102
End: The sample data that lies after the “Edit Range End”
will be deleted.
5 In “Save to No.,” specify the save destination sample
number. By default, an unused sample number will be
selected.
The sample number cannot be specified if “Overwrite” is
checked (☞p.101).
For stereo samples, use “Save to No.(L)” and
“(R)” to specify the save-destination of the L and R chan-
nels.
6 To execute the Truncate command, press the OK button.
To cancel, press the Cancel button.
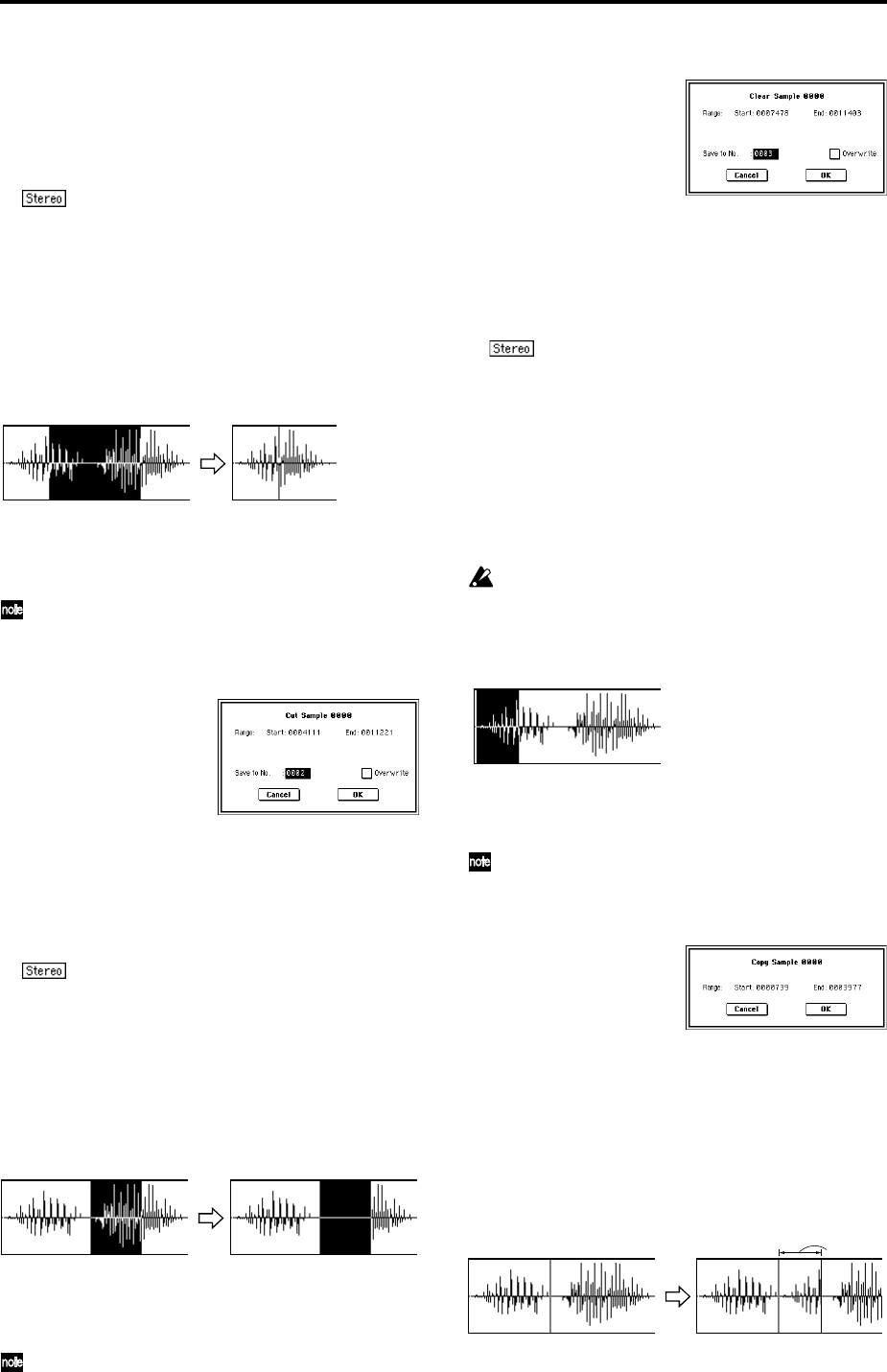
1–1B: Cut
This command deletes the data between the “Edit Range
Start”–“Edit Range End.” Sample data located after the
deleted portion will be moved toward the begining of the
sample.
1 Use “Sample Select” (1–1b) to select the sample that you
wish to edit, and use “Edit Range Start” and “Edit Range
End” to specify the editing range.
You can press the SAMPLING [START/STOP] key to
hear the portion that will be deleted by the “Cut” com-
mand.
2 Select “Cut” to access the dialog box.
3 The range to be edited is shown by Range “Start” and
“End.”
4 In “Save to No.,” specify the save destination sample
number. By default, an unused sample number will be
selected.
The sample number cannot be specified if “Overwrite” is
checked (☞p.101).
For stereo samples, use “Save to No.(L)” and
“(R)” to specify the save-destination of the L and R chan-
nels.
5 To execute the Cut command, press the OK button. To
cancel, press the Cancel button.
1–1C: Clear
This command converts the data between “Edit Range
Start”–“Edit Range End” to zero values. Sample data before
and after the edited range will not move.
1 Use “Sample Select” (1–1b) to select the sample that you
wish to edit, and use “Edit Range Start”–“Edit Range
End” to specify the editing range.
You can press the SAMPLING [START/STOP] key to
hear the portion that will be changed to zero-level by
the “Clear” command.
2 Select “Clear” to access the dialog box.
3 The range to be edited is shown by Range “Start” and
“End.”
4 In “Save to No.,” specify the save destination sample
number. By default, an unused sample number will be
selected.
The sample number cannot be specified if “Overwrite” is
checked (☞p.101).
For stereo samples, use “Save to No.(L)” and
“(R)” to specify the save-destination of the L and R chan-
nels.
5 To execute the Clear command, press the OK button. To
cancel, press the Cancel button.
1–1D: Copy
This command copies the sample data from the area
between “Edit Range Start”–“Edit Range End” into the sam-
ple data buffer. This data can then be used by the “Insert,”
“Mix” or “Paste” commands.
When you execute “Copy,” the data that is copied into
the buffer actually consists only of the copy-source
sample number, the “Edit Range Start” and “Edit
Range End” locations and not the data itself. Do not
delete the copy-source sample until you finish execut-
ing the “Insert,” “Mix,” or “Paste” command.
1 Use “Sample Select” (1–1b) to select the sample that you
wish to edit, and use “Edit Range Start” and “Edit Range
End” to specify the editing range.
You can press the SAMPLING [START/STOP] key to
hear the portion that will be copied by the “Copy” com-
mand.
2 Select “Copy” to access the dialog box.
3 The range to be copied is shown by Range “Start” and
“End.”
4 To execute the Copy command, press the OK button. To
cancel, press the Cancel button.
1–1E: Insert
The sample data that was copied into the buffer by the
“Copy” command will be inserted, starting at the “Edit
Range Start” address. Any data that was located after this
point will be moved toward the end of the sample.
1 Use “Sample Select” (1–1b) to select the sample that you
wish to edit, and set “Edit Range Start” to specify the
starting address. The “Edit Range End” setting is
ignored.
From the
buffer
