DMA S3C2410A
8-2
DMA REQUEST SOURCES
Each channel of the DMA controller can select one of DMA request source among four DMA sources if H/W DMA
request mode is selected by DCON register. (Note that if S/W request mode is selected, this DMA request sources
have no meaning at all.) Table 8-1 shows four DMA sources for each channel.
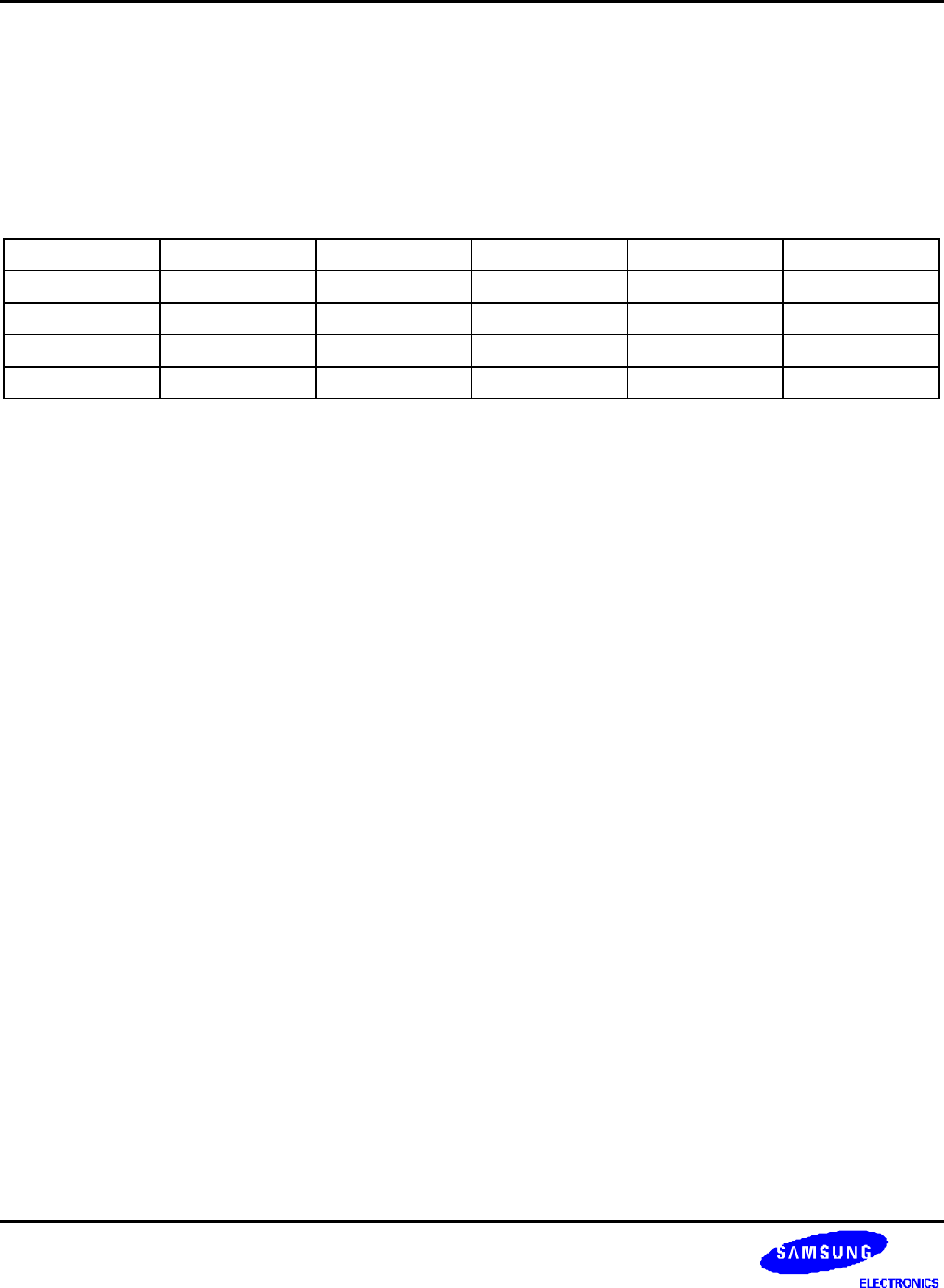
Table 8-1. DMA Request Sources for Each Channel
Source0 Source1 Source2 Source3 Source4
Ch-0 nXDREQ0 UART0 SDI Timer USB device EP1
Ch-1 nXDREQ1 UART1 I2SSDI SPI0 USB device EP2
Ch-2 I2SSDO I2SSDI SDI Timer USB device EP3
Ch-3 UART2 SDI SPI1 Timer USB device EP4
Here, nXDREQ0 and nXDREQ1 represent two external sources(External Devices), and I2SSDO and I2SSDI represent
IIS transmitting and receiving, respectively.
DMA OPERATION
DMA uses three-state FSM (finite state machine) for its operation, which is described in the three following steps:
State-1. As an initial state, the DMA waits for a DMA request. If it comes, it goes to state-2. At this state, DMA ACK
and INT REQ are 0.
State-2. In this state, DMA ACK becomes 1 and the counter (CURR_TC) is loaded from DCON[19:0] register. Note
that the DMA ACK remains 1 until it is cleared later.
State-3. In this state, sub-FSM handling the atomic operation of DMA is initiated. The sub-FSM reads the data from
the source address and then writes it to destination address. In this operation, data size and transfer size
(single or burst) are considered. This operation is repeated until the counter (CURR_TC) becomes 0 in
Whole service mode, while performed only once in Single service mode. The main FSM (this FSM) counts
down the CURR_TC when the sub-FSM finishes each of atomic operation. In addition, this main FSM
asserts the INT REQ signal when CURR_TC becomes 0 and the interrupt setting of DCON[29] register is
set to 1. In addition, it clears DMA ACK if one of the following conditions is met.
1) CURR_TC becomes 0 in the Whole service mode
2) Atomic operation finishes in the Single service mode.
Note that in the Single service mode, these three states of main FSM are performed and then stops, and waits for
another DMA REQ. And if DMA REQ comes in, all three states are repeated. Therefore, DMA ACK is asserted and
then deasserted for each atomic transfer. In contrast, in the Whole service mode, main FSM waits at state-3 until
CURR_TC becomes 0. Therefore, DMA ACK is asserted during all the transfers and then deasserted when TC
reaches 0.
However, INT REQ is asserted only if CURR_TC becomes 0 regardless of the service mode (Single service mode or
Whole service mode).


















