Combination mode
352
Finally, you can optionally send these CCs out to
external MIDI instruments. A global parameter allows
you to enable or disable this MIDI output; by default, it
is disabled.
Program and Combi Vectors work together
In Combi mode, each Timbre’s Program still has its
own Vector EG, which controls volume and CCs as it
did in Program mode. You can disable the Program’s
Vector Volume and CC control separately for each
Timbre, if desired.
Program Vector CCs affect only their own Program,
even if other Timbres are set to the same MIDI channel.
There is also a separate Combi-wide Vector EG, with
its own Vector Volume and CC control settings. Combi
Vector CCs affect all Timbres set to the Global channel.
As with the Program Vector, you can disable the Combi
Volume and CC control separately for each Timbre.
Vector and MIDI
The Vector features interact with MIDI in two different
ways: through the Vector Joystick, and through the
Vector CC Control.
The Vector Joystick sends and receives two MIDI
controllers: one for the X axis, and the other for the Y
axis. In Global mode, you can assign these to any MIDI
CC numbers you like. The defaults are CC#118 for the
X axis, and CC#119 for the Y axis.
The Vector Joystick and its CCs control the Vector
position, in conjunction with the Vector EG.
The Vector CC Control, on the other hand, is generated
by the Vector position. Normally, this will only affect
internal sounds and effects. If you like, however, you
can also enable a Global parameter to send these
generated CCs to external MIDI devices.
Note that, in Combi mode, only the Combi’s Vector
CCs can be sent to external MIDI instruments; the
individual Program’s vector CCs are only used
internally.
Enable CC Control [Off, On]
When this box is checked, the Vector position will
control the CCs assigned to +X, –X, +Y, and –Y, as set
below.
When this box is not checked, the Vector position will
not affect these CCs. However, the joystick will still
send and receive its dedicated MIDI CCs, just like
other physical controllers. See “Vector and MIDI,”
above, for more information.
This parameter affects only the Combi Vector CCs.
Even if this is turned Off, the individual Programs’
Vector CCs will still function normally.
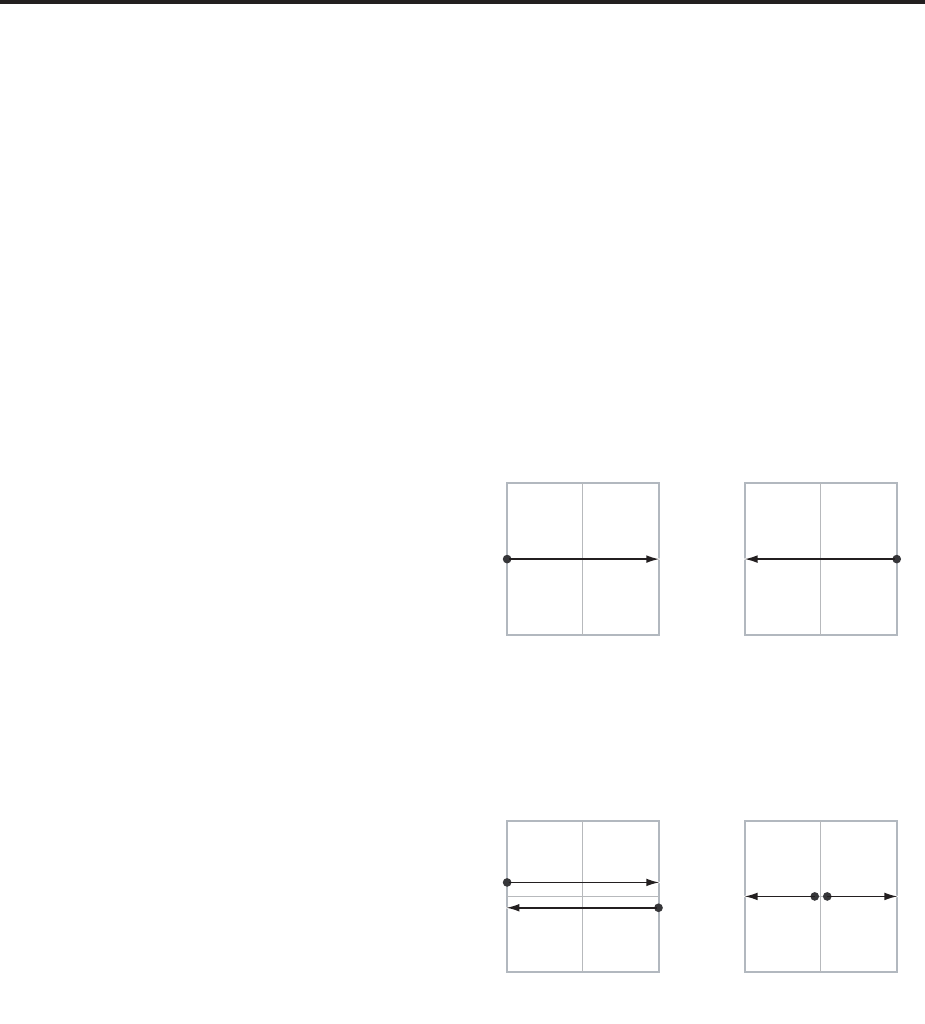
VJS X Mode [Positive, Negative, Xfade, Split]
You can set up the Vector to send out CCs in several
different patterns, as shown in the graphic below. This
controls the pattern for the X axis.
Note that this setting affects only CC Control; it has no
effect on Volume Control. Also, it applies only to the
Combi Vector CCs, and has no effect on the individual
Program Vector CCs.
Positive sends out only +X, starting at 0 at the far left,
and increasing to 127 at the far right. –X is disabled in
this mode.
Negative sends out only –X, starting at 0 at the far
right, and increasing to 127 at the far left. In this mode,
+X is grayed out.
Xfade sends out both +X and –X, overlapping
throughout the X axis. As one increases, the other
decreases.
Split sends out both +X and –X, with a split in the
center. +X is sent when the point moves to the right of
the center, and –X is sent when the point moves to the
left of center.
Vector CC Modes
+X [Off…MIDI CC#119]
This assigns the controller sent by the +X vector. You
can use this as an AMS source to control Program
parameters, or as a Dmod source to control Effects
parameters. It will be grayed out if the VJS X Mode,
above, is set to Negative.
In addition to the standard list of MIDI controllers, you
can also assign the +X vector to duplicate the function
of several front-panel controllers, including JS X, JS+X,
JS-X, Knobs 5–8, and SW 1–2.
For instance, if you assign +X to Knob 6, the vector’s
+X will use the controller assigned to Knob 6 on the
Controller Assign page.
Finally, you can also assign +X to control the Master
Volume.
+127–127
X-Axis
0
Positive
+X CC0 127
+127–127
X-Axis
0
Negative
–X CC127 0
+127–127
X-Axis
0
Xfade
+X CC0 127
–X CC0 127
+127–127
X-Axis
0
Split
+X CC
0 127
–X CC
127 0
Generates only +X,
increasing from left to right.
Generates both +X and –X.
One increases as the other
decreases.
Generates both +X and -X.
Both are 0 in the center.
+X increases to the right;
–X increases to the left.
Generates only –X,
increasing from right to left.


















