8 - 7
MELSEC-Q
8 OPR CONTROL
8.2.3 OPR method (1): Near-point dog method
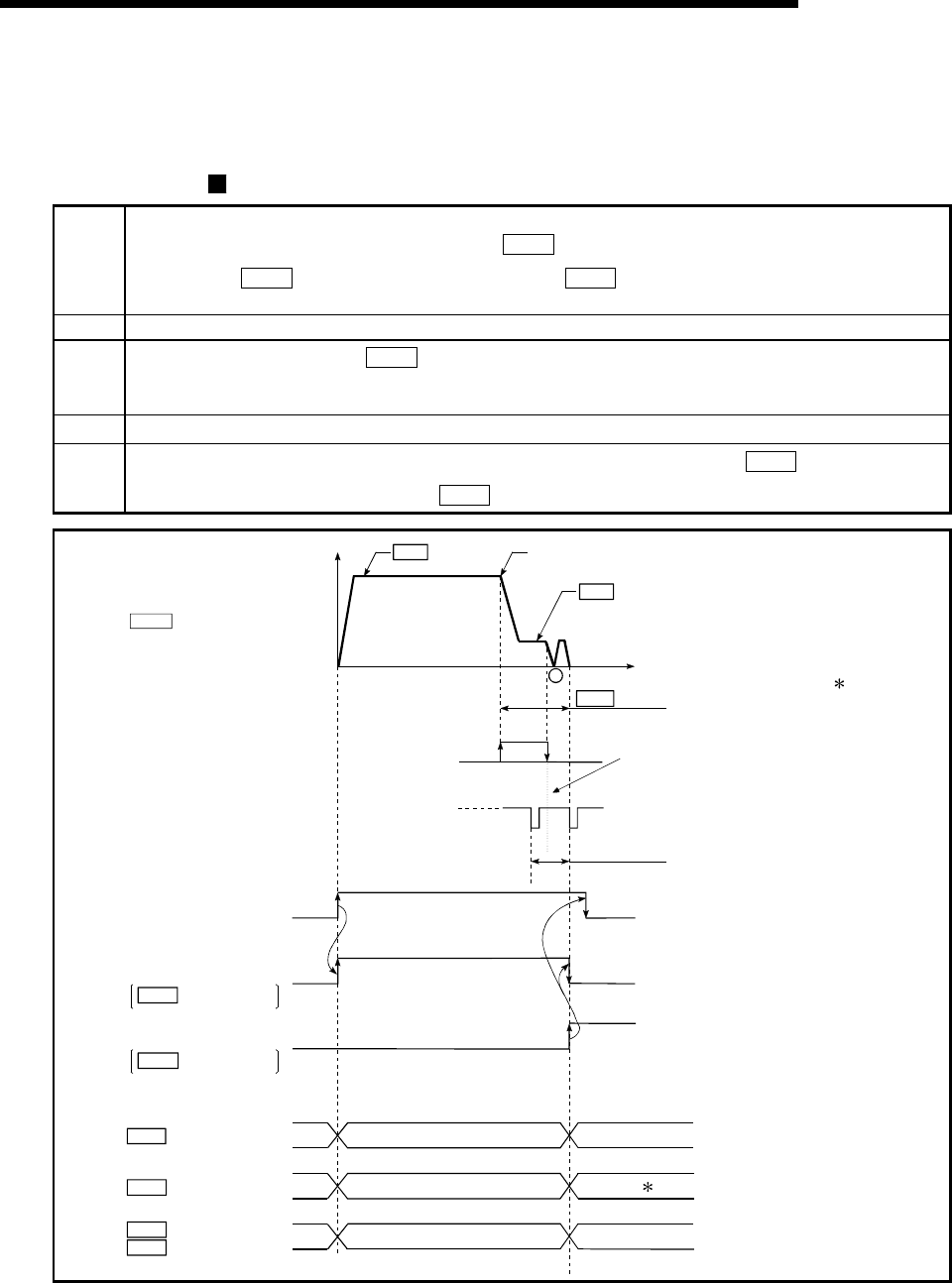
The following shows an operation outline of the "near-point dog method" OPR method.
Operation chart
1)
The machine OPR is started.
(The machine begins the acceleration designated in "
Pr.51
OPR acceleration time selection", in the direction
designated in "
Pr.44
OPR direction". It then moves at the "
Pr.46
OPR speed" when the acceleration is
completed.)
2) The machine begins decelerating when the near-point dog ON is detected.
3)
The machine decelerates to the "
Pr.47
Creep speed", and subsequently moves at that speed.
(At this time, the near-point dog must be ON. The workpiece will continue decelerating and stop if the near-point dog is
OFF.)
4) After the near-point dog turns OFF, the machine stops. It then restarts and stops at the first zero point.
5)
After a "deviation counter clear signal" is output to the drive unit, the OPR complete flag (
Md.31
Status: b4) turns
from OFF to ON and the OPR request flag (
Md.31
status: b3) turns from ON to OFF.
t
Machine OPR start
(Positioning start signal)
ON
OFF
OPR speed
Deceleration at the near-point dog ON
Creep speed
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
Standing by
In OPR
Standing by
Axis operation status
Inconsistent
0
Movement amount after
near-point dog ON
Value of the machine moved is stored.
OP address
Current feed value
Machine feed value
V
Zero signal
Value of 1
Movement amount after near-point dog ON
Near-point dog
ON
OFF
One servo motor rotation
1
OPR request flag
OPR complete flag
Md.34
Adjust so the near-point dog OFF position is
as close as possible to the center of the zero
signal HIGH level.
If the near-point dog OFF position overlaps
with the zero signal, the machine OPR stop
position may deviate by one servomotor
rotation.
1) 2) 3) 4) 5)
Pr.46
Pr.47
Md.34
Md.20
Md.21
Md.26
Md.31
Md.31
Status: b3
Status: b4
Inconsistent
A
After the home position return
(OPR) has been started, the
zero point of the encoder must
be passed at least once before
point A is reached.
POINT
Fig. 8.3 Near-point dog method machine OPR


















