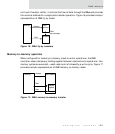
DMA buffer descriptor
132
NS7520 Hardware Reference, Rev. D 03/2006
Buffer descriptor field definitions
Field Description
Source buffer pointer/Buffer
pointer
The source buffer pointer field identifies the starting location of
the data buffer. The source buffer pointer can start on any byte
boundary for fly-by memory-to-peripheral operations. The
source buffer must be aligned on 32-bit boundaries to support
peripheral-to-memory operations.
Status Peripherals can use the 16-bit status field to store transmit and
receive status words. The status field is updated when the
current descriptor is completed.
Buffer length: Peripheral-to-
memory
In fly-by peripheral-to-memory operations, indicates the
maximum number of bytes available in the receive buffer pointed
to by the source buffer pointer. After filling the receive buffer
with peripheral data, the DMA controller updates this field with
the actual receive data byte count.
Buffer length: Memory-to-
peripheral
In fly-by memory-to-peripheral operations, indicates the number
of bytes to move to the peripheral device, pointed to by the
source address pointer. After completing the transfer, the DMA
controller updates this field in a transmit buffer descriptor with
the actual data byte count (useful during error conditions).
Buffer length: Memory-to-
memory
Indicates the number of bytes to move between the source and
destination locations. After completing a memory-to-memory
transfer, the DMA controller updates this field with the
remaining data byte count (useful during error conditions).
Destination buffer pointer Used only when the DMA channel is configured for memory-to-
memory operations. The destination address pointer must start
on the same byte boundary as the source address pointer. If the
source and destination byte boundaries are different, the data
operand size must be set for 8-bit operations (see the SIZE field
in "DMA Control register," beginning on page 136).
Table 48: Buffer descriptor field definitions