Program mode: HD-1
104
Resulting transposed input notes:
Lowest: input notes transposed to E2 G#2 B2 D#3
Highest: input notes transposed to E4 G#4 B4 D#5
C3–B3[1]: all notes near 4th octave (maintain
inversion)
The input notes will be forced to a range near the
middle octave (C3–B3). The “Force Range Wrap”
parameter will become available (see below), and
specifies the scale step at which a wrap around will be
performed. For example, if “Force Range Wrap”= 7: G,
if the pitch of the lowest note is C to F#, it will be
placed in the 4th octave with the other notes grouped
above it. If the pitch of the lowest note is a G to B, it
will be placed in the 3rd octave, with the other notes
grouped above it. Playing the same chord
chromatically up the keyboard will “wrap around”
when the scale step of the root of the chord is
determined to be “G,” dropping the notes down an
octave. This essentially maintains the inversion the
chord was played with - notes may also extend into the
5th octave or 3rd octave.
This is effective when you wish to produce phrases or
patterns having a similar inversion to what was
played, but in a fixed range regardless of where you
are playing on the keyboard. The behavior is similar to
an auto-accompaniment pattern, in that no matter
where you play on the keyboard, the result is in the
same octave.
C3–B3[2]: The input notes will be forced to a range
within the center octave (C3-B3). because of this, the
chord inversion will change significantly; for example,
the bass note may change. This is effective when you
want to absolutely limit the input notes to a specific
octave.
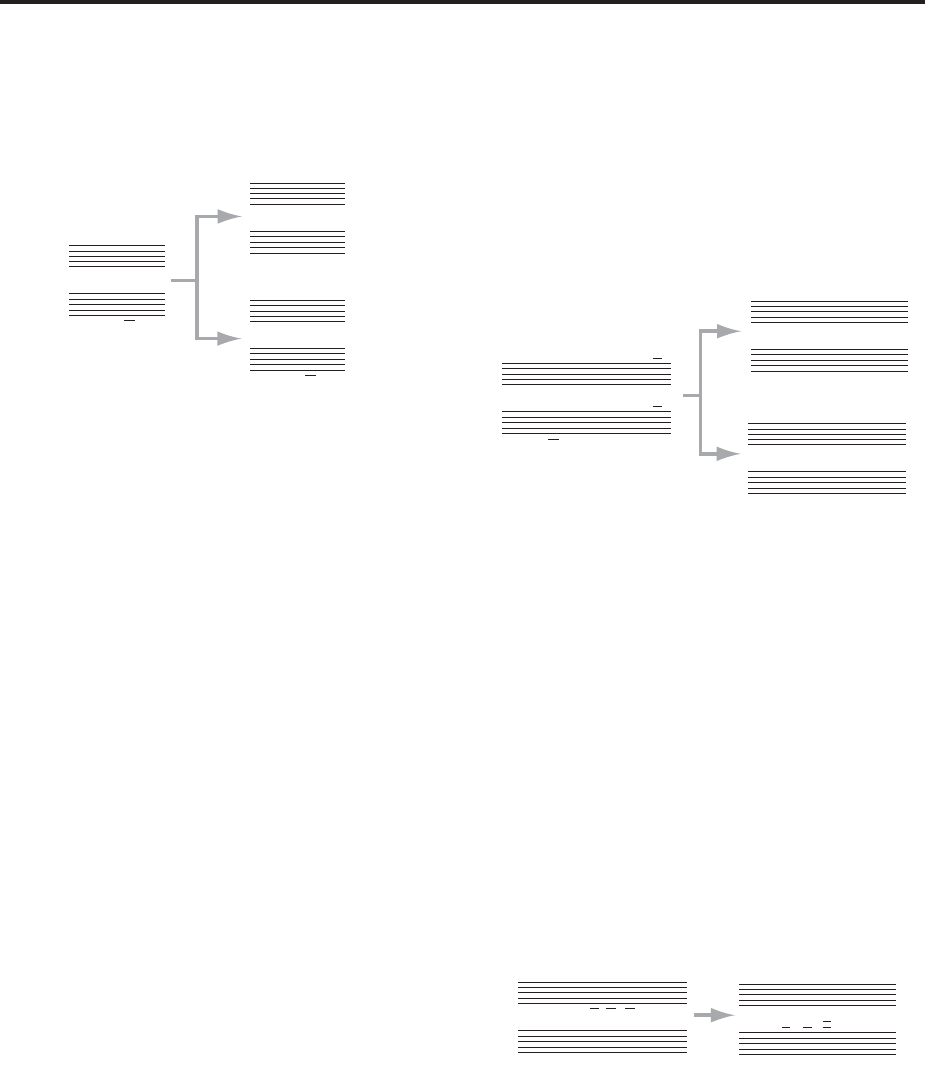
Played on keyboard:
Play chords in the order of
E4 G#4 B4 D#5 (EMaj7 first inversion)
G#4 B4 D#5 E5 (EMaj7 second inversion)
B4 D#5 E5 G#5 (EMaj7 third inversion)
D#5 E5 G#5 B5 (EMaj7 fourth inversion)
C3–B3[1]
Resulting transposed input notes:
E3 G#3 B3 D#4 (EMaj7 first inversion)
G#2 B2 D#3 E3 (EMaj7 second inversion)
B2 D#3 E3 G#3 (EMaj7 third inversion)
D#3 E3 G#3 B3 (EMaj7 fourth inversion)
C3–B3[2]
Resulting transposed input notes:
D#3 E3 G#3 B3 (EMaj7/D#)
D#3 E3 G#3 B3 (EMaj7/D#)
D#3 E3 G#3 B3 (EMaj7/D#)
D#3 E3 G#3 B3 (EMaj7/D#)
(all identical)
Force Range Wrap [C…B]
When “Force Range” (above) is set to C3B3[1], this
parameter sets the highest scale step for the chord’s
root note, after which the range-modified input notes
will be dropped down an octave in order to stay
centered around the 4th octave. For example, if the
value is F#, then starting with G the notes will be
dropped down an octave.
FIG. 4 shows an example where a Maj7 chord in a
variety of voicings is played through 7 scale tones, i.e.
CMaj7, DMaj7, EMaj7, FMaj7, GMaj7 etc. Since “Force
Range Wrap” = F#, the resulting input notes drop
down an octave starting with the GMaj7 chord. This
allows you to keep a GE in a specific range regardless
of where a chord is played on the keyboard, but to
adjust at which point it drops down an octave.
Note: Not available unless “Force Range” is set to
C3B3[1].
Root Position [Off, On]
The phrases and patterns produced by a KARMA
Module are generated by a GE (Generated Effect). In
most cases, this is done based on a Note Series. When
“Root Position” is On (checked), the Note Series will be
created in root position, regardless of the inversion of
the chord, based on chord recognition. In other words,
when this is Off (unchecked), if you play CMaj/E, the
Note Series will start from E and continue up, or if you
play CMaj/G, the Note Series will start with G. By
using “Root Position” On (checked), you can make
sure that any inversion of a chord ends up the same.
For example, CMaj/E and CMaj/G will both be the
same as CMaj, and the Note Series will start from a C.
Input Notes
“Force Range” = Lowest
“Force Range” = Higest
Input Notes
“Force Range” = C3-B3[1]
“Force Range” = C3-B3[2]
Input Notes
“Force Range” = C3-B3[1]
“Force Range Wrap = F#


















