103
Sampling
P0
P1 P2 P3 P4 P5 P8
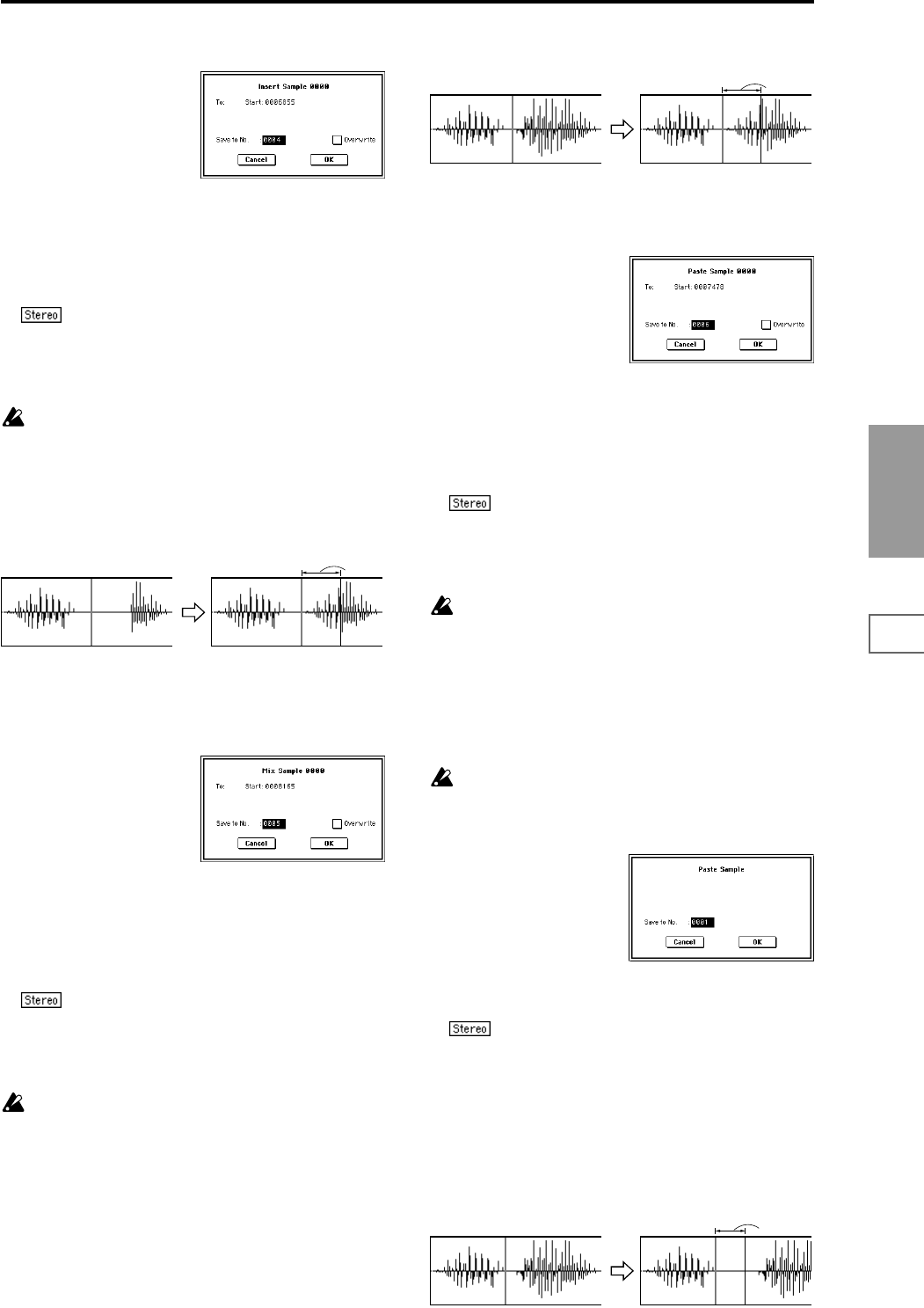
2 Select “Insert” to access the dialog box.
3 To “Start” will indicate the starting address at which the
data will be inserted.
4 In “Save to No.,” specify the save destination sample
number. By default, an unused sample number will be
selected.
The sample number cannot be specified if “Overwrite” is
checked (☞p.101).
For stereo samples, use “Save to No.(L)” and
“(R)” to specify the save-destination of the L and R chan-
nels.
5 To execute the Insert command, press the OK button. To
cancel, press the Cancel button.
If the buffer into which data was placed by the “Copy”
command contains no data, the display will indicate
“Source sample is empty.”
1–1F: Mix
This command mixes the sample data that was placed in the
buffer by “Copy” with the selected sample data. Mixing will
begin at the “Edit Range Start” address.
1 Use “Sample Select” (1–1b) to select the sample that you
wish to edit, and set “Edit Range Start” to specify the
starting address. The “Edit Range End” setting is
ignored.
2 Select “Mix” to access the dialog box.
3 To “Start” will indicate the starting address at which the
data will be mixed.
4 In “Save to No.,” specify the save destination sample
number. By default, an unused sample number will be
selected.
The sample number cannot be specified if “Overwrite” is
checked (☞p.101).
For stereo samples, use “Save to No.(L)” and
“(R)” to specify the save-destination of the L and R chan-
nels.
5 To execute the Mix command, press the OK button. To
cancel, press the Cancel button.
If the buffer into which data was placed by the “Copy”
command contains no data, the display will indicate
“Source sample is empty.”
1–1G: Paste
Beginning at the “Edit Range Start” address, this command
places the sample data that was loaded into the buffer by
“Copy.” The original data will be deleted, and overwritten
by the sample data from the buffer.
You can also place sample data into a blank sample. This is
convenient when you wish to “Copy” part of a sample and
create a new sample based on it.
Pasting to a sample that contains sample data
1
Use “Sample Select” (1–1b) to select the sample that you
wish to edit, and set “Edit Range Start” to specify the
starting address. The “Edit Range End” setting is ignored.
2 Select “Paste” to access the dialog box.
3 To “Start” will indicate the starting address at which the
data will be pasted.
4 In “Save to No.,” specify the save destination sample
number. By default, an unused sample number will be
selected.
The sample number cannot be specified if “Overwrite” is
checked (☞p.101).
For stereo samples, use “Save to No.(L)” and
“(R)” to specify the save-destination of the L and R chan-
nels.
5 To execute the Paste command, press the OK button. To
cancel, press the Cancel button.
If the buffer into which data was placed by the “Copy”
command contains no data, the display will indicate
“Source sample is empty.”
Pasting to a sample that contains no sample data
1 Select the vacant sample number that you wish to paste.
If you select ----:---No Assign---- for “Sample” and then
access the dialog box for this command, a vacant sample
number will be selected automatically.
The “Edit Range Start” and “Edit Range End” settings
will be ignored, and will have no effect. The beginning
of the sample will be placed at address 0.
2 Select “Paste” to access the dialog box.
3 In “Save to No.,” specify the save destination sample
number. If you wish to change it, re-specify the desired
number.
For stereo samples, use “Save to No.(L)” and
“(R)” to specify the save-destination of the L and R chan-
nels.
4 To execute the “Paste” command, press the OK button.
To cancel without executing, press the Cancel button.
1–1H: Insert Zero
This command inserts zero-level sample data (silence),
beginning at the “Edit Range Start” address. The data that
previously occupied that location will be moved toward the
end of the sample.
From the
buffer
From the
buffer
Size
