity (in seconds) at various sample rates.
Mode
Use the Mode parameter to select mono or stereo sampling. (Keep in mind that stereo samples
take up twice as much memory as mono samples.) Use a value of Mono for a mono signal. You
can use either Mono(L) or Mono(R) to isolate either the left or right side of a stereo signal.
Audio sampling input doubles as a two channel “drum” trigger, allowing audio signals to
trigger samples. On the SampleMode page, set Mode to Trigger. Adjust Thresh to control
triggering sensitivity. This triggers the currently assigned click program. The left input will
trigger click key note number +1, right input will trigger click key +2. The click key and click
program can be accessed on the Song-mode MISC page.
There’s also Live mode, which lets you connect any audio source to any of the K2661’s sampling
inputs (assuming you have the Sampling Option), and use that input just like a regular VAST
program (the input goes through a DSP algorithm, then through KDFX, then to the audio
Total
RAM
Sampling
Mode
Sampling Rate in KHz
29.4 32.0 44.1 48.0
64M
Mono 18:40 17:04 12:16 11:12
Total
Sampling
Time
(min:sec)
Stereo 9:04 8:32 5:52 5:20
128M
Mono 37:20 34:08 24:32 22:24
Stereo 18:08 17:04 11:44 10:40
Table 14-1 RAM and Sampling Capacity


















