117
Overview
Appendix
USB Memory
Song Player
Digital Recorder
Synthesizer
Selecting Sounds Perform. Functions Editing/Eects Other Settings
Rec/Play/Edit Eects Rhythm Pattern
Using Reverb E ect
Here we will explain how to edit the reverb settings (parameters).
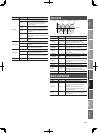
Selecting the Reverb E ect
1. In the RECORDER screen, press the [6] (EFFECT) button.
The recorder’s e ects screen will appear.
2. Press the [2] (REVERB) button.
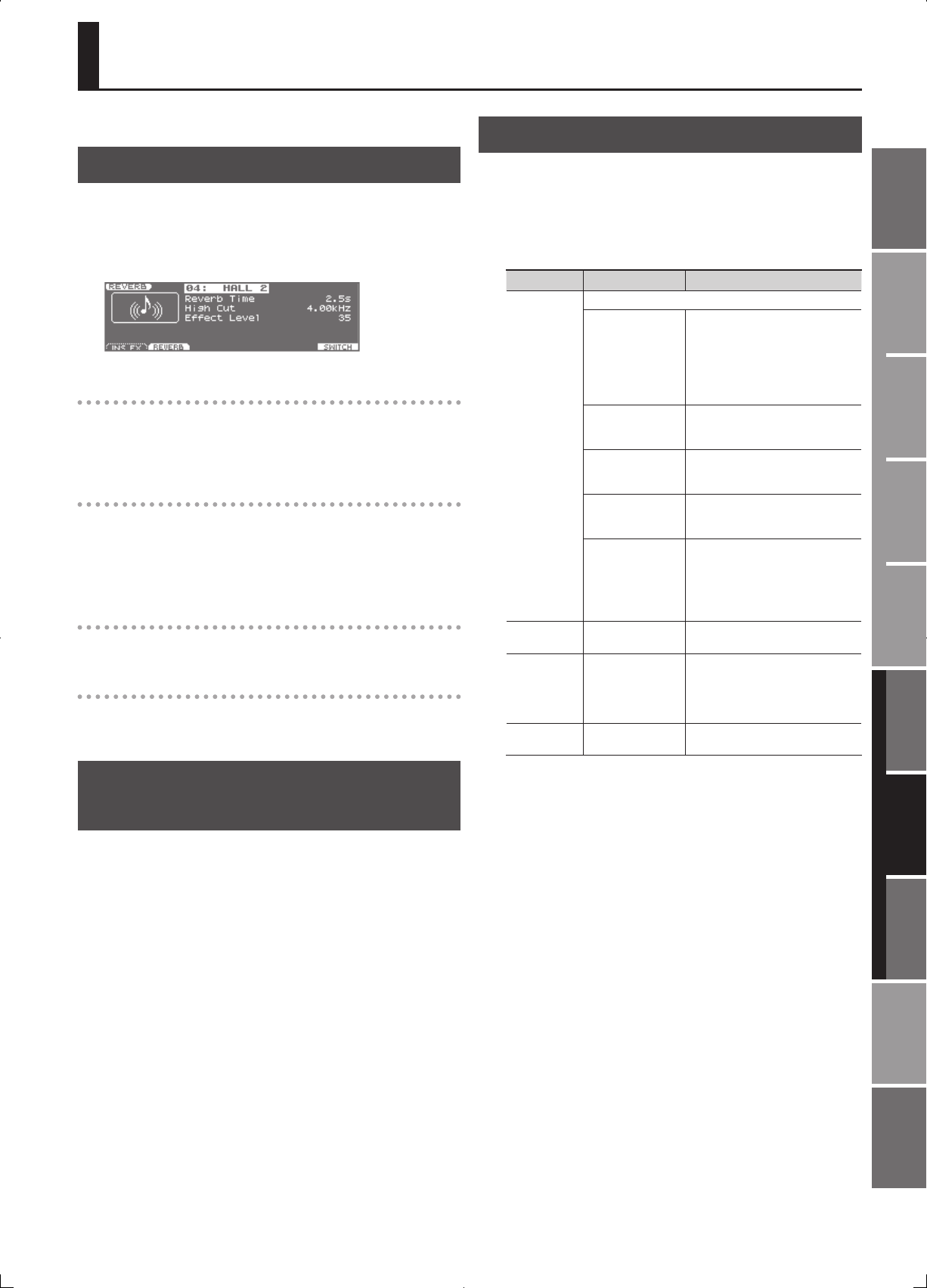
The REVERB screen will appear.
Choosing the reverb type
3. Use the cursor buttons to move the cursor to the Type eld,
and use the VALUE dial or [DEC] [INC] buttons to choose the
type.
Editing the reverb settings
4. Use the cursor buttons to move the cursor to the parameter
that you want to edit, and use the VALUE dial or the [DEC]
[INC] buttons to edit the value.
For details on the reverb parameters refer to “Reverb Parameters” (p. 117).
When you’re nished editing
5. When you’re nished editing, press the [EXIT] button.
Saving the reverb settings
Reverb does not have patches. The reverb settings are saved as part of
the song data. If you want to save the settings to the currently selected
song, press the [WRITE] button in the RECORDER screen.
Adjusting the Reverb Depth for the
Tracks, Rhythm, and External Input
You can vary the reverb depth by adjusting the amount of sound (send
level) that is sent from each track, the rhythm, and the external input
to the reverb.
For the procedure, refer to the following pages.
Track 1–8, Rhythm Pattern
“Adjusting the Pan, Reverb, and EQ (TRACK SETTING)” (p. 89)
External Input
“Selecting an Instrument to Record (REC SOURCE SELECT)” (p. 93)
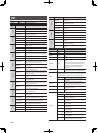
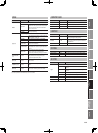
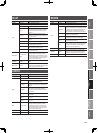
Reverb Parameters
Reverberation (or reverb) is the e ect caused by sound waves decaying
in an acoustic space, or a digital simulation thereof. This decay occurs
because sound waves bounce o many walls, ceilings, objects, etc.
in a very complex way. These re ections, coupled with absorption by
various objects, dissipate the acoustic energy over a certain period of
time (called the decay time). The ear perceives this phenomenon as a
continuous wash of sound.
Parameter Value Explanation
Type
Use this to choose the type of reverb.
AMBIENCE
Simulates an ambience microphone
(o -mic, placed at a distance from
the sound source) used in recording
and other applications. Rather than
emphasizing the reverberation, this
reverb is used to produce a sense of
openness and depth.
ROOM
Simulates the reverberation in
a small room. Provides warm
reverberations.
HALL 1
Simulates the reverberation in a
concert hall. Provides clear and
spacious reverberations.
HALL 2
Simulates the reverberation in a
concert hall. Provides mild reverbera-
tions.
PLATE
Simulates plate reverberation (a
studio e ect unit that uses the
vibration of a large metal plate to
produce reverberation). Provides a
metallic sound with a distinct upper
range.
Time 0.1–10.0 (s)
Adjusts the length (time) of
reverberation.
High Cut
700Hz–11.0kHz,
FLAT
The high cut lter adjusts the
amount of high frequencies in
the reverb sound. When “FLAT” is
selected, the high cut lter will have
no e ect.
E ect Level 0–100
This sets the volume level of the
e ect.