inter
80386
Pipelined address timing is useful
in
typical systems
having address latches.
In
those systems, once
an
address has been latched, pipelined availability of
the next address allows decoding circuitry to gener-
ate chip selects (and other necessary select signals)
in
advance, so selected devices are accessed im-
mediately when the next cycle begins.
In
other
words, the decode time for the next cycle can be
overlapped with the end of the current cycle.
If
a system contains a memory structure of two or
more interleaved memory banks, pipelined address
timing potentially allows even more overlap of activi-
ty.
This is true when the interleaved memory control-
ler
is
designed to allow the next memory operation
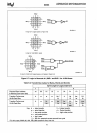
TWO-BANK INTERLEAVED MEMORY
a)
Address signal A2 selects bank
b)
32-bit datapath to each bank
FOUR-BANK INTERLEAVED MEMORY
a)
Address signals
A3
and A2 select bank
b)
32-bit datapath to each bank
to begin
in
one memory bank while the current bus
cycle is still activating another memory bank. Figure
5-10 shows the general structure of the 80386 with
2-bank and 4-bank interleaved memory. Note each
memory bank of the interleaved memory has full
data bus width (32-bit data width typically, unless 16-
bit bus size is selected).
Further details
of
pipelined address timing are given
in
5.4.3.4 Pipelined Address, 5.4.3.5 Initiating and
Maintaining
Pipelined Address, 5.4.3.6 Pipelined
Address
with
Dynamic Bus Sizing, and 5.4.3.7
Maximum
Pipelined Address Usage
with
16-Bit
Bus Size.
231630-13
231630-14
Figure 5-10. 2-Bank and 4-Bank Interleaved Memory Structure
74