MIDI applications Messages transmitted and received by the OASYS
1013
Local Control Off: Notes from the KARMA function
or RPPR will not be transmitted from MIDI OUT. The
OASYS will sound only in response to MIDI messages
received at MIDI IN, or generated by the KARMA
function or RPPR.
Setting example 1
Record the note messages generated by the KARMA
or RPPR function on the external MIDI
sequencer/computer.
Turn on this instrument’s KARMA or RPPR function.
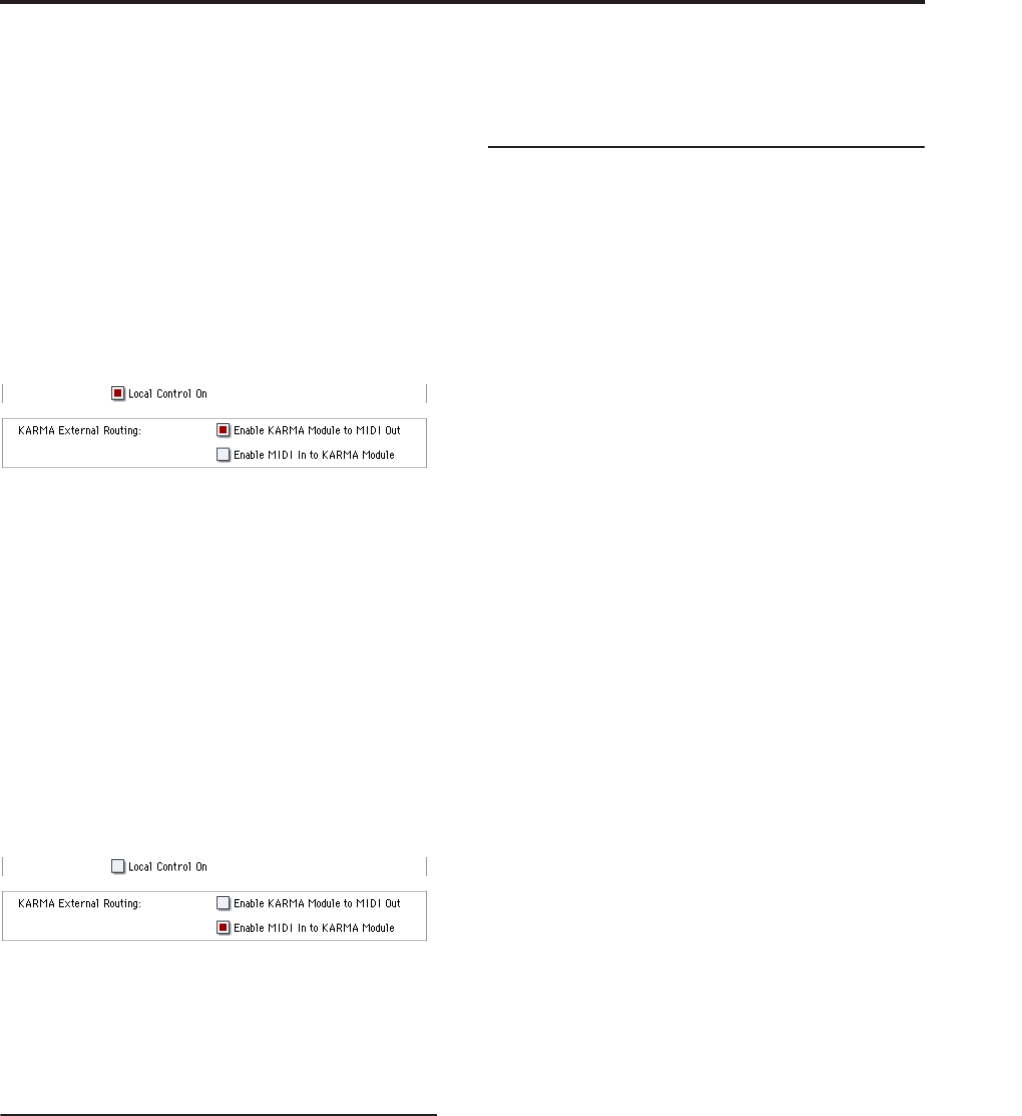
Set this instrument to Local Control On. Make the
following KARMA External Routing settings (Global
1–1b).
