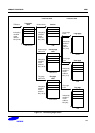
MMU ARM920T PROCESSOR
3-2
TRANSLATED ENTRIES
Each TLB caches 64 translated entries. During CPU memory accesses, the TLB provides the protection information
to the access control logic.
If the TLB contains a translated entry for the modified virtual address, the access control logic determines whether
access is permitted:
• If access is permitted and an off-chip access is required, the MMU outputs the appropriate physical address
corresponding to the modified virtual address.
• If access is permitted and an off-chip access is not required, the cache services the access.
• If access is not permitted, the MMU signals the CPU core to abort.
If a TLB misses (it does not contain an entry for the virtual address) the translation table walk hardware is invoked to
retrieve the translation information from a translation table in physical memory. Once retrieved, the translation
information is written into the TLB, possibly overwriting an existing value.
The entry to be written is chosen by cycling sequentially through the TLB locations. To enable use of TLB locking
features, the location to be written can be specified using CP15 register 10, TLB lockdown.
When the MMU is turned off (as happens on reset), no address mapping occurs and all regions are marked as non-
cacheable and non-bufferable. See About the caches and write buffer on page 4-1.