80386
4.2
ADDRESSING MECHANISM
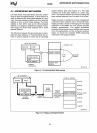
Like Real Mode, Protected Mode uses two compo-
nents to form the logical address, a 16-bit selector
is
used to determine the linear base address of a seg-
ment, the base address
is
added to a 32-bit effective
address to form a 32-bit linear address. The linear
address
is
then either used
as
the 32-bit physical
address, or if paging
is
enabled the paging mecha-
nism maps the 32-bit linear address into a 32-bit
physical address.
The difference between the two modes lies
in
calcu-
lating the base address.
In
Protected Mode the se-
lector
is
used to specify
an
index into
an
operating
48/32
BIT
POINTER
system defined table (see Figure 4-1). The table
contains the 32-bit base address of a given
seg-
ment. The physical address
is
formed by adding the
base address obtained from the table to the offset.
Paging provides
an
additional memory management
mechanism which operates only
in
Protected Mode.
Paging provides a means of managing the very large
segments of the
80386. As such, paging operates
beneath segmentation. The paging mechanism
translates the protected linear address which comes
from the segmentation unit into a physical address.
Figure 4-2 shows the complete
80386 addressing
mechanism with paging enabled.
SEGMENT
LIMIT
~
MEMORY
OPERAND
r
ACCESS
RIGHTS
LIMIT
BASE
ADDRESS
UP
TO
4GB
1
SELECTED
SEGMENT
SEGMENT
DESCRIPTOR
SEGMENT
BASE
ADDRESS
Figure 4-1. Protected Mode Addressing
48
BIT
POINTER
,
,
PHYSICAL
ADDRESS
I
SEGMENT
I
OFFSET
15
31
I
0
80386
ACCESS
RIGHTS
PAGING
MECHANISM
PHYSICAL
LIMIT
,.
ADDRESS
~
~
LlNEAR~
MEMORY
OPERAND
BASE
ADDRESS
PAGE
FRAME
SEGMENT
ADDRESS
ADDRESS
DESCRIPTOR
Figure 4-2. Paging and Segmentation
34
231630-55
!
4K
BYTES
!
4K
BYTES
! 4K
BYTES
!
PHYSICAL
PAGE:
4K
BYTES
!
4K
BYTES
! 4K
BYTES
!
4K
BYTES
231630-56