On your external sequencer or computer, turn the echo
back setting Off. When you’re recording a performance
generated by the KARMA function or RPPR, this
setting will prevent duplicate notes from being
sounded by the echo-back. (Turn the RPPR function off
for playback.)
Setting example 2
Use the external MIDI sequencer/computer to record
only the notes that trigger the KARMA or RPPR
function, and operate this instrument’s KARMA or
RPPR function for monitoring while recording, and
during playback.
Turn on the OASYS’s KARMA or RPPR function. Set
the OASYS to Local Control Off. Make the following
KARMA External Routing settings (Global 1–1b).
Notes generated by the KARMA function or RPPR will
not be output. On your external MIDI sequencer or
computer, turn the echo back setting On. This allows
recording to occur correctly, without the KARMA
function or the RPPR function being applied in
duplicate.
About GM (General MIDI)
The OASYS supports the GM standard. It also
supports the GM2 sound map (including bank select)
with 256 programs and 9 drum programs provided in
ROM banks G, g(1)–g(9), and g(d). (Banks g(1)–g(9) are
GM2 variation programs, and g(d) contains drum
programs.)
GM is a standard that ensures basic compatibility of
sounds and controllers between GM-compatible
instruments made by different manufacturers. When
using GM with OASYS, be aware of the following.
• GM System On is supported in Sequencer mode.
For more information, see “GM Initialize” on
page 526.
• When you wish to play a GM sequence, or load GM
data into a song, set “Bank Map” (Global 0–1d) to
GM(2).
About standard MIDI files
Standard MIDI files (SMF) make it possible for
different computer programs or musical instruments
made by different manufacturers to exchange time-
based MIDI data. Each standard MIDI file contains one
song. The OASYS supports format 0 (type 0) in which
all of the MIDI data is combined into one track, and
format 1 (type 1) in which the data is separated by
track.
When a SMF is loaded into a song in Disk mode, the
program bank that is selected will differ depending on
the “Bank Map” (Global 0–1d) setting. When
playing/loading SMF data that conforms to the GM
specifications, set “Bank Map” to GM(2).
Sequencer mode
In Disk mode when you convert a song into a Standard
MIDI File and save it, you can choose either format 0 or
format 1.
• If OASYS song data that was saved as a format 1
SMF file is loaded into another device, the track
configuration may be different than it was before
being saved. This is because MIDI tracks that
contain no musical data are omitted, and the
remaining tracks are moved into the unused tracks.
This will not affect the playback itself.
• If song data that was saved by another device as a
format 1 SMF file is loaded into the OASYS, the
track configuration may be different than it was
before being saved. This is because tracks that
contain no musical data are omitted, and the
remaining tracks are moved into the unused tracks.
This will not affect the playback itself.
When exchanging sequence data between two OASYS,
we recommend that you save the sequence data in the
OASYS’s native format (“Save SEQ”).
When sequence data is saved in the OASYS’s native
format, all of the settings and patterns unique to the
OASYS will be saved, which will ensure a higher level
of reproducibility than when the data is saved as a
Standard MIDI File (“Save to Std MIDI File”).
Parameter changes and other recorded data is included
in the song data as System Exclusive events, so it can
be saved to or loaded from disk as usual. Exclusive
messages can also be loaded or saved as SMF
(Standard MIDI File) data (“Load Standard MIDI File,”
“Save Song as Standard MIDI File”). This allows
recorded System Exclusive events to be saved as SMF
data, or exclusive messages included in SMF data to be
converted into song data.
During playback, this data can be transmitted to an
external MIDI device, or used to control track
parameters or effect parameters of the song.


















