SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
may take one
of
four values. Privilege level 0
is
the most-privileged level and privilege
level
3
is
the least-privileged
level.
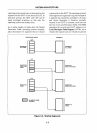
Figure
3-8
shows how the 80386 privilege
levels
can be used to establish different protection
policies. An unprotected system can be imple-
mented by simply placing all procedures in a
segment (or segments) whose privilege level
is
o.
The traditional supervisor/ user distinction can
be
implemented
by
placing user (application)
code
in
a privilege level 3 segment and supervisor
procedures in a segment whose privilege
level
is
O.
An operating system can also use privilege
levels
I and
2,
if desired.
For
example, the most
critical and least-changing operating system proce-
dures (sometimes called the operating system
kernel) might be assigned privilege level
o.
Privilege level I might be used for the services
that are
less
critical and more frequently modified
or
extended, for example, device drivers. Level 2
might be reserved for use
by
original equipment
manufacturers. Such
OEMs could then assign
their code privilege
level
2,
leaving level 3 for the
end users.
In
this
way,
the OEM software
is
protected from the end users, the operating
system
is
protected from both the OEM and the
end users, and the operating system kernel
is
protected from all other software, including that
part of the operating system that
is
subject to
frequent change.
As will be amplified in succeeding sections, a
task's privilege level determines what instructions
it
may execute and what subset
of
the segments
and/
or
pages in its address space
it
may reference.
The processor checks for consistency between a
task's privilege level and the privilege level
of
the
segment
or
page that
is
the target
of
an instruc-
tion. Any attempt by a task to use a more
privileged segment
or
page makes the processor
stop execution
of
the instruction and raise a
general protection exception. (Exceptions are
discussed later in the chapter, as are system calls,
which provide a controlled way for a less
privileged procedure to call a more privileged
one.)
3-11
A.
UNPROTECTED SYSTEM
B.
SUPERVISOR/USER PROTECTION
C.
FOUR LEVELS OF PROTECTION
Figure 3-8. USing Privilege Levels