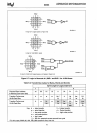
80386
The fastest 80386
bus
cycle requires only two bus
states. For example, three consecutive bus read cy-
cles, each consisting of two bus states,
are
shown
by Figure
5-8.
The bus states
in
each cycle
are
named
T1
and
T2.
Any
memory or
1/0
address
may
be
accessed
by
such a two-state bus cycle, if the
external hardware
is
fast enough. The high-band-
width, two-clock
bus
cycle realizes the full potential
of fast main memory, or cache memory.
Every bus cycle continues until it
is
acknowledged
by the external system hardware, using the 80386
READY # input. Acknowledging the bus cycle at the
end of the first
T2
results
in
the shortest bus cycle,
requiring
only
T1
and
T2.
If READY # is not immedi-
ately asserted, however,
T2
states are repeated
in-
definitely until the READY # input
is
sampled assert-
ed.
5.4.2 Address Pipelining
The address pipelining option provides a choice of
bus cycle timings.
Pipelined or non-pipelined
ad-
dress timing
is
selectable
on
a cycle-by-cycle basis
with the Next Address
(NA#)
input.
CLK2[
(INPUT)
BED#-BE3#.A2-A31.
[
M/IO#.
D/C#.
W/R#
(OUTPUTS)
ADS#[
(OUTPUT)
NA# [
(INPUT)
READY#
[
(INPUT)
LOCK#
[
(OUTPUT)
00-031
[
(INPUT
DURING
READ)
CYCLE
1
PIPELINED
(READ)
T1P
T2P
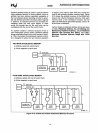
When address pipelining
is
not selected, the current
address and bus cycle definition remain stable
throughout the bus cycle.
When address pipelining
is
selected, the address
(BEO#-BE3#,
A2-A31) and definition
(W/R#,
D/C#
and
M/IO#)
of the next cycle are available
before the end of the current cycle.
To
signal their
availability, the 80386 address status output (ADS#)
is also asserted. Figure
5-9
illustrates the fastest
read cycles with pipe lined address timing.
Note from Figure
5-9
the fastest
bus
cycles using
pipelined address require only two bus states,
named T1P and T2P. Therefore
cycles with pipe-
lined address timing allow the
same
data bandwidth
as
non-pipelined cycles, but address-to-data access
time
is
increased compared to that of a non-pipe-
lined cycle.
By
increasing the address-to-data access time, pipe-
lined address timing reduces wait state require-
ments. For example, if one wait state is required with
non-pipelined address timing,
no
wait states would
be
required with pipelined address.
CYCLE
2
PIPELINED
(READ)
T1P
T2P
CYCLE
3
PIPELINED
(READ)
T1P
T2P
Fastest
pipelined bus cycles consist
of
T1
P and T2P
231630-12
Figure 5·9. Fastest Read Cycles
with
Pipelined Address Timing
73